Final ID: Mo1015
The Role of Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Indonesian Patients with COVID-19
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The clinical impact of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and right ventricular (RV) dysfunction on clinical outcomes in COVID-19 have not been studied in the often-underrepresented Indonesian population.
Aim: To investigate the role of NLR and RV dysfunction in Indonesian patients hospitalized for COVID-19.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted at a COVID-19 referral hospital in Indonesia. We included all adult patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between April 2020 – April 2021 who had transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) during admission. Clinical data were extracted from electronic medical records. TTE variables were defined according to the American Society of Echocardiography criteria. All statistical analyses were conducted using the SPSS software. This study was approved by the IRB at Universitas Indonesia (#2022-01-135).
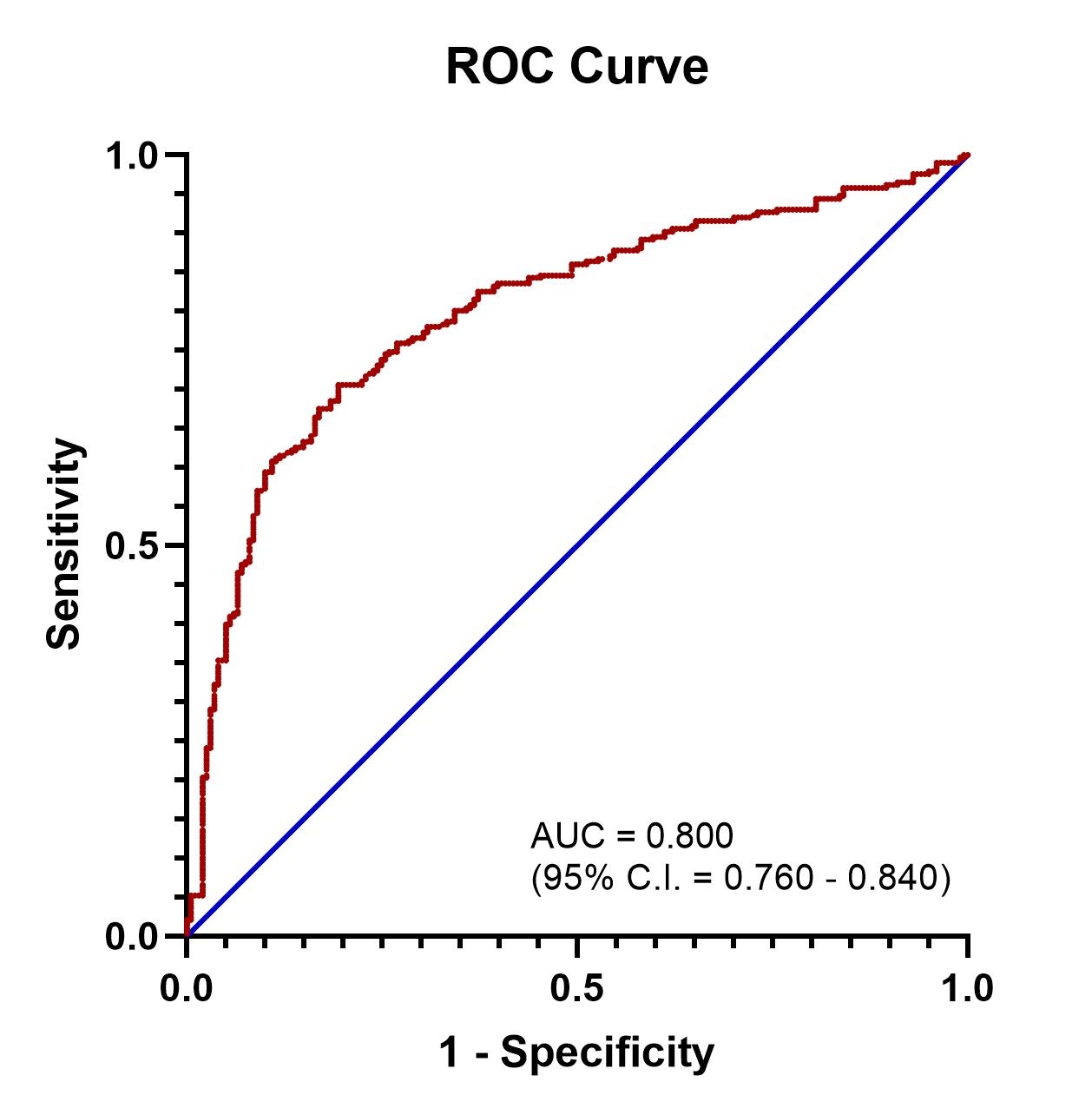
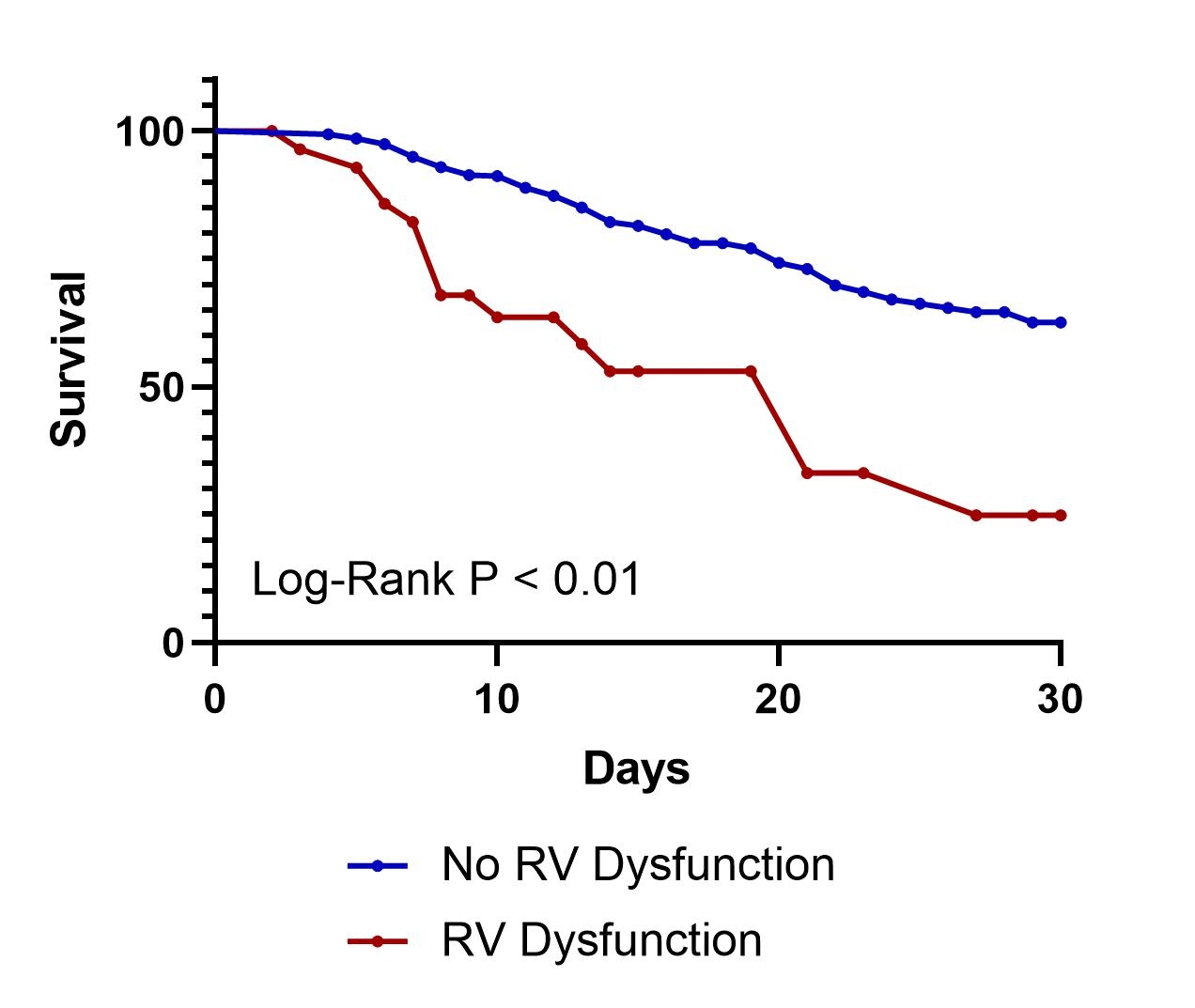
Results: A total of 488 patients were included – 29 with and 459 without RV dysfunction. The mean age of the population was 54.8 (SD ± 13.5), and 42% were females. Receiver operating curve analysis and Youden’s J statistics were used to determine the optimal NLR cut-off (Figure 1). An NLR > 4.79 was considered elevated, and had a sensitivity of 70.6% and a specificity of 80.6% in predicting