Final ID: MDP1109
Re-Exploration of the Pulmonary Resistance-Compliance Relationship: a Universal Time Constant and Hyperbolic Fit?
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) and arterial compliance (PAC) represent the two major hemodynamic determinants of PA load, and their interdependence (the PVR-PAC relationship), critical to our understanding of RV-PA coupling. Previously, it has been reported that the two are physiologically linked through an inverse hyperbolic relationship, such that any rise in PVR is followed by an inverse reduction in PAC, and vice versa. Recent modelling has questioned the 'physiological correctedness' of this relationship as both share stroke volume (SV) in their determination. Accordingly, we sought to re-explore the PVR-PAC relationship, comparing PACclinical with a new, modified area under the curve method, termed PACpcwp.
Methods: PACclinical was calculated as the ratio of SV to PAPP. For PACpcwp, the time constant was estimated as: τ = (A-dt*PCWP)/(P1-P2), where A is the integral over the time period from t1 to t2 of the pressure wave, dt is the time difference between P1 and P2, PCWP is the mean post capillary wedge pressure, P1 is the arterial pressure at t1 and P2 the arterial pressure at t2. Once τ was determined, PACpcwp was measured as the τ/PVR ratio.
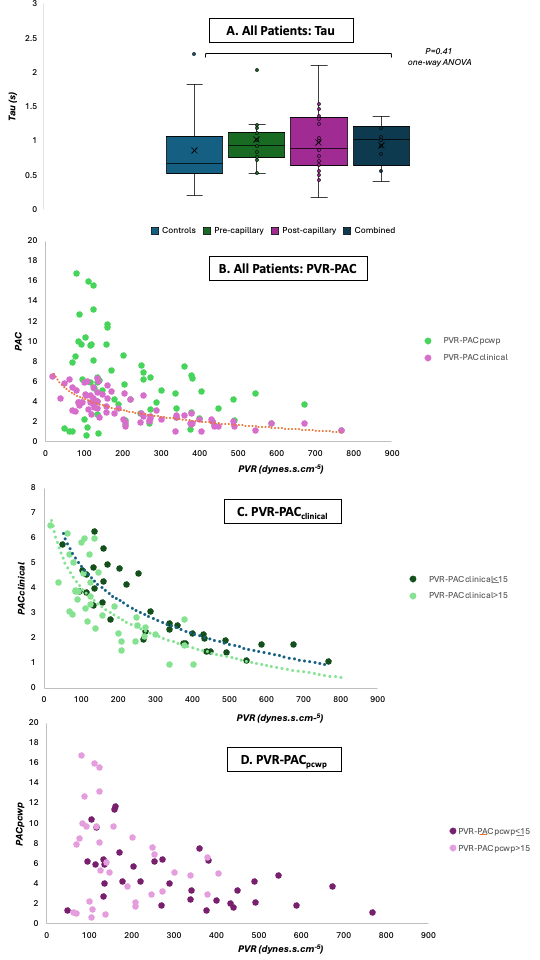
Results: Hemodynamic data from 79-patients with dyspnoea who underwent sequential right heart catheterisation/cardiac magnetic resonance for investigation of PH were analysed (24 pre-capillary PH, 25 post-capillary, 17 combined and 13 controls). PACpcwp values were significantly higher than PACclinical (5.5±4.0 vs 3.4±1.6 mL/mmHg; P<0.01), with a non-signifcant increase in τ amongst subjects with PH (Figure 1a). Whereas PVR demonstrated a strong inverse hyperbolic correlation with PACclinical (R2-0.77, P<0.01), it did not with PACpcwp (R2-0.09, P=0.59; Figure 1b) where there was significant random scatter at lower PVR values. Compared with data in those with a PCWP <15mmHg, the relationship was predictably shift downward in an almost parallel manner for PVR-PACclinical but not so PVR-PACpcwp (Figure 1c&d).
Conclusions: Although these observations may seem trivial at first, they bring into question the invariability of (i) a constant R-C time product and (ii) a hyperbolic resistance-compliance relationship, signalling the potential for greater fluctuations in PAC for any given change in PVR. Reconsideration of PAC determination using the PACpcwp method in those with a low PVR and/or PAM (i.e., at the steep end of the PVR-PAC curve) may be the key to unlocking the prognostic utility of this index.
Methods: PACclinical was calculated as the ratio of SV to PAPP. For PACpcwp, the time constant was estimated as: τ = (A-dt*PCWP)/(P1-P2), where A is the integral over the time period from t1 to t2 of the pressure wave, dt is the time difference between P1 and P2, PCWP is the mean post capillary wedge pressure, P1 is the arterial pressure at t1 and P2 the arterial pressure at t2. Once τ was determined, PACpcwp was measured as the τ/PVR ratio.
Results: Hemodynamic data from 79-patients with dyspnoea who underwent sequential right heart catheterisation/cardiac magnetic resonance for investigation of PH were analysed (24 pre-capillary PH, 25 post-capillary, 17 combined and 13 controls). PACpcwp values were significantly higher than PACclinical (5.5±4.0 vs 3.4±1.6 mL/mmHg; P<0.01), with a non-signifcant increase in τ amongst subjects with PH (Figure 1a). Whereas PVR demonstrated a strong inverse hyperbolic correlation with PACclinical (R2-0.77, P<0.01), it did not with PACpcwp (R2-0.09, P=0.59; Figure 1b) where there was significant random scatter at lower PVR values. Compared with data in those with a PCWP <15mmHg, the relationship was predictably shift downward in an almost parallel manner for PVR-PACclinical but not so PVR-PACpcwp (Figure 1c&d).
Conclusions: Although these observations may seem trivial at first, they bring into question the invariability of (i) a constant R-C time product and (ii) a hyperbolic resistance-compliance relationship, signalling the potential for greater fluctuations in PAC for any given change in PVR. Reconsideration of PAC determination using the PACpcwp method in those with a low PVR and/or PAM (i.e., at the steep end of the PVR-PAC curve) may be the key to unlocking the prognostic utility of this index.
More abstracts on this topic:
Improved Skeletal Muscle Metabolism and Exercise Capacity Following Hydrogen Sulfide Therapy in Cardiometabolic HFpEF
Allerton Timothy, Shah Sanjiv, Irving Brian, Lefer David, Quiriarte Heather, Li Zhen, Stampley James, Davis Iii Gregory, Noland Robert, Doiron Jake, Sharp Thomas, Xia Huijing
A Genome-wide CRISPRi Screen Implicates Coronary Artery Disease GWAS Genes as Key Regulators of Adventitial Fibroblast ProliferationJackson William, Zhu Ashley, Gu Wenduo, Berezowitz Alexa, Iyer Meghana, Cheng Paul