Final ID: Su2012
Variant Burden and Severity of Cardiac Phenotype in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Cardiomyopathy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) has cardiac phenotype variability ranging from mild ventricular dysfunction to death from heart failure in the second decade. This variability has not been explained by specific DMD variants.
Question: This study was designed to identify target genes, other than DMD, as cardiomyopathy (CMP) severity modifiers.
Methods: Genome sequencing results were analyzed from 54 well phenotyped DMD males and either severe CMP (cardiac mortality or left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) < 40% at < 20 years of age, n = 18) or mild CMP (EF > 40% at > 20 years of age, n = 36). We compared variants within CMP groups as follows: 1) all study subjects, 2) siblings discordant for CMP severity, and 3) subjects without relatives. Combined Annotation-Dependent Depletion (CADD) was used to assess individual rare variant burden by filtering to retain coding variants with a raw CADD-generated C-Score >2.5. Using the C-Score, we calculated the difference between group mean (DBGM) between the CMP groups for each gene. For each of the three analyses groups, we normalized DBGM summative C-Score and determined which genes had a DBGM summative C-Score >3 standard deviations from the mean (SDM). We evaluated genes that were present on the gene list for all three analyses.
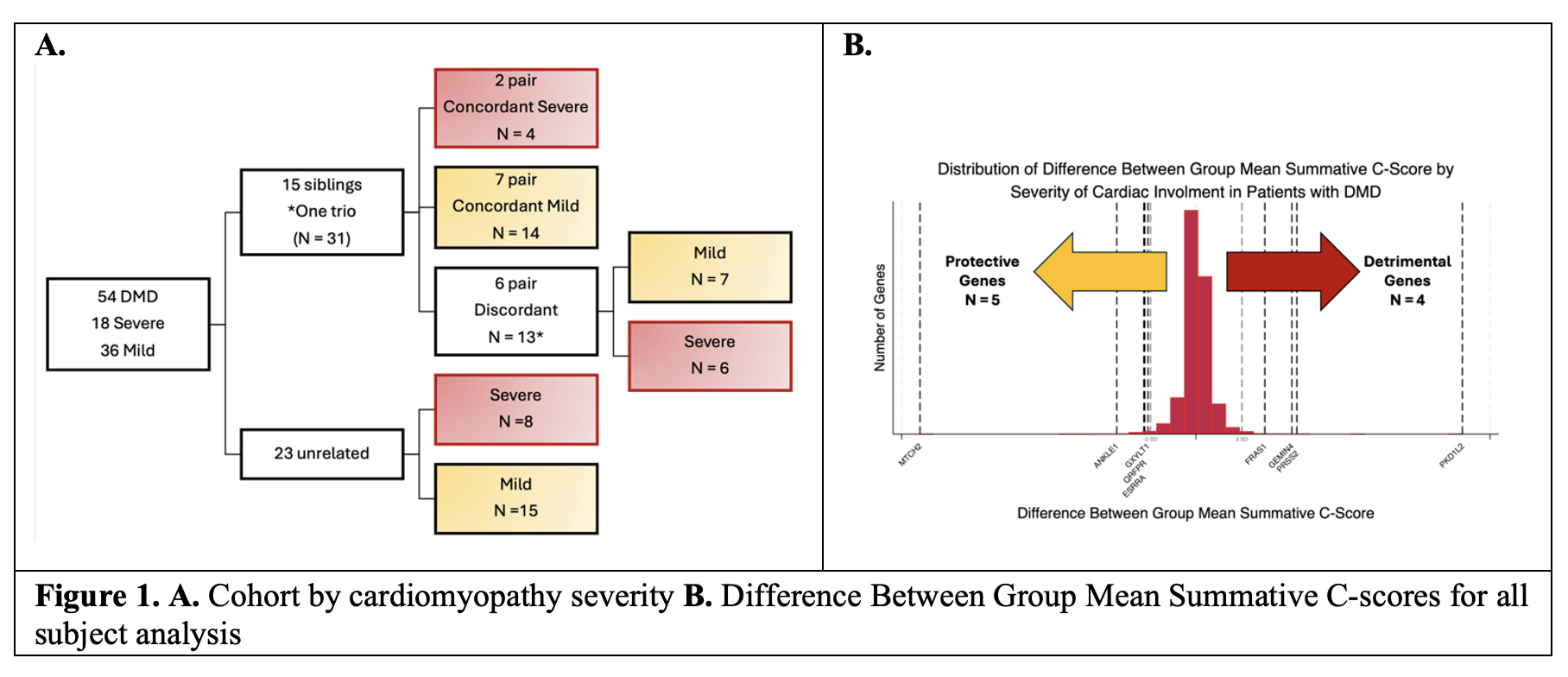
Results: The cohort by CMP severity is depicted in Figure 1a. Comparisons yielded 8,155 genes with a C-Score > 2.5 in at least one patient. Number of genes with DBGM >3SDM in respective CMP group analysis above: 1) 159 genes 2) 134 genes 3) 136 genes. Nine genes had DBGM summative C-Scores >3 SDM in all three analyses. Of these, 5 genes, ANKLE1, ESRRA, GXYLT1, MTCH2, and QRFPR, had scores suggestive that these genetic variants could be protective against severe CMP. Whereas 4 genes, FRAS1, GEMIN4, PKD1L2, and PRSS2 had scores suggestive that these genetic variants could be a risk factor for severe CMP.
