Final ID: MDP1404
AI-enabled Cardiac Chambers Volumetry in Non-Contrast Cardiac CT scans (AI-CAC) Detects HFrEF vs. HFpEF
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Coronary artery calcium (CAC) scans contain more information than is currently reported. We have previously shown in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) that AI-enabled left atrial (LA) volumetry in CAC scans (AI-CAC) enabled prediction of atrial fibrillation (AF) as early as one year. Furthermore, we have shown adding AI-CAC LA volumetry to CHA2DS2-VASc risk score improved stroke prediction in MESA. We have recently reported that AI-CAC left ventricular (LV) volumetry and mass significantly predicted incident heart failure (HF) and outperformed NT-proBNP. In this report, we examined whether AI-CAC can distinguish heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) versus heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Methods: We applied the AutoChamberTM (HeartLung.AI, Houston, TX) component AI-CAC to data from 75 patients who underwent both a cardiac CT scan and echocardiography at Harbor UCLA medical center. AI-CAC took on average 21 seconds per scan and reported estimated volume for left atrium (LA), left ventricle (LV), right atrium (RA), and right ventricle (RV). LV volume was indexed (LVVI) by dividing LV volume by body surface area (BSA) to allow a more accurate assessment of the size of the left ventricle relative to the size of the individual. The average BSA for males and female were 1.59 ± 0.3 and 1.29 ± 0.2, respectively. HFrEF and HFpEF were defined as EF<40% and EF>50% respectively.
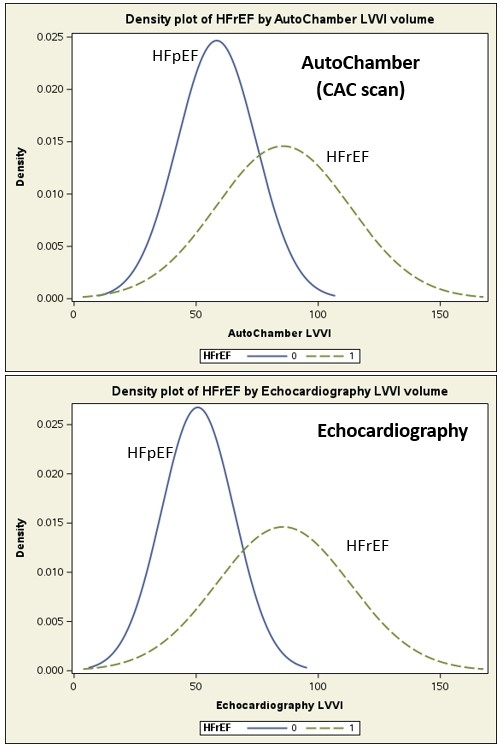
Results: Average EF was 57.5 ± 7.0 in males and 59.7 ± 8.1 in females, respectively. AutoChamber volume for HFpEF vs HFrEF were LA (84.8+35.3 vs 113.2+32.8 p=0.002), LV (109.9+36.7 vs 170.7+65.9 p=0.0007), RA (97.5+58.3 vs 117.2+51.1 p=0.18), RV (135.6+52.1 vs 176.2+70.8 p=0.008), LVW (116.1+39.1 vs 170.6+56.9 p=0.0005). Density plots in the figure show a clear distinction between HFpEF and HFrEF using AI measured LVVI and comparable results.
Conclusion: AI-enabled automated cardiac chambers volumetry in CAC scans correlates well with echocardiography-based LVVI and detects HFrEF vs. HFpEF. Further studies are needed to evaluate the clinical utility of AI-CAC and the ability of AutoChamber for prospective detection of patients at risk of HFrEF vs. HFpEF.
Methods: We applied the AutoChamberTM (HeartLung.AI, Houston, TX) component AI-CAC to data from 75 patients who underwent both a cardiac CT scan and echocardiography at Harbor UCLA medical center. AI-CAC took on average 21 seconds per scan and reported estimated volume for left atrium (LA), left ventricle (LV), right atrium (RA), and right ventricle (RV). LV volume was indexed (LVVI) by dividing LV volume by body surface area (BSA) to allow a more accurate assessment of the size of the left ventricle relative to the size of the individual. The average BSA for males and female were 1.59 ± 0.3 and 1.29 ± 0.2, respectively. HFrEF and HFpEF were defined as EF<40% and EF>50% respectively.
Results: Average EF was 57.5 ± 7.0 in males and 59.7 ± 8.1 in females, respectively. AutoChamber volume for HFpEF vs HFrEF were LA (84.8+35.3 vs 113.2+32.8 p=0.002), LV (109.9+36.7 vs 170.7+65.9 p=0.0007), RA (97.5+58.3 vs 117.2+51.1 p=0.18), RV (135.6+52.1 vs 176.2+70.8 p=0.008), LVW (116.1+39.1 vs 170.6+56.9 p=0.0005). Density plots in the figure show a clear distinction between HFpEF and HFrEF using AI measured LVVI and comparable results.
Conclusion: AI-enabled automated cardiac chambers volumetry in CAC scans correlates well with echocardiography-based LVVI and detects HFrEF vs. HFpEF. Further studies are needed to evaluate the clinical utility of AI-CAC and the ability of AutoChamber for prospective detection of patients at risk of HFrEF vs. HFpEF.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Deep Learning Digital Biomarker for Mitral Valve Prolapse using Echocardiogram Videos
Al-alusi Mostafa, Khurshid Shaan, Sanborn Danita, Picard Michael, Ho Jennifer, Maddah Mahnaz, Ellinor Patrick, Lau Emily, Small Aeron, Reeder Christopher, Shnitzer Dery Tal, Andrews Carl, Kany Shinwan, Ramo Joel, Haimovich Julian
A Cross-scale Causal Machine Learning Framework Pinpoints Mgl2+ Macrophage Orchestrators of Balanced Arterial GrowthHan Jonghyeuk, Kong Dasom, Schwarz Erica, Takaesu Felipe, Humphrey Jay, Park Hyun-ji, Davis Michael E