Final ID: MDP1570
Digital Health Intervention Yields Modest Improvements in Diet and Blood Pressure Among Adults with Hypertension
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background. The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is an evidence-based treatment for adults with hypertension and has health benefits for other cardiovascular disease risk factors. Yet, DASH has not been fully disseminated. Digital health solutions offer a promising approach to disseminate DASH. However, the efficacy of these approaches is unknown.
Aims. To evaluate the efficacy of a digital health intervention on DASH adherence and blood pressure (BP) among adults with hypertension.
Methods. Nourish was a 2-arm RCT to evaluate the efficacy of a 12-month digital health intervention, compared to attention control, among adults with hypertension. The intervention, delivered virtually, included skills training, goal setting, self-monitoring, personalized feedback, and dietitian coaching. The primary and secondary outcomes were 6-month changes in DASH adherence and BP, respectively. DASH scores ranged from 1 (lowest) -9 (highest). Outcomes were also assessed at 12 months to evaluate long term effect. We used linear mixed models to test the efficacy of the intervention on change in DASH score and BP. BP models adjusted for change in BP medications.
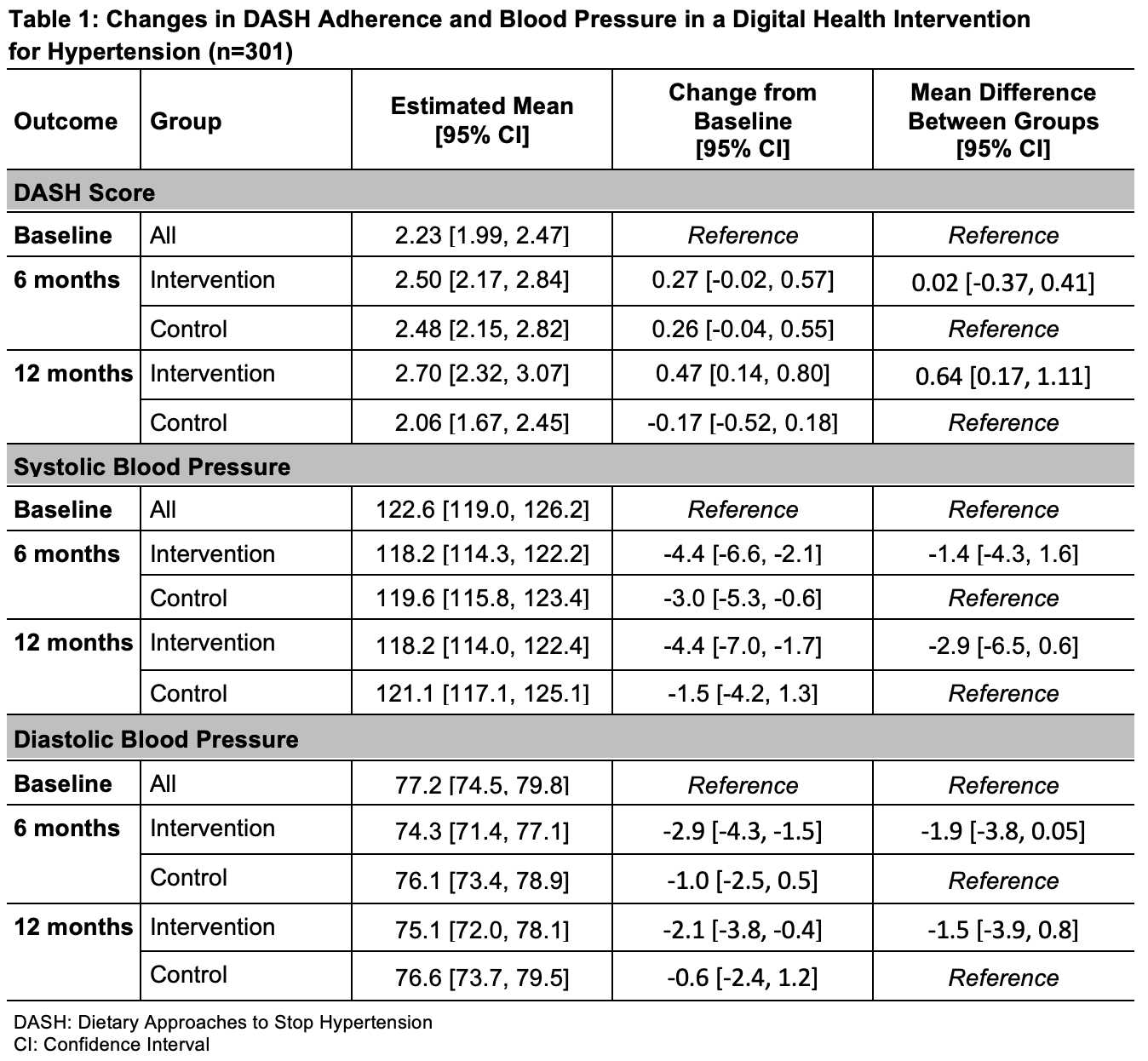
Results. Nourish randomized 301 adults: 150 to the intervention and 151 to attention control. The mean age of participants was 54.4 (SD=13.4) years. Most participants identified as female (65%); over half identified as white (53%); and 31% identified as Black. Change in DASH score was not significantly different between arms at 6 months (Mdiff=0.02, 95% CI=-0.37,0.41), yet the intervention arm had a greater increase in DASH score, relative to attention control, at 12 months (Mdiff =0.64, 95% CI=0.17,1.11). Mean SBP and DBP were significantly reduced in the intervention arm at 6-months compared to baseline (mean SBP change=-4.4 mm Hg, 95% CI=-6.6,-2.1; mean DBP change=-2.9, 95% CI:-4.3,-1.5). However, no significant between-group differences were found. Findings were similar at 12 months (Table 1).
Conclusions. A 12-month digital health intervention led to modest improvements in DASH and BP among adults with hypertension. Further research is needed to elucidate the effectiveness of smartphone interventions to promote DASH. Trial registration: NCT03875768
