Final ID: Mo4063
Cardiovascular Adverse Events And Comparative Safety Of Ibrutinib Plus Venetoclax In Untreated Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: A Meta-Analysis Of Randomized Controlled Trials And Systematic Review
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: The combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax has emerged as a promising therapeutic option for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), demonstrating significant advantages compared to traditional chemotherapy-based approaches. However, the potential adverse cardiovascular effects, especially in patients who have not previously undergone treatment, have not been fully elucidated.
Hypothesis: The use of ibrutinib and venetoclax is associated with a higher incidence of cardiovascular adverse events.
Aims: This study aims to analyze the incidence of cardiovascular adverse effects in patients treated with ibrutinib and venetoclax for CLL, who were previously naïve to treatment.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Central databases were systematically searched in April 2024 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared ibrutinib plus venetoclax to standard care therapies (ST) (chlorambucil-obinutuzumab; ibrutinib only and fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab) in untreated patients with CLL and reported the outcomes of (1) atrial fibrillation; (2) hypertension and (3) sudden death. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis using RStudio version 2024.04.0. Heterogeneity was examined with the Cochran Q test and I2 statistics.
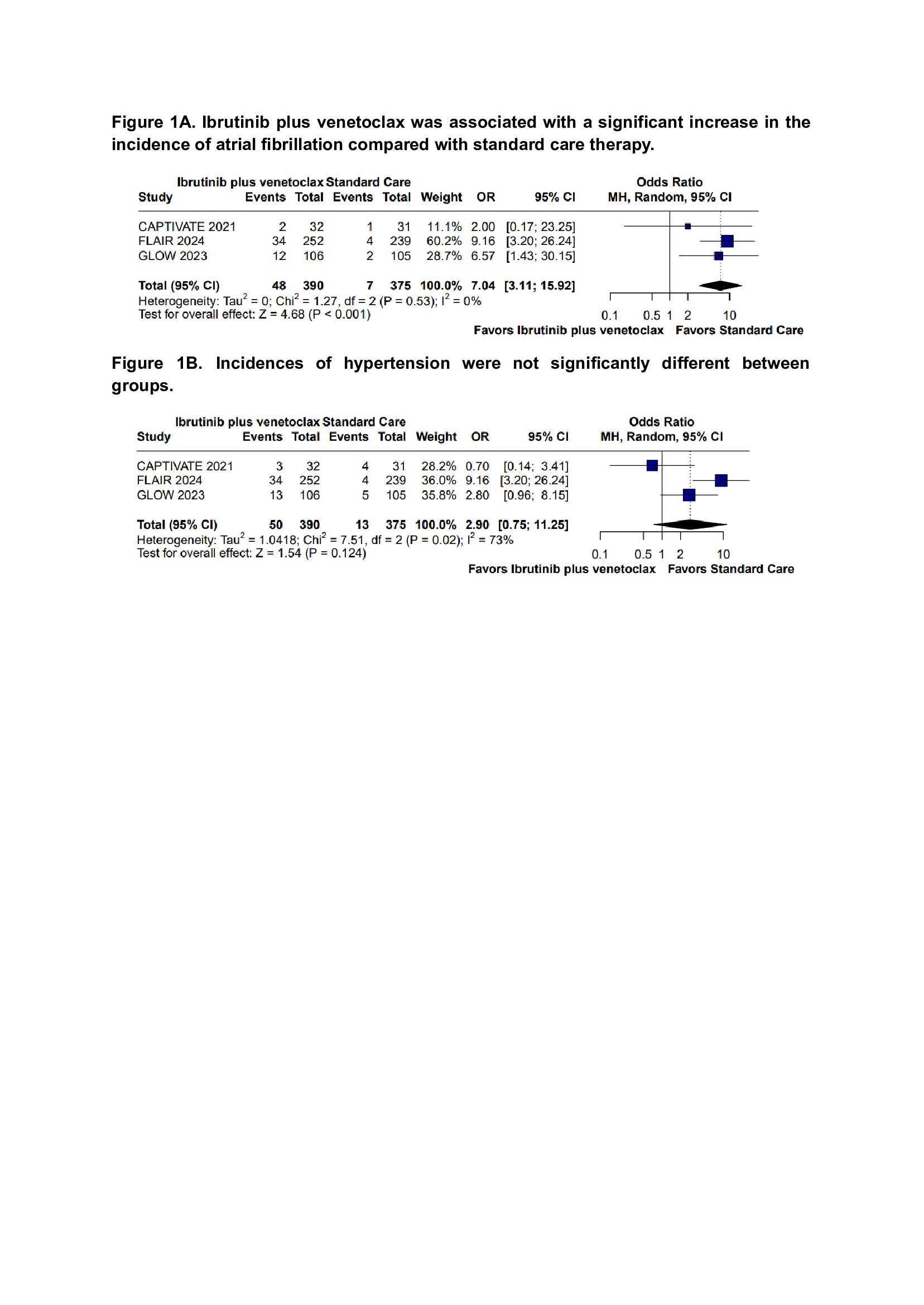
Results: We included 4 RCTs in the final analysis, with a total of 885 participants, of whom 450 (50.8%) were on ibrutinib plus venetoclax. Ibrutinib plus venetoclax was associated with a significant increase in the incidence of atrial fibrillation compared with standard care therapy (OR 7.04; 95% CI 3.11-15.92; p<0.01; I2=0%; figure 1A). Hypertension (OR 2.90; 95% CI 0.75-11.25; p=0.124; figure 1B) and sudden death (OR 0.16; 95% CI 0.16-3.11; p=0.655) were not significantly different between groups.
