Final ID: 4142394
HDL/ApoA1 inhibits macrophage ferroptosis via upregulating NRF2/SLC7A11/GSH pathway
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Ferroptosis is a novel type of programmed cell death characterized by excessive lipid peroxides and iron overload inside the cell. SLC7A11/GSH is one of the most important anti-ferroptotic pathways. Macrophage ferroptosis contributes to the progression of atherosclerosis. HDL exerts anti-atherosclerotic effects primarily by promoting cholesterol efflux. Whether HDL also inhibits macrophage ferroptosis is unknown.
Research Questions: This research was aimed to explore the effects and mechanisms of HDL on macrophage ferroptosis.
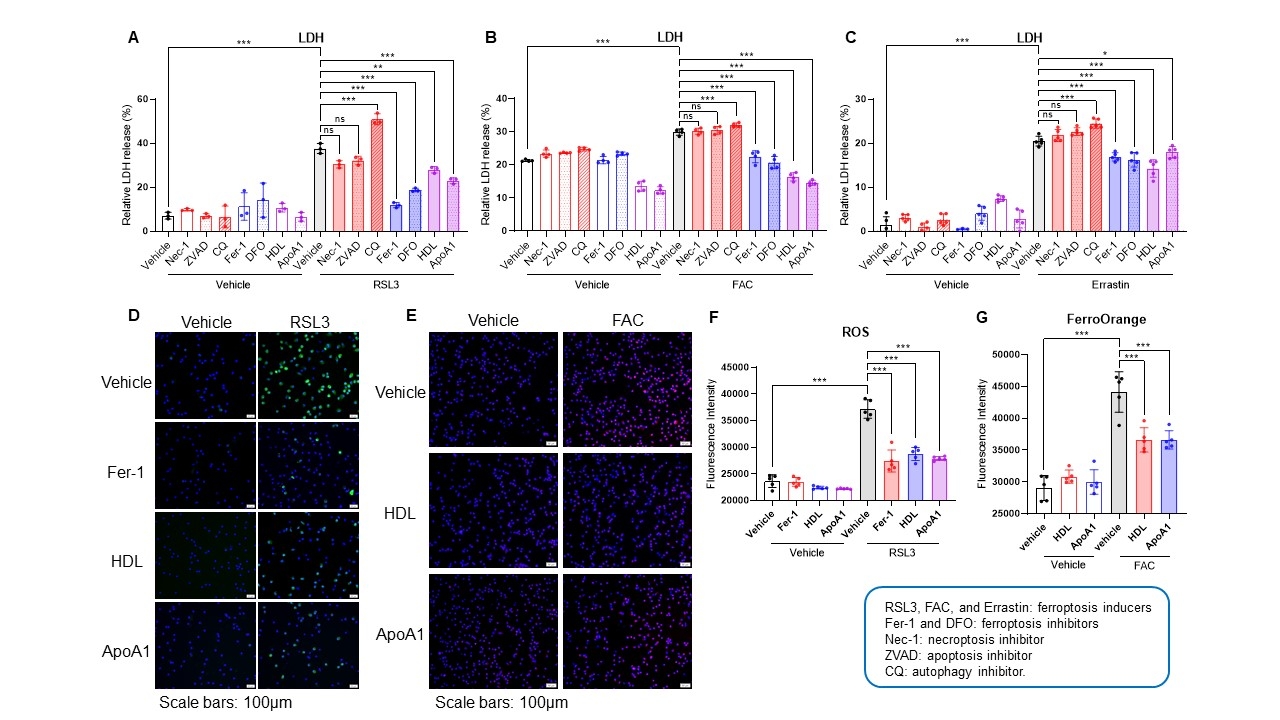
Methods: Macrophage ferroptosis was detected in plaques from patients with coronary artery disease. In vitro, macrophage was induced ferroptosis by multiple inducers and then the cells were treated with either vehicle or HDL or ApoA1. Ferroptosis was measured by detecting multiple ferroptosis markers (lipid peroxide, LDH release, ROS production, and cellular ferrous ion level).
