Final ID: Su1141
Carotid 3D Plaque Composition after Carnitine Supplementation in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: L-Carnitine (L-C) is a widely used nutritional supplement, but its effect on cardiovascular disease (CVD) is controversial. L-C has been shown to have benefits for CVD but is also believed to be associated with pro-atherogenic mechanisms. We have previously shown that L-C does not cause plaque progression (no effect) in metabolic syndrome patients supplemented with L-C but indicated an increase in stenosis. Carotid plaque ultrasound pixel distribution analysis (PDA) can identify plaque tissue types (soft vs calcified) indicating if a plaque is prone to rupture and to cause cardiovascular events. Beyond plaque volume (quantity), a change in plaque composition may have a role in causing cardiovascular events (increased lipid core).
Research Questions/Hypothesis: Is there a change in 3D plaque composition from baseline to 6-month when taking an L-C supplement in metabolic syndrome patients? If L-C is associated with pro-atherogenic mechanisms, perhaps plaque composition may change (increased fat), increasing risk for events.
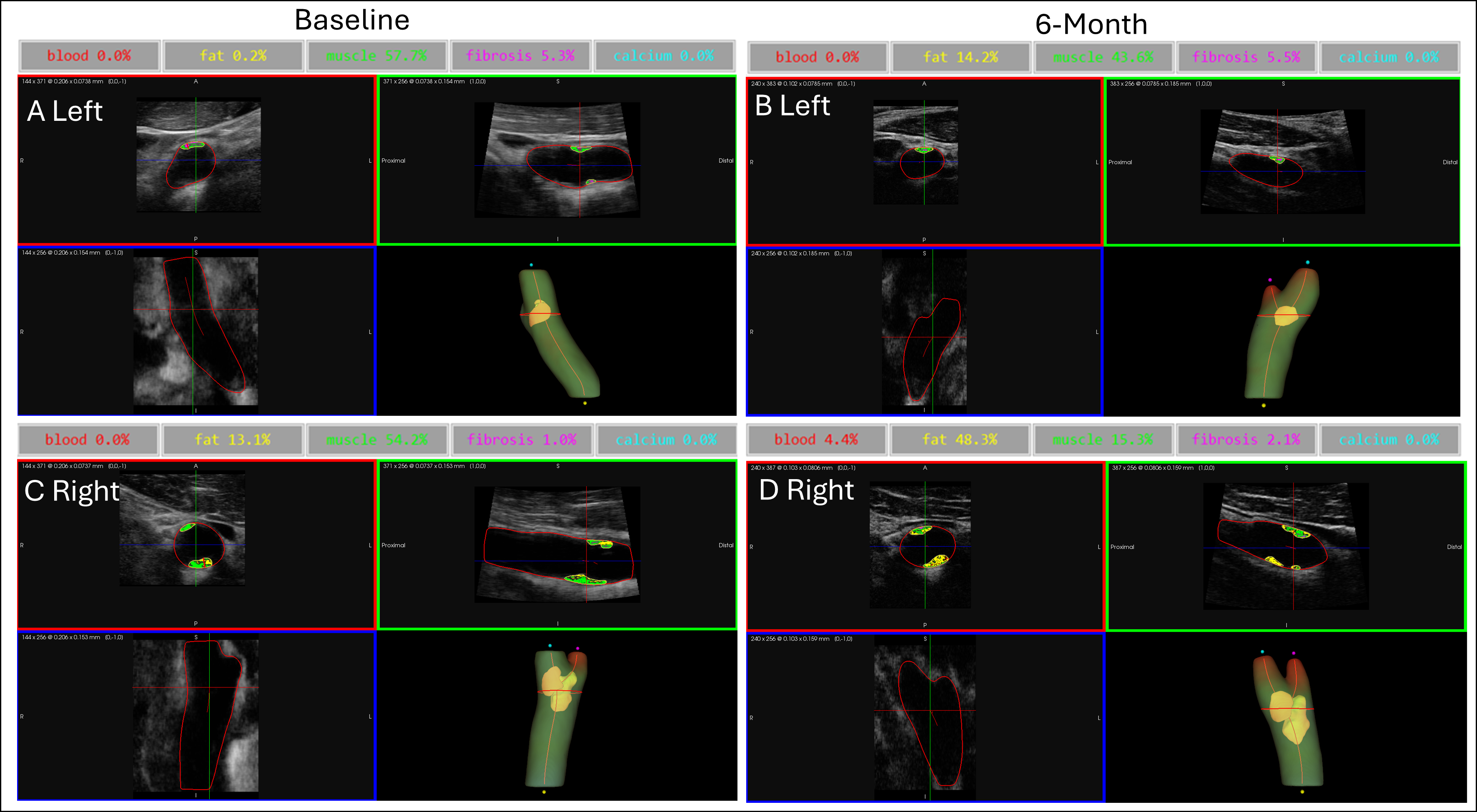
Methods: Patients were selected from cardiology and stroke clinics who met the diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome. Participants (n=157) were randomized to 6-month L-C (2g/day, n=76) or placebo (n=81). Participants received a 3D carotid ultrasound at baseline and 6-months. Carotid plaques were analyzed using a novel 3D carotid arterial plaque composition analysis software (Carotid Model, Figure) that uses deep learning artery and plaque classifications with grayscale PDA (Philips Healthcare). 3D percent change in plaque volume, blood, fat, muscle, fibrous, and calcium due to L-C supplementation was assessed by pairwise t-test.