Conclusion: In patients with CLL who were previously naïve to treatment, the combination of ibrutinib plus venetoclax was associated with a higher incidence of atrial fibrillation as compared with ST, whereas hypertension and sudden death were not significantly different between groups.
Hypothesis: The use of ibrutinib and venetoclax is associated with a higher incidence of cardiovascular adverse events.
Aims: This study aims to analyze the incidence of cardiovascular adverse effects in patients treated with ibrutinib and venetoclax for CLL, who were previously naïve to treatment.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Central databases were systematically searched in April 2024 for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared ibrutinib plus venetoclax to standard care therapies (ST) (chlorambucil-obinutuzumab; ibrutinib only and fludarabine-cyclophosphamide-rituximab) in untreated patients with CLL and reported the outcomes of (1) atrial fibrillation; (2) hypertension and (3) sudden death. We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis using RStudio version 2024.04.0. Heterogeneity was examined with the Cochran Q test and I2 statistics.
Results: We included 4 RCTs in the final analysis, with a total of 885 participants, of whom 450 (50.8%) were on ibrutinib plus venetoclax. Ibrutinib plus venetoclax was associated with a significant increase in the incidence of atrial fibrillation compared with standard care therapy (OR 7.04; 95% CI 3.11-15.92; p<0.01; I2=0%; figure 1A). Hypertension (OR 2.90; 95% CI 0.75-11.25; p=0.124; figure 1B) and sudden death (OR 0.16; 95% CI 0.16-3.11; p=0.655) were not significantly different between groups.
Conclusion: In patients with CLL who were previously naïve to treatment, the combination of ibrutinib plus venetoclax was associated with a higher incidence of atrial fibrillation as compared with ST, whereas hypertension and sudden death were not significantly different between groups.
More abstracts on this topic:
2-Methoxyestradiol By Inhibiting Central Action of 12S-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid Protects Ovariectomized Mice From Hypertension
Dutta Shubha, Singh Purnima, Song Chi Young, Shin Ji Soo, Malik Kafait
Social Vulnerability, Cardiovascular Risk, and Sudden Death: Insights from the SUDDEN projectKoehler Andreas, Besh Jordan, Davy-mendez Thibaut, Watson James, Simpson Ross