Final ID: MDP15
Cross-species single-cell RNA sequencing reveals divergent phenotypes and activation states of adaptive immunity in human carotid and experimental murine atherosclerosis
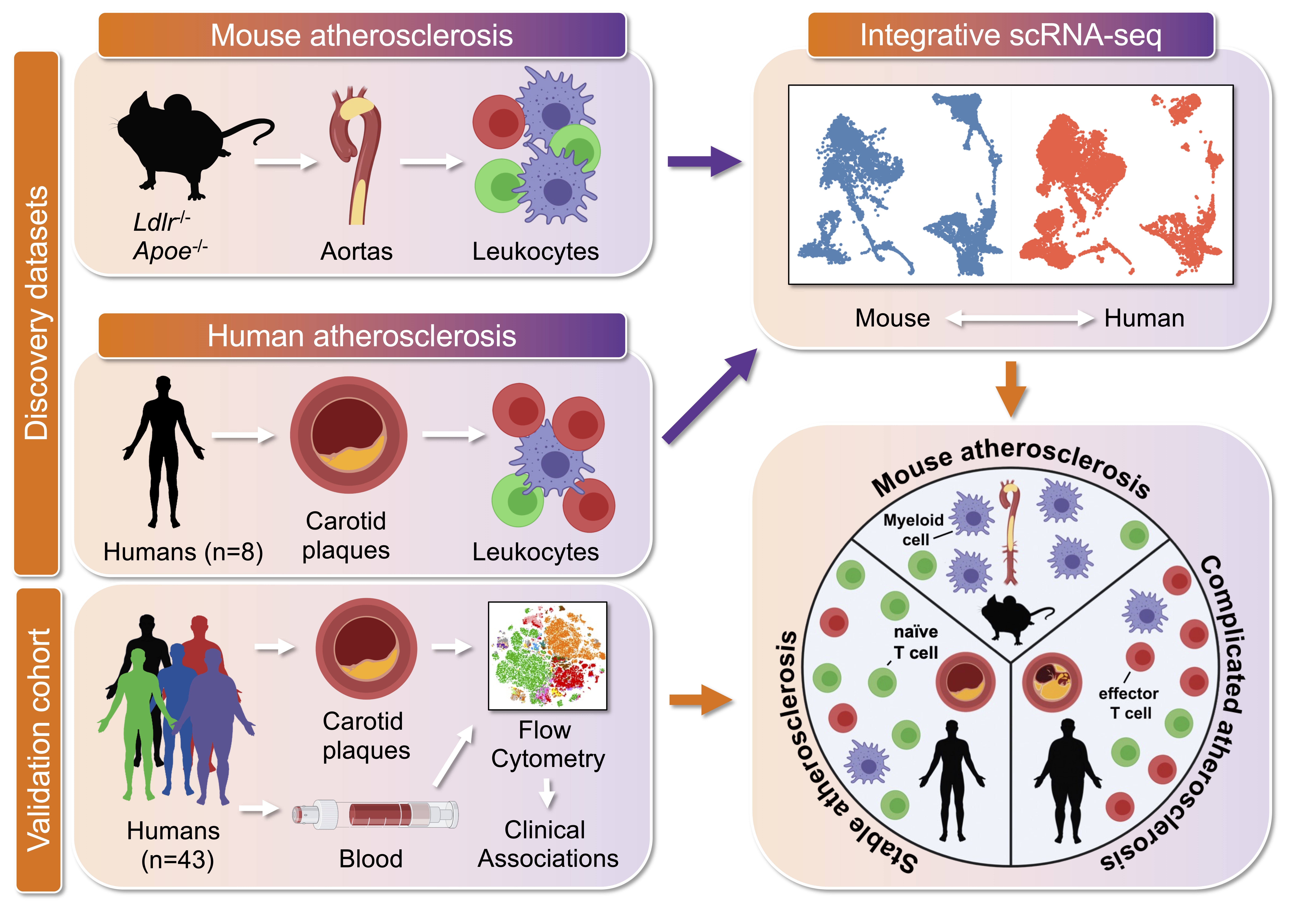
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background and Aims: The distinct functions of immune cells in atherosclerosis have been mostly defined by preclinical mouse studies. Contrastingly, the immune cell composition of human atherosclerotic plaques and their contribution to disease progression is only poorly understood. It remains uncertain whether genetic animal models allow for valuable translational approaches.
