Final ID: MDP1353
Prognostic Value of Different Definitions of Iron Deficiency in Light Chain Cardiac Amyloidosis Patients
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Previous research on the iron deficiency (ID) of patients with light chain cardiac amyloidosis (AL-CA) has been limited.
Aims: The purpose of this study was to investigate how different definitions of ID affect its prevalence and association with prognosis in patients with AL-CA.
Methods: Consecutive patients diagnosed with AL-CA at Heart failure Center, Fuwai hospital between September 2017 and July 2023 with available iron status were included. ID was defined as (1) serum ferritin concentration of <100 ng/ml, or 100-299 ng/ml with transferrin saturation (TSAT) <20% (according to international guidelines on heart failure), (2) TSAT<20%, (3) serum iron <13 μmol/L. The primary outcome measure was all-cause mortality. Kaplan–Meier cumulative endpoint curves were used to compare groups. Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate the effects of variables on the primary outcome.
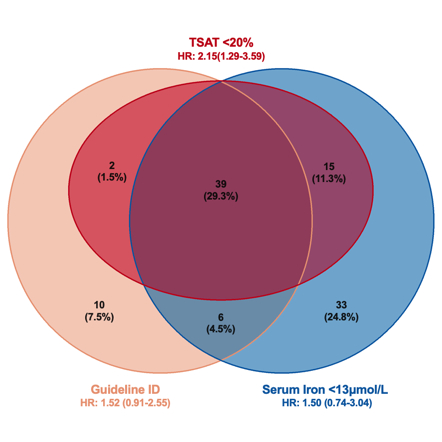
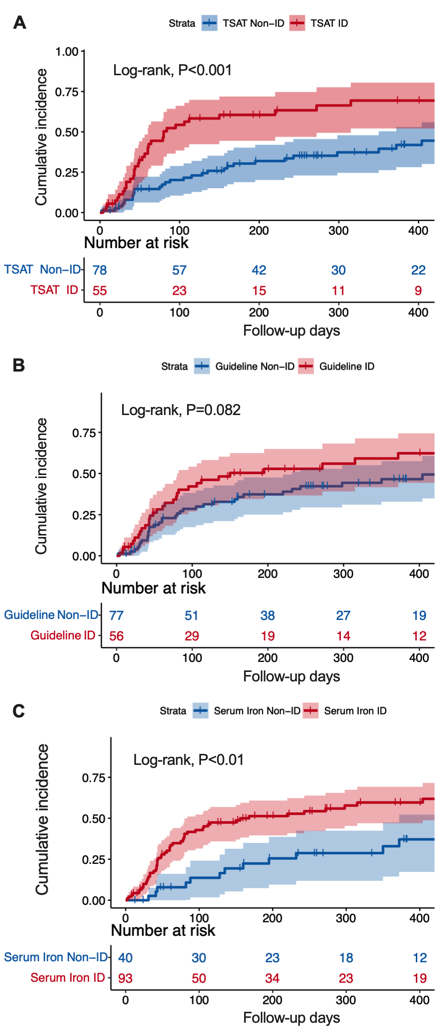
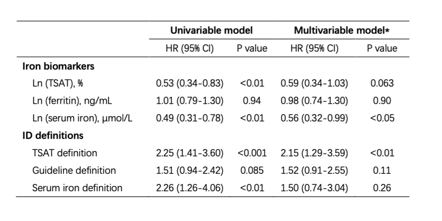
Results: Overall, 133 patients were included, and the prevalence of ID was 41.4%, 42.1% and 69.9% respectively depending on the definition used. ID defined by TSAT and serum iron was associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR] 2.25, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.41-3.60, and HR 2.26, 95% CI: 1.26-4.06), but the same association was not seen with the guideline definition of ID (HR 1.51, 95% CI: 0.945-2.42). In the multivariable model adjusting for age, gender, hemoglobin, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), troponin I (cTnI) and difference between involved and uninvolved free light chain (dFLC) levels, the predictive value of TSAT<20% remained (adjusted HR 2.15, 95% CI: 1.29-3.59).
Conclusions: Different definitions of ID yield inconsistent results in terms of prevalence and prognosis. ID, as defined by TSAT<20%, emerged as an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in patients with AL-CA.
Aims: The purpose of this study was to investigate how different definitions of ID affect its prevalence and association with prognosis in patients with AL-CA.
Methods: Consecutive patients diagnosed with AL-CA at Heart failure Center, Fuwai hospital between September 2017 and July 2023 with available iron status were included. ID was defined as (1) serum ferritin concentration of <100 ng/ml, or 100-299 ng/ml with transferrin saturation (TSAT) <20% (according to international guidelines on heart failure), (2) TSAT<20%, (3) serum iron <13 μmol/L. The primary outcome measure was all-cause mortality. Kaplan–Meier cumulative endpoint curves were used to compare groups. Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate the effects of variables on the primary outcome.
Results: Overall, 133 patients were included, and the prevalence of ID was 41.4%, 42.1% and 69.9% respectively depending on the definition used. ID defined by TSAT and serum iron was associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR] 2.25, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.41-3.60, and HR 2.26, 95% CI: 1.26-4.06), but the same association was not seen with the guideline definition of ID (HR 1.51, 95% CI: 0.945-2.42). In the multivariable model adjusting for age, gender, hemoglobin, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), troponin I (cTnI) and difference between involved and uninvolved free light chain (dFLC) levels, the predictive value of TSAT<20% remained (adjusted HR 2.15, 95% CI: 1.29-3.59).
Conclusions: Different definitions of ID yield inconsistent results in terms of prevalence and prognosis. ID, as defined by TSAT<20%, emerged as an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in patients with AL-CA.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acoramidis Effect on All-Cause Mortality in Patients with p.V142I (V122I) Variant ATTR-CM: Findings From the ATTRibute-CM Study
Alexander Kevin, Bhatt Kunal, Judge Daniel, Grodin Justin, Akinboboye Olakunle, Chen Chris, Tamby Jean-francois, Castano Adam, Fox Jonathan, Fontana Marianna, Gillmore Julian, Sarswat Nitasha, Grogan Martha, Solomon Scott, Davis Margot, Cuddy Sarah, Kittleson Michelle, Shah Keyur, Griffin Jan, Ruberg Frederick, Khouri Michel
A Scoping Review Exploring Cardiovascular Risk and Health Metrics and Cancer PredictionKim Ji-eun, Henriquez Santos Gretell, Kumar Sant, Livinski Alicia, Vo Jacqueline, Joo Jungnam, Shearer Joe, Hashemian Maryam, Roger Veronique