Conclusion: DBGM summative C-Scores from DMD genome sequencing generated 9 candidate genes from 8,155 genes for stratifying CMP phenotypic variability. Further translational evaluation of these genes as modifiers of DMD CMP severity is warranted. If confirmed, these modifiers could provide therapeutic insight specific to DMD CMP.
Question: This study was designed to identify target genes, other than DMD, as cardiomyopathy (CMP) severity modifiers.
Methods: Genome sequencing results were analyzed from 54 well phenotyped DMD males and either severe CMP (cardiac mortality or left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) < 40% at < 20 years of age, n = 18) or mild CMP (EF > 40% at > 20 years of age, n = 36). We compared variants within CMP groups as follows: 1) all study subjects, 2) siblings discordant for CMP severity, and 3) subjects without relatives. Combined Annotation-Dependent Depletion (CADD) was used to assess individual rare variant burden by filtering to retain coding variants with a raw CADD-generated C-Score >2.5. Using the C-Score, we calculated the difference between group mean (DBGM) between the CMP groups for each gene. For each of the three analyses groups, we normalized DBGM summative C-Score and determined which genes had a DBGM summative C-Score >3 standard deviations from the mean (SDM). We evaluated genes that were present on the gene list for all three analyses.
Results: The cohort by CMP severity is depicted in Figure 1a. Comparisons yielded 8,155 genes with a C-Score > 2.5 in at least one patient. Number of genes with DBGM >3SDM in respective CMP group analysis above: 1) 159 genes 2) 134 genes 3) 136 genes. Nine genes had DBGM summative C-Scores >3 SDM in all three analyses. Of these, 5 genes, ANKLE1, ESRRA, GXYLT1, MTCH2, and QRFPR, had scores suggestive that these genetic variants could be protective against severe CMP. Whereas 4 genes, FRAS1, GEMIN4, PKD1L2, and PRSS2 had scores suggestive that these genetic variants could be a risk factor for severe CMP.
Conclusion: DBGM summative C-Scores from DMD genome sequencing generated 9 candidate genes from 8,155 genes for stratifying CMP phenotypic variability. Further translational evaluation of these genes as modifiers of DMD CMP severity is warranted. If confirmed, these modifiers could provide therapeutic insight specific to DMD CMP.
More abstracts on this topic:
Exon-skipping therapy can restore functional dystrophin attenuating calcium overload for DMD cardiomyopathy with mutations in actin-binding domain 1
Shiba Naoko, Yang Xiao, Agata Masahiro, Nagamine Kohei, Kadota Shin, Mitsuto Sato, Nakamura Akinori, Shiba Yuji
A Multi-Population-First Approach Leveraging UK Biobank (UKBB) and All of Us (AoU) Datasets Reveals Higher Cardiomyopathy Variant Burden in Individuals with MyocarditisGurumoorthi Manasa, Khanji Mohammed, Munroe Patricia, Petersen Steffen, Landstrom Andrew, Chahal Anwar, Hesse Kerrick, Asatryan Babken, Shah Ravi, Sharaf Dabbagh Ghaith, Wolfe Rachel, Shyam Sundar Vijay, Mohiddin Saidi, Aung Nay