Methods and Results: Single cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) was performed to define the immune cell landscape in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques. The human immune cell repertoire demonstrated an unexpectedly high heterogeneity and was dominated by cells of the T-cell lineage, a finding confirmed by immunohistochemistry. Bioinformatical integration with 7 mouse scRNA-seq data sets from adventitial and atherosclerotic vascular tissue revealed a total of 51 identities of cell types and differentiation states, of which some were only poorly conserved between species and exclusively found in humans. Locations, frequencies, and transcriptional programs of immune cells in mouse models did not resemble the immune cell landscape in human carotid atherosclerosis. In contrast to standard mouse models of atherosclerosis, human plaque leukocytes were dominated by several T-cell phenotypes with transcriptional hallmarks of T-cell activation and memory formation, T-cell receptor-, and pro-inflammatory signaling. Only mice at the age of 22 months partially resembled the activated T-cell phenotype. In a validation cohort of 43 patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy, the abundance of activated immune cell subsets in the plaque defined by multi-color flow cytometry associated with the extend of clinical atherosclerosis.
Conclusions: Integrative scRNA-seq reveals a substantial difference in the immune cell composition of murine and human carotid atherosclerosis – a finding that questions the translational value of standard mouse models for adaptive immune cell studies. Clinical associations suggest a specific role for T-cell driven (auto-) immunity in human plaque formation and -instability.
Methods and Results: Single cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) was performed to define the immune cell landscape in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques. The human immune cell repertoire demonstrated an unexpectedly high heterogeneity and was dominated by cells of the T-cell lineage, a finding confirmed by immunohistochemistry. Bioinformatical integration with 7 mouse scRNA-seq data sets from adventitial and atherosclerotic vascular tissue revealed a total of 51 identities of cell types and differentiation states, of which some were only poorly conserved between species and exclusively found in humans. Locations, frequencies, and transcriptional programs of immune cells in mouse models did not resemble the immune cell landscape in human carotid atherosclerosis. In contrast to standard mouse models of atherosclerosis, human plaque leukocytes were dominated by several T-cell phenotypes with transcriptional hallmarks of T-cell activation and memory formation, T-cell receptor-, and pro-inflammatory signaling. Only mice at the age of 22 months partially resembled the activated T-cell phenotype. In a validation cohort of 43 patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy, the abundance of activated immune cell subsets in the plaque defined by multi-color flow cytometry associated with the extend of clinical atherosclerosis.
Conclusions: Integrative scRNA-seq reveals a substantial difference in the immune cell composition of murine and human carotid atherosclerosis – a finding that questions the translational value of standard mouse models for adaptive immune cell studies. Clinical associations suggest a specific role for T-cell driven (auto-) immunity in human plaque formation and -instability.
More abstracts on this topic:
Anti-CD47 therapy induces early macrophage-specific transcriptomic changes associated with the resolution of inflammation in a murine model of atherosclerosis
Klarin Derek, Cheruvu Pavan, Basson Craig, Kaplan Charles, Gao Hua, Signore Pierre, Jeyaseelan Jey, Paavola Kevin, Cheung Eric, Yun Rui, Zhang Meng, Leeper Nicholas
A Platelet Transcriptomic Signature Predicts Cardiovascular Risk in Peripheral Artery DiseaseMuller Matthew, Boothman Isabelle, Luttrell-williams Elliot, Xia Yuhe, Barrett Tessa, Ruggles Kelly, Berger Jeffrey