Final ID: MDP1011
Association of Cumulative Cardiovascular Health Score Through Young Adulthood With Cardiovascular-Kidney Outcomes in Midlife
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Little is known about cumulative cardiovascular health (CVH) measures and associated health outcomes. This gap, together with the AHA’s recent focus on cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic interactions, led to the hypothesis that greater cumulative CVH (cumCVH), through young adulthood, is associated with a lower combined risk of cardiovascular and kidney events in midlife.
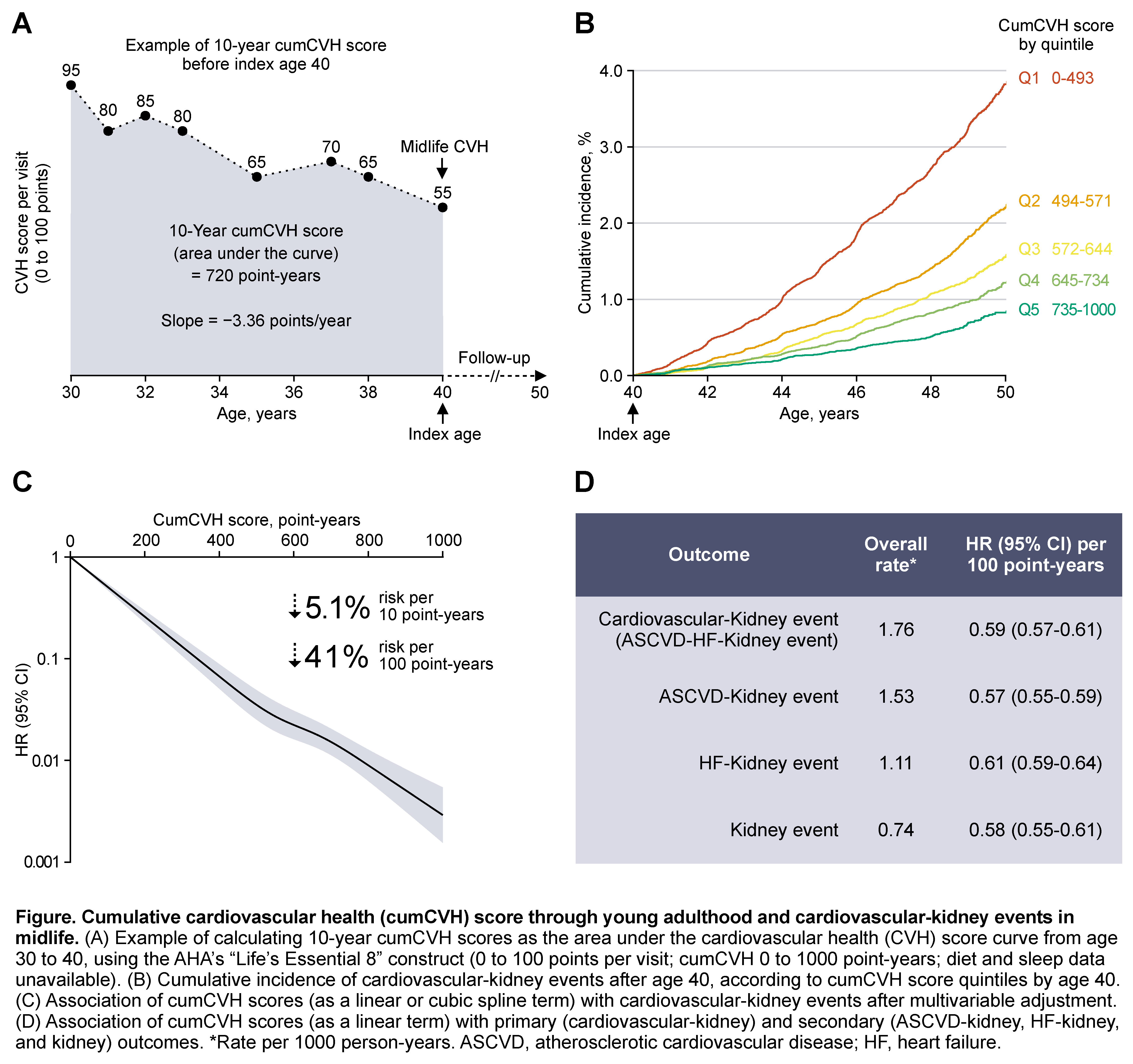
Methods: This study included 241,924 participants from the 2012-2014 Korean National Health Insurance general health screening without prior cardiovascular disease (CVD) or chronic kidney disease (CKD) at index age 40. Each participant had ≥3 examination visits: Y0 (age 30), Y10 (age 40), and ≥1 in between (median, 8 visits total). We calculated a 10-year cumCVH score as the area under the CVH score curve from age 30 to 40, using the AHA’s “Life’s Essential 8” construct (0 to 100 points per visit; cumCVH 0 to 1000 point-years; Fig A). The primary outcome was a composite of CVD events (myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, heart failure, or death from CVD) or kidney events (high-risk CKD, kidney replacement therapy, or death from kidney disease).
