Final ID: MDP527
The Presence of Arm Pain Predicts Coronary Artery Occlusion Requiring Revascularization in Patients with NSTEMI
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) represents about 70% of ACS cases, and nearly one-third of these patients have an occluded coronary artery that may benefit from revascularization. The 13-item ACS Symptom Checklist is a validated tool designed for rapid assessment of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) symptoms. We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of the ACS Symptom Checklist in differentiating NSTEMI patients with and without an occluded artery.
Methods: All NSTEMI patients treated at the University of Rochester Medical Center between 2015-2023 (n=3515) were included. The 13-items from the ACS Symptom Checklist were extracted using natural language processing (NLP) before coronary angiography or within 24 hours of presentation. An occluded coronary artery was one requiring revascularization with percutaneous coronary intervention. Chi-Square was used to assess the sensitivity and specificity of each symptom for an acutely occluded coronary artery. We used logistic regression models to assess the odds of an acutely occluded artery after controlling for age, obesity, and diabetes and stratified by sex.
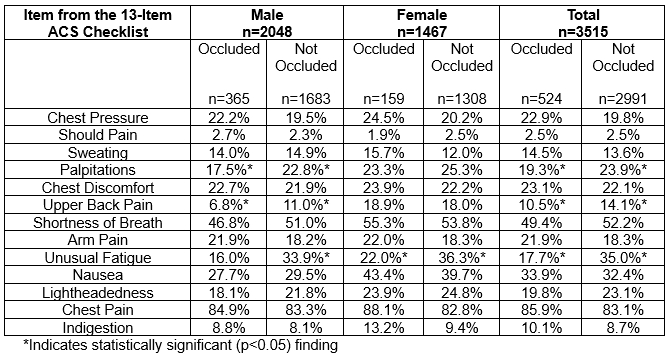
Results: Patients were predominantly male (58%, n=2048), older (69+13 years), and White (85%, n=2988), and 15% (n=524) underwent revascularization. Diabetes (18%, n=629) and obesity (40%, n=1387) were common comorbidities. Upper back pain (10.5% vs. 14.1%, p=0.03), palpitations (19.3% vs. 23.9%, p=0.02), arm pain (21.0% vs 16.7%, p=0.05), unusual fatigue (8.9% vs. 22.2%, p<0.01) significantly differentiated between NSTEMI patients with and without an occluded coronary artery as observed in Table 1. Among men, less upper back pain (OR=0.559, 95% CI 0.361-0.865), palpitations (OR=0.678, 95% CI 0.503-0.915), and unusual fatigue (OR=0.365 95% CI 0.270-0.493) were significant predictors of coronary occlusion. Only a higher likelihood of arm pain (OR=1.184, 95% CI 0.893-1.569) predicted occlusion. Results were similar for women.
Conclusion: Only arm pain, a common symptom of ischemia, predicted an occluded coronary artery in patients with NSTEMI and there were few sex differences. NLP confirmed that the presence of arm pain can cue clinicians into the probability of ischemia in this large sample of patients. Prospective studies are needed to validate these findings.
Methods: All NSTEMI patients treated at the University of Rochester Medical Center between 2015-2023 (n=3515) were included. The 13-items from the ACS Symptom Checklist were extracted using natural language processing (NLP) before coronary angiography or within 24 hours of presentation. An occluded coronary artery was one requiring revascularization with percutaneous coronary intervention. Chi-Square was used to assess the sensitivity and specificity of each symptom for an acutely occluded coronary artery. We used logistic regression models to assess the odds of an acutely occluded artery after controlling for age, obesity, and diabetes and stratified by sex.
Results: Patients were predominantly male (58%, n=2048), older (69+13 years), and White (85%, n=2988), and 15% (n=524) underwent revascularization. Diabetes (18%, n=629) and obesity (40%, n=1387) were common comorbidities. Upper back pain (10.5% vs. 14.1%, p=0.03), palpitations (19.3% vs. 23.9%, p=0.02), arm pain (21.0% vs 16.7%, p=0.05), unusual fatigue (8.9% vs. 22.2%, p<0.01) significantly differentiated between NSTEMI patients with and without an occluded coronary artery as observed in Table 1. Among men, less upper back pain (OR=0.559, 95% CI 0.361-0.865), palpitations (OR=0.678, 95% CI 0.503-0.915), and unusual fatigue (OR=0.365 95% CI 0.270-0.493) were significant predictors of coronary occlusion. Only a higher likelihood of arm pain (OR=1.184, 95% CI 0.893-1.569) predicted occlusion. Results were similar for women.
Conclusion: Only arm pain, a common symptom of ischemia, predicted an occluded coronary artery in patients with NSTEMI and there were few sex differences. NLP confirmed that the presence of arm pain can cue clinicians into the probability of ischemia in this large sample of patients. Prospective studies are needed to validate these findings.
More abstracts on this topic:
Cardiac Rupture as a Life-Threatening Outcome of Takotsubo Syndrome: A Systematic Review.
Denicolai Martin, Morello Matteo, Del Buono Marco, Sanna Tommaso, Agatiello Carla, Abbate Antonio
Are Females More Fraily than Males at Time of Heart Failure Diagnosis?Roberts Davis Mary, Dieckmann Nathan, Chien Christopher, Hansen Lissi, Erickson Elise, Alkayed Nabil, Shannon Jackilen, Denfeld Quin