Final ID: Mo3036
The Effect of Fenofibrate Added to Statin Therapy on Patients with High Baseline Remnant Cholesterol in the Primary Prevention Setting: An Analysis of the National Health Insurance Service–National Sample Cohort, 2010–2015
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Studies have shown that lipid-lowering therapies have greater CV benefits in patients with higher baseline CV risk and lipid profiles including low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglyceride (TG). There is limited data on the effect of fenofibrate based on baseline remnant cholesterol (RC) levels or whether there is varying benefit in higher RC concentrations. Herein, we analyzed the REFRESH (REmnant cholesterol and Fenofibrate RESearch by the Korean national Health insurance data) cohort to investigate the effect of fenofibrate based on baseline RC levels in a primary prevention setting.
Methods: The REFRESH cohort was divided into subjects based on median RC levels (RC ≥ 26.1 and RC < 26.1 mg/dL groups). Propensity score matching (PSM) was performed between subjects who did or did not take fenofibrate within the RC ≥ median and RC < median groups. The primary endpoint was major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular event (MACE), a composite of CV death, stroke, and incident coronary artery disease.
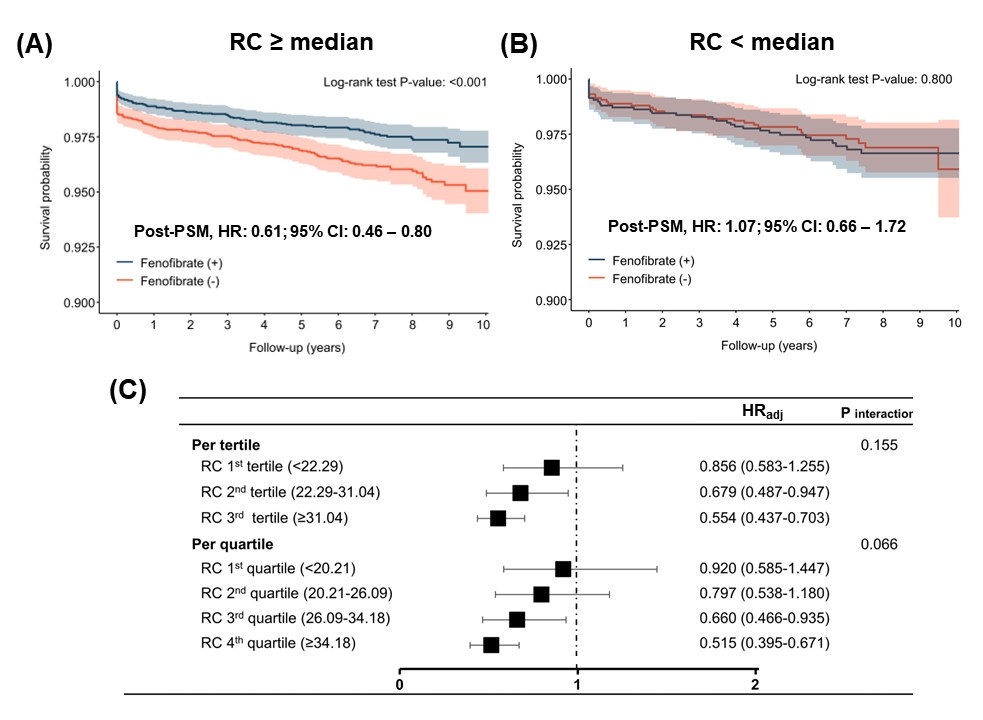
Results: The final REFRESH cohort included 49,507 statin-taking individuals (mean age: 58.2 years; body mass index: 24.7 kg/m2; hypertension: 75.7%; diabetes: 30.9%; mean follow-up duration: 84.1 months). Patients in the RC ≥ median group had worse lipid profiles than the RC < median group (RC ≥ median vs. < median; LDL-C: 151.1 vs. 144.3 mg/dL; TG: 232.4 vs. 94.9 mg/dL; RC: 38.2 vs. 20.1 mg/dL). Fenofibrate was associated with a reduction of MACE (HR: 0.61; 95% CI: 0.46 – 0.80) in the RC ≥ median group (Figure A), while there was no benefit in the RC < median group (HR: 1.07; 95% CI: 0.66 – 1.72) in the post-PSM analysis (Figure B). A trend of dose-dependent decrease in adjusted hazard ratio with fenofibrate was also observed with rising RC quartiles (Figure C).
Conclusions: In the REFRESH study, we observed that fenofibrate was linked to notable CV benefits for patients with elevated RC levels in the primary prevention setting.
Methods: The REFRESH cohort was divided into subjects based on median RC levels (RC ≥ 26.1 and RC < 26.1 mg/dL groups). Propensity score matching (PSM) was performed between subjects who did or did not take fenofibrate within the RC ≥ median and RC < median groups. The primary endpoint was major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular event (MACE), a composite of CV death, stroke, and incident coronary artery disease.
Results: The final REFRESH cohort included 49,507 statin-taking individuals (mean age: 58.2 years; body mass index: 24.7 kg/m2; hypertension: 75.7%; diabetes: 30.9%; mean follow-up duration: 84.1 months). Patients in the RC ≥ median group had worse lipid profiles than the RC < median group (RC ≥ median vs. < median; LDL-C: 151.1 vs. 144.3 mg/dL; TG: 232.4 vs. 94.9 mg/dL; RC: 38.2 vs. 20.1 mg/dL). Fenofibrate was associated with a reduction of MACE (HR: 0.61; 95% CI: 0.46 – 0.80) in the RC ≥ median group (Figure A), while there was no benefit in the RC < median group (HR: 1.07; 95% CI: 0.66 – 1.72) in the post-PSM analysis (Figure B). A trend of dose-dependent decrease in adjusted hazard ratio with fenofibrate was also observed with rising RC quartiles (Figure C).
Conclusions: In the REFRESH study, we observed that fenofibrate was linked to notable CV benefits for patients with elevated RC levels in the primary prevention setting.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies Comparing Short and Longterm Outcomes of Trans-Catheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Patient with and without Cancer:
Khan Muhammad Aslam, Haider Adnan, Haider Taimoor, Bhattarai Shraddha, Khan Bilal, Lamichhane Bikal, Shafique Nouman, Rahman Hammad, Aafreen Asna, Muhammad Anza, Bhatia Hitesh, Khan Abid Nawaz Khan, Akbar Usman, Khan Alamzaib
A drug target Mendelian randomization study of triglyceride lowering therapies for aortic stenosisCiofani Jonathan, Han Daniel, Gill Dipender, Rao Karan, Allahwala Usaid, Bhindi Ravinay