Results: Over a median follow-up of 9.2 years, 3560 cardiovascular-kidney events occurred. Participants with a higher cumCVH score by age 40 had a lower cumulative incidence of cardiovascular-kidney events in the following decade (Fig B). After adjustment, every 10 point-years of cumCVH score (i.e., 1 year lived with 10-point greater CVH) was associated with a 5.1% lower risk of cardiovascular-kidney events after age 40 (Fig C). Every 100 point-years of cumCVH score (i.e., 10 years lived with 10-point greater CVH) was associated with a 41% lower risk of cardiovascular-kidney events. The associations were similar for secondary cardiovascular-kidney outcomes (Fig D) and remained significant when adjusted for the slope of CVH change or the midlife CVH score, both of which were independently associated with the outcomes.
Conclusions: Greater cumulative CVH through young adulthood was associated with a lower combined risk of cardiovascular-kidney events in midlife. The results underscore the importance of maintaining better early-life CVH for the prevention of cardiovascular and kidney diseases.
Methods: This study included 241,924 participants from the 2012-2014 Korean National Health Insurance general health screening without prior cardiovascular disease (CVD) or chronic kidney disease (CKD) at index age 40. Each participant had ≥3 examination visits: Y0 (age 30), Y10 (age 40), and ≥1 in between (median, 8 visits total). We calculated a 10-year cumCVH score as the area under the CVH score curve from age 30 to 40, using the AHA’s “Life’s Essential 8” construct (0 to 100 points per visit; cumCVH 0 to 1000 point-years; Fig A). The primary outcome was a composite of CVD events (myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, heart failure, or death from CVD) or kidney events (high-risk CKD, kidney replacement therapy, or death from kidney disease).
Results: Over a median follow-up of 9.2 years, 3560 cardiovascular-kidney events occurred. Participants with a higher cumCVH score by age 40 had a lower cumulative incidence of cardiovascular-kidney events in the following decade (Fig B). After adjustment, every 10 point-years of cumCVH score (i.e., 1 year lived with 10-point greater CVH) was associated with a 5.1% lower risk of cardiovascular-kidney events after age 40 (Fig C). Every 100 point-years of cumCVH score (i.e., 10 years lived with 10-point greater CVH) was associated with a 41% lower risk of cardiovascular-kidney events. The associations were similar for secondary cardiovascular-kidney outcomes (Fig D) and remained significant when adjusted for the slope of CVH change or the midlife CVH score, both of which were independently associated with the outcomes.
Conclusions: Greater cumulative CVH through young adulthood was associated with a lower combined risk of cardiovascular-kidney events in midlife. The results underscore the importance of maintaining better early-life CVH for the prevention of cardiovascular and kidney diseases.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Nationwide Italian Network for the Clinical and Genetic Diagnosis of Familial Dyslipidemias: The LIPIGEN registry
__PRESENT
Casula Manuela, Galimberti Federica, Olmastroni Elena, Arca Marcello, Averna Maurizio, Catapano Alberico
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) and Cardiovascular Health: Future of Families and Child Wellbeing Study (FFCWS)__PRESENT
Pedamallu Havisha, Van Horn Linda, Stein James, Korcarz Claudia, Hansen Kristin, Mitchell Colter, Heard-garris Nia, Lloyd-jones Donald, Allen Norrina, Gauen Abigail, Ning Hongyan, Wilkins John, Goldman Noreen, Notterman Daniel, Hou Lifang, Zheng Yinan, Marma Amanda