Final ID: MDP67
Ficolin-1 Genetic Polymorphisms in Chronic Chagasic Cardiomyopathy
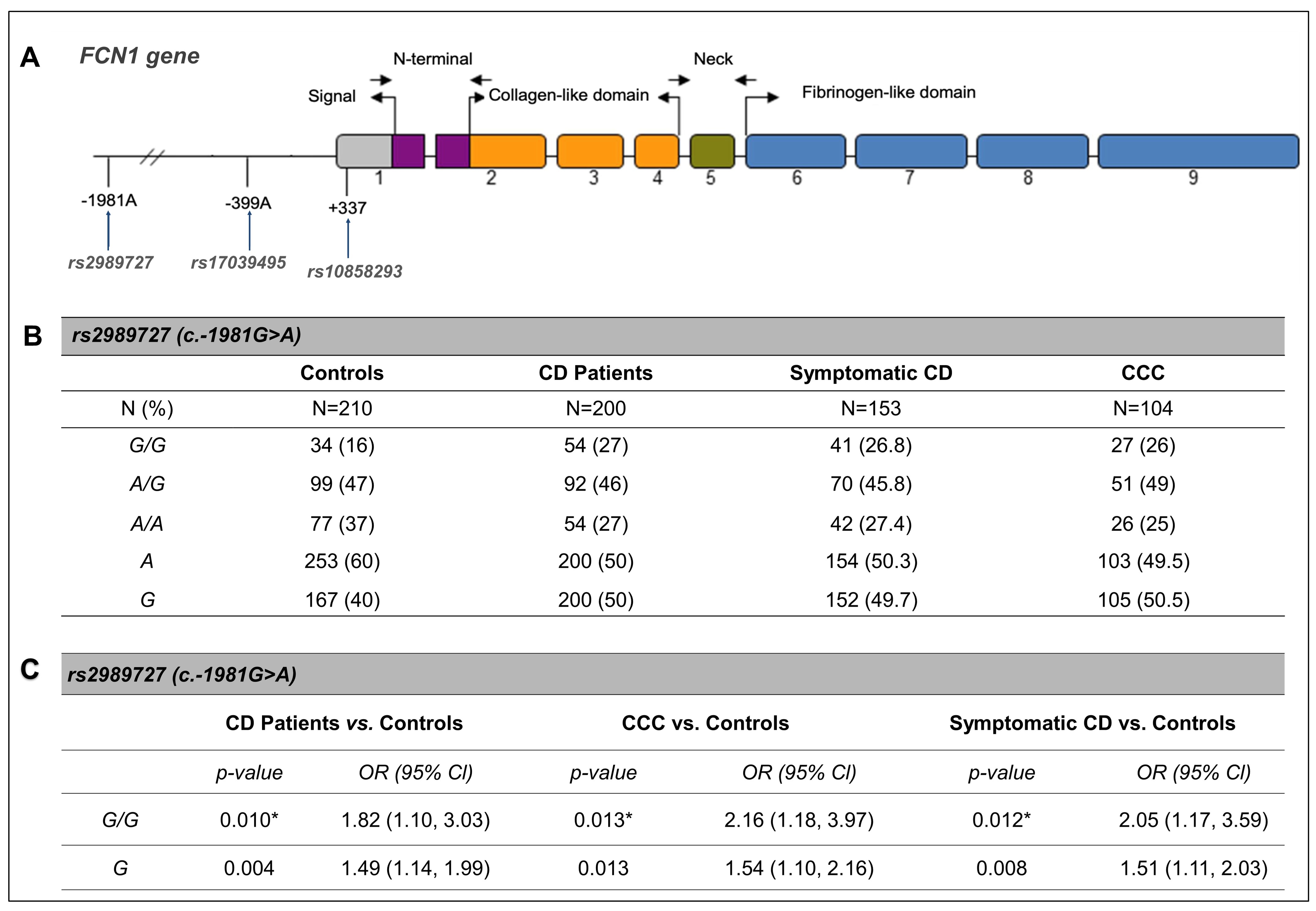
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Chagas disease (CD) is an infectious disease caused by the protozoa Trypanosoma cruzi, affecting around 6-7 million people in Latin America. Although most infected individuals remain asymptomatic throughout their lives, annually 2-5% of them progress to chronic chagasic cardiomyopathy (CCC), digestive megasyndromes, or both. Ficolins are innate immunity proteins that play a crucial role in the lectin pathway (LP) of complement activation. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns and mediate the clearance of apoptotic cells and cellular debris. Genetic polymorphisms of components of LP have been associated with clinical forms of CD; however, the relationship between Ficolin-1 (FCN1) gene polymorphisms and CD remains unclear. Hypothesis: We hypothesize that polymorphisms in the FCN1 gene, previously related to its expression, are associated with clinical forms of CD, possibly impacting LP activation. Goals: To investigate the association of genetic variants of the FCN1 gene with the clinical forms of chronic CD. Methods: We evaluated three single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs): rs2989727G>A (c.-1981G>A), rs17039495 (-399G>A) and rs10858293 (+33G>T) by sequence-specific amplification in 200 patients with chronic CD (23.5% asymptomatic, 52% CCC, 10% digestive form, and 14.5% cardiodigestive form) from Southern Brazil, and 210 T. cruzi seronegative controls. Logistic regression models were adjusted for sex, age, and self-identified ethnicity, followed by Bonferroni correction. Results: The haplotypes GGG, AGT, AGG, GAT, and AAT were more frequently found in patients, while GGG, AGT, AGG, and AAT were more common in controls. We observed a higher frequency of the G allele (p=0.004; OR 1.49; 95% CI 1.14, 1.99) of SNP rs2989727 and the GG genotype (p=0.010; OR 1.82; 95% CI 1.10, 3.03) in CD patients, particularly those with symptomatic forms (p=0.008; OR 1.51; 95% CI 1.11, 2.03; and p=0.012; OR 2.05; 95% CI 1.17, 3.59) and CCC (p=0.013; OR 1.54; 95% CI 1.10, 2.16, and p=0.013; OR 2.16; 95% CI 1.18, 3.97), compared to the control group. Conclusion: The FCN1 rs2989727 variant is associated with chronic CD and CCC, likely due to its impact on FCN1 gene expression.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Hypertrophic Cardimyopathy: Digenic Variants of Uncertain Significance Mutations in MHY7 and RYR2 Genes
Durukan Selina, Uzunoglu Ekin, Farahmandsadr Maryam, Soffer Daniel
Acceptability and Gain of Knowledge of Community Educational Tools About Rheumatic Heart Disease Integrated With Screening In Low-Income SettingsAbrams Jessica, Nunes Maria, Diniz Marina, Fraga Lucas, Paula Luiza, Coelho Cecilia, Tacuri Chavez Luz Marina, Lemos Larissa, Correia Julliane, Ribeiro Antonio, Nascimento Bruno, Sable Craig, Spaziani Alison, Zuhlke Liesl, Cardoso Clareci, Vinhal Wanessa, Ribeiro Isabely, Oliveira Kaciane, Amaral Ingred Beatriz