Final ID: Sa4057
Intravascular Ultrasound Guided Versus Coronary Angiography Guided Complex Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) examining the efficacy of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS)-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) when compared with coronary angiography (CA)-guided PCI, for complex coronary artery disease, have produced varied findings. We aim to provide conclusive evidence by pooling all RCTs, including the latest IVUS-ACS trial, on the clinical outcomes of IVUS- and CA-guided complex PCI.
Methods
MEDLINE, Scopus, and EMBASE were queried from inception till June 2024 for RCTs comparing IVUS and CA in patients undergoing complex PCI for lesions defined as type B2/C according to the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines of classification of coronary lesions. The primary outcome was major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), a composite of cardiac death, myocardial infarction (MI), or ischemia-driven repeat revascularization. Secondary outcomes were cardiac death, MI, probable/definite stent thrombosis (ST), target lesion revascularization (TLR), target vessel revascularization (TVR), and post-procedural minimal lumen diameter (MLD). A random-effects meta-analysis was performed to derive risk ratios (RR) and mean differences (MD) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results
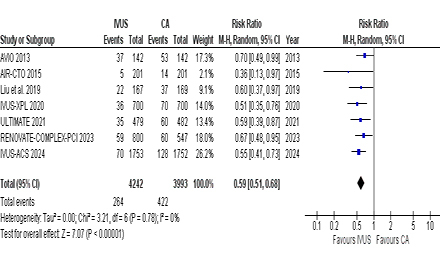
This meta-analysis included 11 RCTs with a total of 9,828 patients (5,037 in IVUS and 4,791 in CA) with a mean age of 63.8 years. IVUS-guided PCI was associated with significantly lower MACE (RR 0.59; 95% CI 0.51–0.68, p<0.00001) than CA. Similarly, patients in the IVUS group were significantly associated with a reduced risk of cardiac death (RR 0.47; 95% CI 0.29–0.73), MI (RR 0.77; 95% CI 0.60–0.99), TLR (RR 0.58; 95% CI 0.45–0.75), and TVR (RR 0.54; 95% CI 0.41–0.71). IVUS was also significantly associated with a greater MLD (MD 0.09; 95% CI 0.05–0.13) when compared with CA. However, no significant association could be ascertained in all-cause death (RR 0.66; 95% CI 0.40–1.10) and ST (RR 0.59; 95% CI 0.34–1.01). All outcomes reported non-significant heterogeneity and no publication bias was evident upon Egger’s regression (p=0.12).
Conclusion
Patients undergoing complex PCI with IVUS showed significantly lower MACE, cardiac death, MI, TLR, and TVR while having a greater MLD when compared with CA-guided PCI.
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) examining the efficacy of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS)-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) when compared with coronary angiography (CA)-guided PCI, for complex coronary artery disease, have produced varied findings. We aim to provide conclusive evidence by pooling all RCTs, including the latest IVUS-ACS trial, on the clinical outcomes of IVUS- and CA-guided complex PCI.
Methods
MEDLINE, Scopus, and EMBASE were queried from inception till June 2024 for RCTs comparing IVUS and CA in patients undergoing complex PCI for lesions defined as type B2/C according to the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association guidelines of classification of coronary lesions. The primary outcome was major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), a composite of cardiac death, myocardial infarction (MI), or ischemia-driven repeat revascularization. Secondary outcomes were cardiac death, MI, probable/definite stent thrombosis (ST), target lesion revascularization (TLR), target vessel revascularization (TVR), and post-procedural minimal lumen diameter (MLD). A random-effects meta-analysis was performed to derive risk ratios (RR) and mean differences (MD) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results
This meta-analysis included 11 RCTs with a total of 9,828 patients (5,037 in IVUS and 4,791 in CA) with a mean age of 63.8 years. IVUS-guided PCI was associated with significantly lower MACE (RR 0.59; 95% CI 0.51–0.68, p<0.00001) than CA. Similarly, patients in the IVUS group were significantly associated with a reduced risk of cardiac death (RR 0.47; 95% CI 0.29–0.73), MI (RR 0.77; 95% CI 0.60–0.99), TLR (RR 0.58; 95% CI 0.45–0.75), and TVR (RR 0.54; 95% CI 0.41–0.71). IVUS was also significantly associated with a greater MLD (MD 0.09; 95% CI 0.05–0.13) when compared with CA. However, no significant association could be ascertained in all-cause death (RR 0.66; 95% CI 0.40–1.10) and ST (RR 0.59; 95% CI 0.34–1.01). All outcomes reported non-significant heterogeneity and no publication bias was evident upon Egger’s regression (p=0.12).
Conclusion
Patients undergoing complex PCI with IVUS showed significantly lower MACE, cardiac death, MI, TLR, and TVR while having a greater MLD when compared with CA-guided PCI.
More abstracts on this topic:
Angiography-based pulmonary capillary transit time is a promising diagnostic tool for single ventricle pulmonary arteriovenous malformations
Bergstrand David, Spearman Andrew
Artificial Intelligence for Predicting Primary Antegrade Wiring Success of Chronic Total Occlusion CrossingAlexandrou Michaella, Alaswad Khaldoon, Basir Mir, Davies Rhian, Jaffer Farouc, Nicholson William, Azzalini Lorenzo, Gorgulu Sevket, Khatri Jaikirshan, Bangalore Sripal, Rangan Bavana, Rempakos Athanasios, Mastrodemos Olga, Burke M Nicholas, Sandoval Yader, Brilakis Emmanouil, Mutlu Deniz, Strepkos Dimitrios, Carvalho Pedro, Al-ogaili Ahmed, Bahbah Ali, Anastasios Milkas, Tsiafoutis Ioannis