Aims. To evaluate the efficacy of a digital health intervention on DASH adherence and blood pressure (BP) among adults with hypertension.
Methods. Nourish was a 2-arm RCT to evaluate the efficacy of a 12-month digital health intervention, compared to attention control, among adults with hypertension. The intervention, delivered virtually, included skills training, goal setting, self-monitoring, personalized feedback, and dietitian coaching. The primary and secondary outcomes were 6-month changes in DASH adherence and BP, respectively. DASH scores ranged from 1 (lowest) -9 (highest). Outcomes were also assessed at 12 months to evaluate long term effect. We used linear mixed models to test the efficacy of the intervention on change in DASH score and BP. BP models adjusted for change in BP medications.
Results. Nourish randomized 301 adults: 150 to the intervention and 151 to attention control. The mean age of participants was 54.4 (SD=13.4) years. Most participants identified as female (65%); over half identified as white (53%); and 31% identified as Black. Change in DASH score was not significantly different between arms at 6 months (Mdiff=0.02, 95% CI=-0.37,0.41), yet the intervention arm had a greater increase in DASH score, relative to attention control, at 12 months (Mdiff =0.64, 95% CI=0.17,1.11). Mean SBP and DBP were significantly reduced in the intervention arm at 6-months compared to baseline (mean SBP change=-4.4 mm Hg, 95% CI=-6.6,-2.1; mean DBP change=-2.9, 95% CI:-4.3,-1.5). However, no significant between-group differences were found. Findings were similar at 12 months (Table 1).
Conclusions. A 12-month digital health intervention led to modest improvements in DASH and BP among adults with hypertension. Further research is needed to elucidate the effectiveness of smartphone interventions to promote DASH. Trial registration: NCT03875768
More abstracts on this topic:
A Small, Convenient, and Calibration-Free Absolute Blood Pressure Measurement Device Based on the Oscillometric Method
Inan Omer, Ozmen Goktug, Berkebile John, Dubuque Shaun, Tourian Dikran, Chan Michael
A Real-world Evaluation of Longitudinal Healthcare Expenses in a Health System Registry of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease Enabled by the 21st Century Cures ActDhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Pedroso Aline, Rajpura Jigar, Mehanna Sherif, Tonnu-mihara Ivy, Khera Rohan