severe - critical COVID-19. A high NLR (OR: 3.38, P = 0.02) and LV systolic dysfunction (OR: 9.76, P < 0.01) were independently associated with RV dysfunction. In multivariate cox regression analysis, older age (HR: 1.02, P = 0.01), obesity (HR: 1.85, P < 0.01), chronic kidney disease (HR: 1.69, P = 0.01), high NLR (HR: 2.75, P < 0.01), and RV dysfunction (HR: 2.07, P = 0.02) increased the risk of 30-day mortality.
Conclusions: In Indonesian patients hospitalized with COVID-19, A high NLR is predictive of severe – critical COVID-19 and is associated with RV dysfunction. A high NLR at admission and RV dysfunction independently increase the risk of 30-day mortality in hospitalized Indonesian adults with COVID-19.
Aim: To investigate the role of NLR and RV dysfunction in Indonesian patients hospitalized for COVID-19.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted at a COVID-19 referral hospital in Indonesia. We included all adult patients hospitalized with COVID-19 between April 2020 – April 2021 who had transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) during admission. Clinical data were extracted from electronic medical records. TTE variables were defined according to the American Society of Echocardiography criteria. All statistical analyses were conducted using the SPSS software. This study was approved by the IRB at Universitas Indonesia (#2022-01-135).
