Final ID: Su1005
Demographics and Regional Trends in Mortality associated with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases in the Nicotine-Dependent Population: A Retrospective Study in the United States from 1999 to 2020
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases (ASCVD) are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality, causing four out of every five cardiovascular (CV) deaths. Nicotine is a significant risk factor for ASCVDs. While there is comprehensive data available on mortality trends for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) in general, the mortality data for ASCVDs in the nicotine-dependent population is still lacking.
Objective: We aim to explore the mortality trends and patterns related to ASCVDs in the nicotine-dependent population of the US, stratified by different demographic and regional variables.
Methods: We retrieved the data from the CDC Wonder database and determined the crude death rates (CRs) and age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) per 100,000 individuals. We targeted the middle-aged and older adult nicotine-dependent population. Our study examined the changes in AAMR through annual percentage change (APC) and average annual percentage change (AAPC) using Joinpoint regression program.
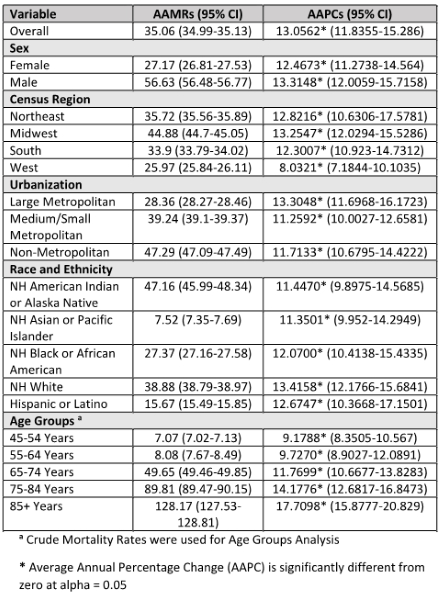
Results: From 1999 to 2020, a total of 912,565 deaths were reported due to ASCVDs in the nicotine-dependent population of the US, demonstrating an increasing trend (AAPC = 13.06). Males (56.63) had a higher AAMR than females (19.05). Non-Hispanic (NH) American Indians or Alaska Natives had the highest AAMR (47.16), while the NH Asians or Pacific Islanders had the lowest (7.52). The AAMRs also varied by regions, with Midwest having the highest AAMR (44.88) followed by Northeast (35.72), South (33.9), and West (25.97). The states with the highest percentage change in AAMR were New Jersey and Tennessee, while those with the lowest percentage change were California and North Dakota. Non-metropolitan areas had the highest AAMR (47.29), followed by medium/small metropolitan (39.24) and large metropolitan (28.36). Most deaths occurred at the decedent’s home (39.46%) and the medical facility (39.37%).
Conclusion: We reported increasing ASCVDs-related age-adjusted mortality trends in the nicotine-dependent population of the US, with the highest AAMRs in males, NH American Indians/Alaska Natives, the midwestern region, and the non-metropolitan areas. Targeted health policy measures must be taken to address these alarming trends.
Objective: We aim to explore the mortality trends and patterns related to ASCVDs in the nicotine-dependent population of the US, stratified by different demographic and regional variables.
Methods: We retrieved the data from the CDC Wonder database and determined the crude death rates (CRs) and age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) per 100,000 individuals. We targeted the middle-aged and older adult nicotine-dependent population. Our study examined the changes in AAMR through annual percentage change (APC) and average annual percentage change (AAPC) using Joinpoint regression program.
Results: From 1999 to 2020, a total of 912,565 deaths were reported due to ASCVDs in the nicotine-dependent population of the US, demonstrating an increasing trend (AAPC = 13.06). Males (56.63) had a higher AAMR than females (19.05). Non-Hispanic (NH) American Indians or Alaska Natives had the highest AAMR (47.16), while the NH Asians or Pacific Islanders had the lowest (7.52). The AAMRs also varied by regions, with Midwest having the highest AAMR (44.88) followed by Northeast (35.72), South (33.9), and West (25.97). The states with the highest percentage change in AAMR were New Jersey and Tennessee, while those with the lowest percentage change were California and North Dakota. Non-metropolitan areas had the highest AAMR (47.29), followed by medium/small metropolitan (39.24) and large metropolitan (28.36). Most deaths occurred at the decedent’s home (39.46%) and the medical facility (39.37%).
Conclusion: We reported increasing ASCVDs-related age-adjusted mortality trends in the nicotine-dependent population of the US, with the highest AAMRs in males, NH American Indians/Alaska Natives, the midwestern region, and the non-metropolitan areas. Targeted health policy measures must be taken to address these alarming trends.
More abstracts on this topic:
Nicotine Exposure: A Catalyst for Nitrosative and Oxidative Stress in Glomerular Podocytes and Renal Impairment
Jones Adam, Palygin Oleg, Semenikhina Marharyta, Fedoriuk Mykhailo, Stefanenko Mariia, Cherezova Alena, Spires Denisha, Veit Acosta Martina, Stadler Krisztian, Ilatovskaya Daria
A multi-task deep learning algorithm for detecting obstructive coronary artery disease using fundus photographsZeng Yong, Ding Yaodong