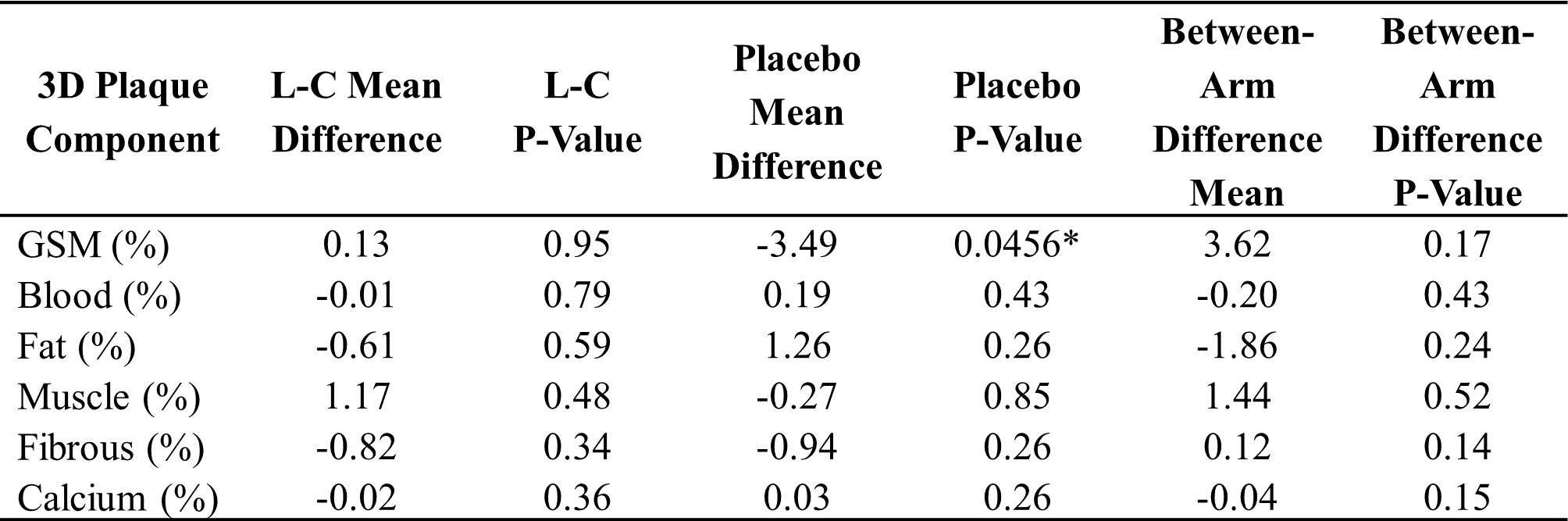
Results: We found no difference in baseline characteristics between placebo and L-C arms. There was no change in percent total plaque volume (L-C=4.18% vs Placebo=17.0%; P=0.24). Each plaque composition component remained similar from baseline to 6-month within arms and between arms (Table). There was a slight increase in grayscale median value in the placebo arm.
Conclusion(s): We did not observe a change in carotid 3D plaque volume or plaque composition following 6-month treatment with L-C. Our findings support the theory that L-C may not be directly involved in a pro-atherogenic mechanism. Although L-C supplementation did not influence plaque composition in this population, the software has great potential in determining changes in plaque vulnerability over time in response to drug therapy.
Research Questions/Hypothesis: Is there a change in 3D plaque composition from baseline to 6-month when taking an L-C supplement in metabolic syndrome patients? If L-C is associated with pro-atherogenic mechanisms, perhaps plaque composition may change (increased fat), increasing risk for events.
Methods: Patients were selected from cardiology and stroke clinics who met the diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome. Participants (n=157) were randomized to 6-month L-C (2g/day, n=76) or placebo (n=81). Participants received a 3D carotid ultrasound at baseline and 6-months. Carotid plaques were analyzed using a novel 3D carotid arterial plaque composition analysis software (Carotid Model, Figure) that uses deep learning artery and plaque classifications with grayscale PDA (Philips Healthcare). 3D percent change in plaque volume, blood, fat, muscle, fibrous, and calcium due to L-C supplementation was assessed by pairwise t-test.
Results: We found no difference in baseline characteristics between placebo and L-C arms. There was no change in percent total plaque volume (L-C=4.18% vs Placebo=17.0%; P=0.24). Each plaque composition component remained similar from baseline to 6-month within arms and between arms (Table). There was a slight increase in grayscale median value in the placebo arm.
Conclusion(s): We did not observe a change in carotid 3D plaque volume or plaque composition following 6-month treatment with L-C. Our findings support the theory that L-C may not be directly involved in a pro-atherogenic mechanism. Although L-C supplementation did not influence plaque composition in this population, the software has great potential in determining changes in plaque vulnerability over time in response to drug therapy.
More abstracts on this topic:
10-Year Trend Analysis of Medicare Payment in Stroke Inpatient Hospital Admission
Wong Ka-ho, Krothapalli Neeharika, Littig Lauren, Champagne Alison, Majersik Jennifer, Reddy Vivek, De Havenon Adam
A multifaceted family intervention for blood pressure management in rural China: an open label, parallel group, cluster randomized trial (Healthy Family Program)Jiang Chao, Dong Jianzeng, Cai Jun, Anderson Craig, Du Xin, Tang Yangyang, Han Rong, Song Yanna, Wang Chi, Lin Xiaolei, Yi Yang, Rodgers Anthony, Ma Changsheng