Results: A total of 488 patients were included – 29 with and 459 without RV dysfunction. The mean age of the population was 54.8 (SD ± 13.5), and 42% were females. Receiver operating curve analysis and Youden’s J statistics were used to determine the optimal NLR cut-off (Figure 1). An NLR > 4.79 was considered elevated, and had a sensitivity of 70.6% and a specificity of 80.6% in predicting severe - critical COVID-19. A high NLR (OR: 3.38, P = 0.02) and LV systolic dysfunction (OR: 9.76, P < 0.01) were independently associated with RV dysfunction. In multivariate cox regression analysis, older age (HR: 1.02, P = 0.01), obesity (HR: 1.85, P < 0.01), chronic kidney disease (HR: 1.69, P = 0.01), high NLR (HR: 2.75, P < 0.01), and RV dysfunction (HR: 2.07, P = 0.02) increased the risk of 30-day mortality.
Conclusions: In Indonesian patients hospitalized with COVID-19, A high NLR is predictive of severe – critical COVID-19 and is associated with RV dysfunction. A high NLR at admission and RV dysfunction independently increase the risk of 30-day mortality in hospitalized Indonesian adults with COVID-19.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of right ventricular size and function parameters in Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma with obesity and cardiovascular risk factors: What matters the most?
Villa Pallares Eduardo, Brenner Muslera Eduardo, Perez Nuques Maria Jose, Gomez Ardila Maria F., Tellez Garcia Eduardo, Villarraga Hector
84 Immune checkpoint profiling in major aortic diseases leads to identification of potential roles of CD155-CD206 pathway in suppressing inflammation and immune responsesShao Ying, Saaoud Fatma, Xu Keman, Lu Yifan, Jiang Xiaohua, Wang Hong, Yang Xiaofeng