Final ID: Su2037
Pulmonary Valve Replacement-Related Change in Biventricular Global Function Index in Repaired Tetralogy Of Fallot
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Reduced biventricular global function index (BVGFI)—a novel indicator of ventricular performance—is associated with adverse clinical outcomes in patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot (rTOF). The impact of pulmonary valve replacement (PVR) on BVGFI has not been characterized.
Research Question: What is the impact of PVR on BVGFI in rTOF?
Objectives: To characterize the impact of PVR on BVGFI and identify pre-PVR determinants of depressed BVGFI after PVR in rTOF.
Methods: This is a single-center retrospective cohort study of rTOF patients fulfilling the following criteria: 1) Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) prior to and after PVR, utilizing the most proximal CMR to PVR within 2 years before and 3 years after the procedure; and 2) No interval cardiac procedure other than PVR. Patients with rTOF were compared with a control group free of heart disease. Based on the distribution of BVGFI in the control group, BVGFI was categorized as normal (>46), intermediate (40-46), or depressed (<40). Associations between pre-PVR characteristics and post-PVR depressed BVGFI were explored.
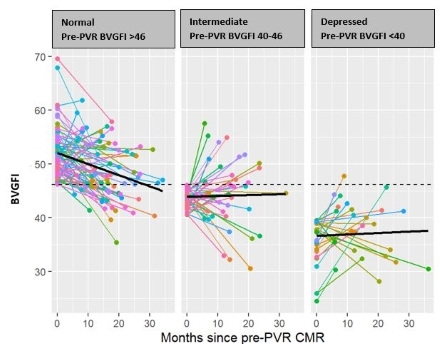
Results: Compared with controls (n=136), BVGFI was lower in rTOF (n=141) pre-PVR (46.6±7.6 vs 56.5±5.1, p<0.001). In rTOF, right ventricular volumes, mass, and ejection fraction decreased after PVR while BVGFI did not differ (46.6±7.6 vs 45.5±6.8, p=0.051). Individual changes in BVGFI from pre- to post-PVR varied as shown in Figure 1. In multivariable analysis, pre-PVR factors independently associated with depressed post-PVR BVGFI were lower BVGFI (adjusted-OR 0.81, 95% CI 0.76-0.89; p<0.001), male sex (OR 3.56, 95% CI 1.47, 8.66; p=0.005), ≥moderate pulmonary regurgitation (OR 7.01, 95% CI 1.33, 37.1; p=0.022), and left ventricular end-systolic volume index >41 ml/m2 vs < 33 ml/m2 (OR 2.8, 95% 1.33-7.31; p<0.001).
Conclusions: On average, pre-PVR BVGFI remained stable after PVR with notable variation among individual patients. Lower pre-PVR BVGFI, ≥moderate pre-PVR pulmonary regurgitation, male sex, and higher pre-PVR left ventricular end-systolic volume index are independently associated with depressed post-PVR BVGFI. Further research is warranted to elucidate the role of BVGFI in informing timing of PVR.
Research Question: What is the impact of PVR on BVGFI in rTOF?
Objectives: To characterize the impact of PVR on BVGFI and identify pre-PVR determinants of depressed BVGFI after PVR in rTOF.
Methods: This is a single-center retrospective cohort study of rTOF patients fulfilling the following criteria: 1) Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) prior to and after PVR, utilizing the most proximal CMR to PVR within 2 years before and 3 years after the procedure; and 2) No interval cardiac procedure other than PVR. Patients with rTOF were compared with a control group free of heart disease. Based on the distribution of BVGFI in the control group, BVGFI was categorized as normal (>46), intermediate (40-46), or depressed (<40). Associations between pre-PVR characteristics and post-PVR depressed BVGFI were explored.
Results: Compared with controls (n=136), BVGFI was lower in rTOF (n=141) pre-PVR (46.6±7.6 vs 56.5±5.1, p<0.001). In rTOF, right ventricular volumes, mass, and ejection fraction decreased after PVR while BVGFI did not differ (46.6±7.6 vs 45.5±6.8, p=0.051). Individual changes in BVGFI from pre- to post-PVR varied as shown in Figure 1. In multivariable analysis, pre-PVR factors independently associated with depressed post-PVR BVGFI were lower BVGFI (adjusted-OR 0.81, 95% CI 0.76-0.89; p<0.001), male sex (OR 3.56, 95% CI 1.47, 8.66; p=0.005), ≥moderate pulmonary regurgitation (OR 7.01, 95% CI 1.33, 37.1; p=0.022), and left ventricular end-systolic volume index >41 ml/m2 vs < 33 ml/m2 (OR 2.8, 95% 1.33-7.31; p<0.001).
Conclusions: On average, pre-PVR BVGFI remained stable after PVR with notable variation among individual patients. Lower pre-PVR BVGFI, ≥moderate pre-PVR pulmonary regurgitation, male sex, and higher pre-PVR left ventricular end-systolic volume index are independently associated with depressed post-PVR BVGFI. Further research is warranted to elucidate the role of BVGFI in informing timing of PVR.
More abstracts on this topic:
Aortic Valve Neocuspidization Using Autologous Insertion Of Pulmonary SinusTm: A Proof Of Concept
Faateh Muhammad, Raees Muhammad Aanish, Ahmed Hosam, Almiqlash Bushray, Villalobos Lizardi Jose, Ricci Marco, Ashfaq Awais
A Pressure-Volume Loops Approach Predicts Outcomes After Double Switch Operation For Congenitally Corrected Transposition Of The Great Arteries with Intact Ventricular SeptumThatte Nikhil, Del Nido Pedro, Ghelani Sunil, Hammer Peter, Marx Gerald, Beroukhim Rebecca, Gauvreau Kimberlee, Callahan Ryan, Prakash Ashwin, Emani Sitaram, Hoganson David