Final ID: Mo2062
The Power Duo: Combining LA Volume Index and Strain to predict AF Recurrence after ablation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Catheter ablation (CA) is an effective treatment for atrial fibrillation (AF), but many patients experience recurrence post-intervention. Evaluating left atrial strain (LAS) to measure LA reservoir strain (LASr), conduit strain (LAScd), and contractile strain (LASct) could help predict AF recurrence, especially in patients with no evident signs of severe LA myopathy.
Goal: This study aims to assess the prognostic value of pre-ablation LAS in both paroxysmal AF (paAF) and persistent AF(peAF) in patients with no evident signs of severe LA myopathy.
Methods:
This retrospective study encompassed AF patients who underwent their first CA procedure at Mayo Clinic Arizona from October 2018 to February 2022 and had a LAVI <40 ml/m2 and LVEF >55%. Transthoracic echocardiography parameters, including the three LAS phases, were collected using TOMTEC software on the closest date before the CA procedure. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to evaluate the capability of LAS to detect patients with AF recurrence after CA from those without recurrence.
Results:
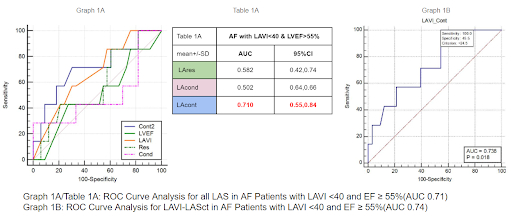
Out of 335 AF patients who underwent CA during the study period, 40 cases had LAVI <40 ml/m2 and LVEF >55% (72.5% male; mean age 69.2 ± 8 years). Of these, 15% (6/40) experienced recurrence, while 85% (34/40) maintained sinus rhythm. The mean values of LASr, LAScd, and LASct for all patients were 16.82, 11.23, and 6.87, respectively. ROC analysis indicated that the area under the curve (AUC) for LASr, LAScd, and LASct was 0.582, 0.502, and 0.710, respectively. (Graph 1A, Table 1A) LASct was the only parameter associated with AF recurrence (AUC: 0.71). Additionally, we developed a novel marker termed LAVI-LASct by combining LAVI and LASct values, which demonstrated improved discrimination with an ROC value of 0.74 (Graph 1B).
Conclusions:
LASct demonstrated predictive capability for AF recurrence in patients with no severe LA dilation and preserved LVEF, potentially due to its ability to detect early atrial dysfunction preceding visible structural changes or myocardial pathology. The addition of LAVI values provided better discrimination for the ROC model. Further research is needed to confirm the clinical relevance of LAS in AF patients undergoing ablation.
Catheter ablation (CA) is an effective treatment for atrial fibrillation (AF), but many patients experience recurrence post-intervention. Evaluating left atrial strain (LAS) to measure LA reservoir strain (LASr), conduit strain (LAScd), and contractile strain (LASct) could help predict AF recurrence, especially in patients with no evident signs of severe LA myopathy.
Goal: This study aims to assess the prognostic value of pre-ablation LAS in both paroxysmal AF (paAF) and persistent AF(peAF) in patients with no evident signs of severe LA myopathy.
Methods:
This retrospective study encompassed AF patients who underwent their first CA procedure at Mayo Clinic Arizona from October 2018 to February 2022 and had a LAVI <40 ml/m2 and LVEF >55%. Transthoracic echocardiography parameters, including the three LAS phases, were collected using TOMTEC software on the closest date before the CA procedure. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to evaluate the capability of LAS to detect patients with AF recurrence after CA from those without recurrence.
Results:
Out of 335 AF patients who underwent CA during the study period, 40 cases had LAVI <40 ml/m2 and LVEF >55% (72.5% male; mean age 69.2 ± 8 years). Of these, 15% (6/40) experienced recurrence, while 85% (34/40) maintained sinus rhythm. The mean values of LASr, LAScd, and LASct for all patients were 16.82, 11.23, and 6.87, respectively. ROC analysis indicated that the area under the curve (AUC) for LASr, LAScd, and LASct was 0.582, 0.502, and 0.710, respectively. (Graph 1A, Table 1A) LASct was the only parameter associated with AF recurrence (AUC: 0.71). Additionally, we developed a novel marker termed LAVI-LASct by combining LAVI and LASct values, which demonstrated improved discrimination with an ROC value of 0.74 (Graph 1B).
Conclusions:
LASct demonstrated predictive capability for AF recurrence in patients with no severe LA dilation and preserved LVEF, potentially due to its ability to detect early atrial dysfunction preceding visible structural changes or myocardial pathology. The addition of LAVI values provided better discrimination for the ROC model. Further research is needed to confirm the clinical relevance of LAS in AF patients undergoing ablation.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Multi-Center Clinic Site Comparison of Patient-level factors Affecting Oral Anticoagulation Prescription for Atrial Fibrillation
Iqbal Fatima, Hoang Kenneth, Chiadika Simbo
A novel risk score predicts the prevalence of left atrial low-voltage areas and rhythm outcome in patients undergoing long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation ablationOoka Hirotaka, Nakao Sho, Kusuda Masaya, Ariyasu Wataru, Kudo Satoshi, Fujii Subaru, Mano Toshiaki, Matsuda Yasuhiro, Masuda Masaharu, Okamoto Shin, Ishihara Takayuki, Nanto Kiyonori, Tsujimura Takuya, Hata Yosuke, Uematsu Hiroyuki