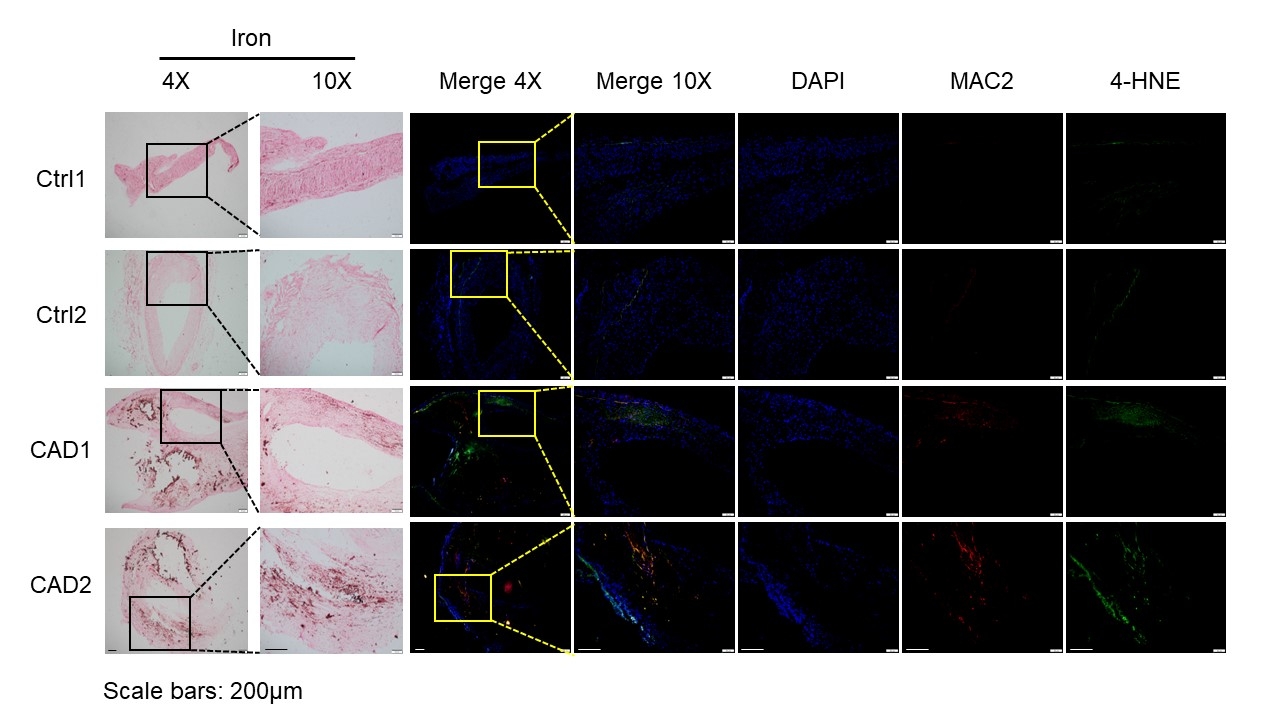
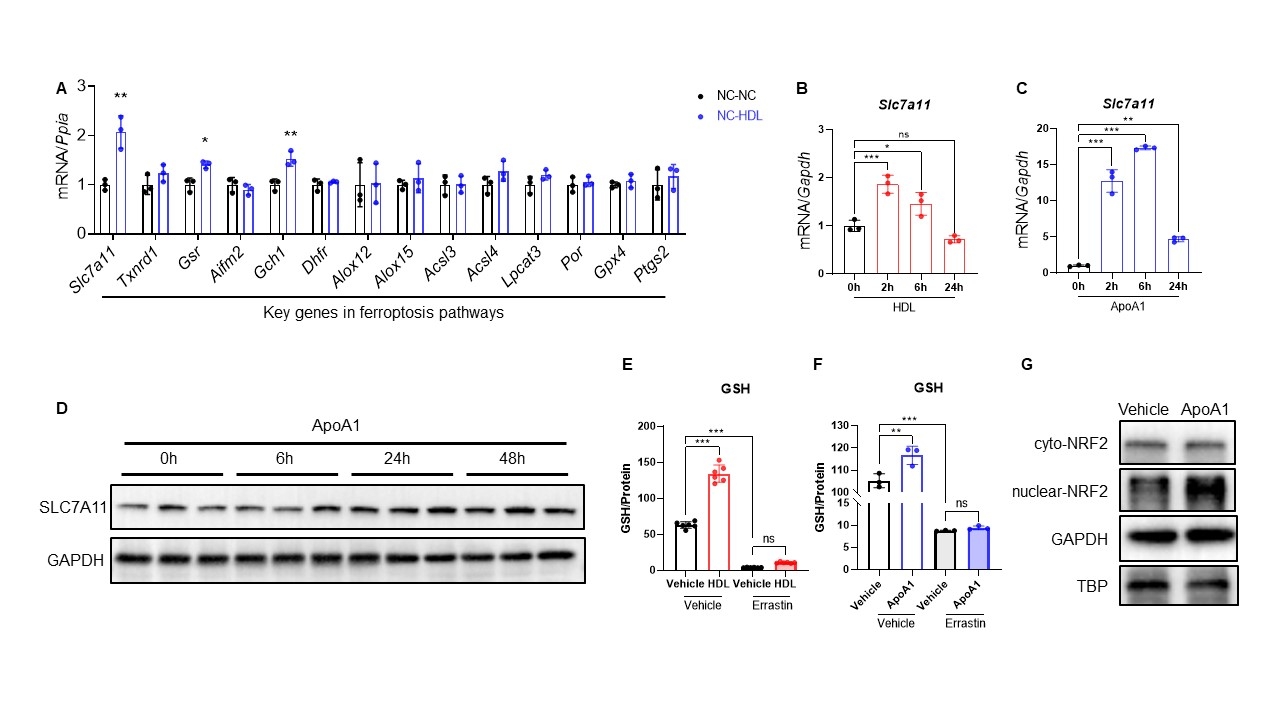
Results: Compared to controls, iron, lipid peroxide and macrophages were co-localized and significantly increased in coronary plaques, suggesting increased macrophage ferroptosis in atherosclerosis. In mouse macrophages, ferroptosis-inducers increased ferroptosis significantly, which was inhibited by HDL and ferroptosis inhibitors, but not neither by inhibitors of apoptosis, necroptosis, or autophagy. ApoA1, the main apolipoprotein on HDL, may account for HDL’s anti-ferroptotic effect. Mechanically, ApoA1 upregulated System Xc- (encoded by SLC7A11), an amino acid antiporter that exchanges intracellular glutamate and extracellular cysteine, thus elevating intracellular GSH and reducing ferroptosis. We further elucidated that ApoA1 activated NRF2, the transcription factor of SLC7A11, by promoting its nuclear translocation.
Conclusion: Our results imply that HDL/ApoA1 inhibits macrophage ferroptosis via upregulating NRF2/SLC7A11/GSH pathway, enriching the regulation and mechanisms of HDL/ApoA1’s anti-atherosclerotic effects.
Research Questions: This research was aimed to explore the effects and mechanisms of HDL on macrophage ferroptosis.
Methods: Macrophage ferroptosis was detected in plaques from patients with coronary artery disease. In vitro, macrophage was induced ferroptosis by multiple inducers and then the cells were treated with either vehicle or HDL or ApoA1. Ferroptosis was measured by detecting multiple ferroptosis markers (lipid peroxide, LDH release, ROS production, and cellular ferrous ion level).
