Final ID: MDP1675
Significant Reduction in Left Atrial Epicardial Adipose Tissue Following Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is closely associated with obesity, and epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) has been proposed as a possible promoter of fibrosis and predictor of AF recurrence post-ablation. The impact of ablation on left atrial (LA) EAT, as well as that of LAEAT on ablation-induced scarring, have not been explored. Our aim was to assess changes in LAEAT volume following ablation and the association of LAEAT with ablation-induced scarring and AF recurrence.
Methods
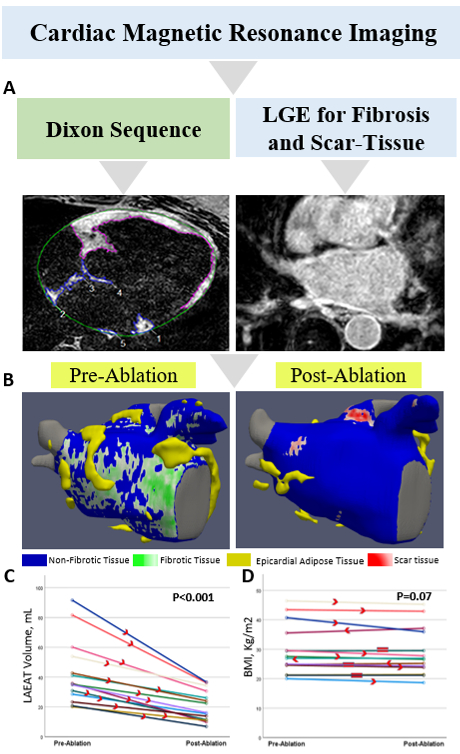
This is a single-center observational study of AF patients undergoing their first catheter ablation at the University of Washington. Cardiac MRIs were done pre- and post-ablation. LGE-MRI and Dixon sequences were used to assess ablation-induced scarring and LAEAT (Panel A). 3D atrial models of fibrosis and ablation-induced scar with superimposed EAT were created (Panel B). Patients were followed prospectively for AF recurrence.
Results
We included 14 patients, aged 68 (60-74) years, 64% male, and 71% with paroxysmal AF. Radiofrequency ablation was performed in 8 (57%) patients and cryoballoon ablation in 6 (43%) for pulmonary vein isolation. Median BMI was 27.2kg/m2 and left atrial volume (LAV) was 115.65 ml. LAEAT decreased from 35.47ml (28.6-53.9) to 19.37ml (11.48-30.65) post-ablation (p<0.001) (Panel C), despite minimal BMI change (median change 0.5kg/m2, p=0.07) (Panel D). The reduction was higher in persistent AF patients compared to paroxysmal (35.61ml vs. 14.46ml, p=0.016). LAEAT reduction was correlated with pre-ablation LAV (r=0.675, p=0.008), LA fibrosis (r=0.82, p<0.001), and BMI (r=0.815, p<0.001); and post-ablation LAV (r=0.676, p=0.011), and BMI (r=0.798, p<0.001). There was no correlation between LAEAT reduction and ablation-induced scarring. AF recurred in 9 patients (64.2%). Pre- and post-ablation LAEAT trended higher in those with recurrence compared to those without (42.72mL vs. 34.87ml, p=0.11 and 26.09ml vs. 13.85ml, p=0.11). LAEAT reduction relative to pre-ablation LAEAT was similar between groups.
Conclusion
AF ablation was associated with a significant decrease in LAEAT. LAEAT did not affect ablation-induced scarring. The mechanisms and potential implications of these findings require further investigation.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is closely associated with obesity, and epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) has been proposed as a possible promoter of fibrosis and predictor of AF recurrence post-ablation. The impact of ablation on left atrial (LA) EAT, as well as that of LAEAT on ablation-induced scarring, have not been explored. Our aim was to assess changes in LAEAT volume following ablation and the association of LAEAT with ablation-induced scarring and AF recurrence.
Methods
This is a single-center observational study of AF patients undergoing their first catheter ablation at the University of Washington. Cardiac MRIs were done pre- and post-ablation. LGE-MRI and Dixon sequences were used to assess ablation-induced scarring and LAEAT (Panel A). 3D atrial models of fibrosis and ablation-induced scar with superimposed EAT were created (Panel B). Patients were followed prospectively for AF recurrence.
Results
We included 14 patients, aged 68 (60-74) years, 64% male, and 71% with paroxysmal AF. Radiofrequency ablation was performed in 8 (57%) patients and cryoballoon ablation in 6 (43%) for pulmonary vein isolation. Median BMI was 27.2kg/m2 and left atrial volume (LAV) was 115.65 ml. LAEAT decreased from 35.47ml (28.6-53.9) to 19.37ml (11.48-30.65) post-ablation (p<0.001) (Panel C), despite minimal BMI change (median change 0.5kg/m2, p=0.07) (Panel D). The reduction was higher in persistent AF patients compared to paroxysmal (35.61ml vs. 14.46ml, p=0.016). LAEAT reduction was correlated with pre-ablation LAV (r=0.675, p=0.008), LA fibrosis (r=0.82, p<0.001), and BMI (r=0.815, p<0.001); and post-ablation LAV (r=0.676, p=0.011), and BMI (r=0.798, p<0.001). There was no correlation between LAEAT reduction and ablation-induced scarring. AF recurred in 9 patients (64.2%). Pre- and post-ablation LAEAT trended higher in those with recurrence compared to those without (42.72mL vs. 34.87ml, p=0.11 and 26.09ml vs. 13.85ml, p=0.11). LAEAT reduction relative to pre-ablation LAEAT was similar between groups.
Conclusion
AF ablation was associated with a significant decrease in LAEAT. LAEAT did not affect ablation-induced scarring. The mechanisms and potential implications of these findings require further investigation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Association of Epicardial Adipose Tissue with Lipomatous Metaplasia and Ventricular Tachycardia Recurrence Following Ablation in Patients with Non-Ischemic Cardiomyopathy
Xu Lingyu, Liao Ting-wei Ernie, Callans David, Marchlinski Francis, Witschey Walter, Desjardins Benoit, Nazarian Saman
A comparison of the efficacy of initial high energy versus initial low energy biphasic shocks for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter – a real-life experienceAlampoondi Venkataramanan Sai Vikram, Vunnam Ramarao, Voruganti Dinesh, Tsai Shane