Results: Compared to controls, iron, lipid peroxide and macrophages were co-localized and significantly increased in coronary plaques, suggesting increased macrophage ferroptosis in atherosclerosis. In mouse macrophages, ferroptosis-inducers increased ferroptosis significantly, which was inhibited by HDL and ferroptosis inhibitors, but not neither by inhibitors of apoptosis, necroptosis, or autophagy. ApoA1, the main apolipoprotein on HDL, may account for HDL’s anti-ferroptotic effect. Mechanically, ApoA1 upregulated System Xc- (encoded by SLC7A11), an amino acid antiporter that exchanges intracellular glutamate and extracellular cysteine, thus elevating intracellular GSH and reducing ferroptosis. We further elucidated that ApoA1 activated NRF2, the transcription factor of SLC7A11, by promoting its nuclear translocation.
Conclusion: Our results imply that HDL/ApoA1 inhibits macrophage ferroptosis via upregulating NRF2/SLC7A11/GSH pathway, enriching the regulation and mechanisms of HDL/ApoA1’s anti-atherosclerotic effects.
More abstracts on this topic:
Associations between High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Efflux and Brain Health
Giacona John, Rohatgi Anand, Vongpatanasin Wanpen, Wang Jijia, Zhang Rong, Kelley Brendan, Hajjar Ihab, Thomas Binu, Lacritz Laura, Yu Fang, De Lemos James
Association of HDL-2b and HDL-3 with severe coronary stenosis in acute myocardial infarction patients: effects of age, gender, and comorbiditiesWang Bin, Zhang Ping, Li Dong, Geng Yu, Wang Yujie, Cao Han, Tang Mingkun, Lv Changhua, Lv Tingting, Xue Yajun