Final ID: Sa4176
Continuous nitric oxide inhalation in a murine model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and pulmonary hypertension
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Abnormal lung development is associated with respiratory disease and pulmonary hypertension (PH) in children. PH associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) carries significantly morbidity and mortality due to right ventricular (RV) failure.
Aim: to develop an animal model of BPD and PH and examine the effects of chronic nitric oxide (NO) inhalation.
Methods: We exposed C57bl/6J mouse pups to 11% FiO2 starting on post-natal day 2-4 with (11%-NO) or without (11%) continuous inhalation of 10 ppm NO for 8 weeks. Control mice breathed air (21%). At age 8 weeks we evaluated the degree of lung injury by measuring arterial PO2 while breathing 11% FiO2, by obtaining lung pressure-volume curves and by pathological evaluation; on transthoracic echocardiography we evaluated the degree of PH by assessing the ratio between the pulmonary artery acceleration time and the ejection time (PAAT/ET), and the RV function by assessing the tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE). We measured RV systolic pressure (RVSP) and RV hypertrophy with the Fulton’s ratio.
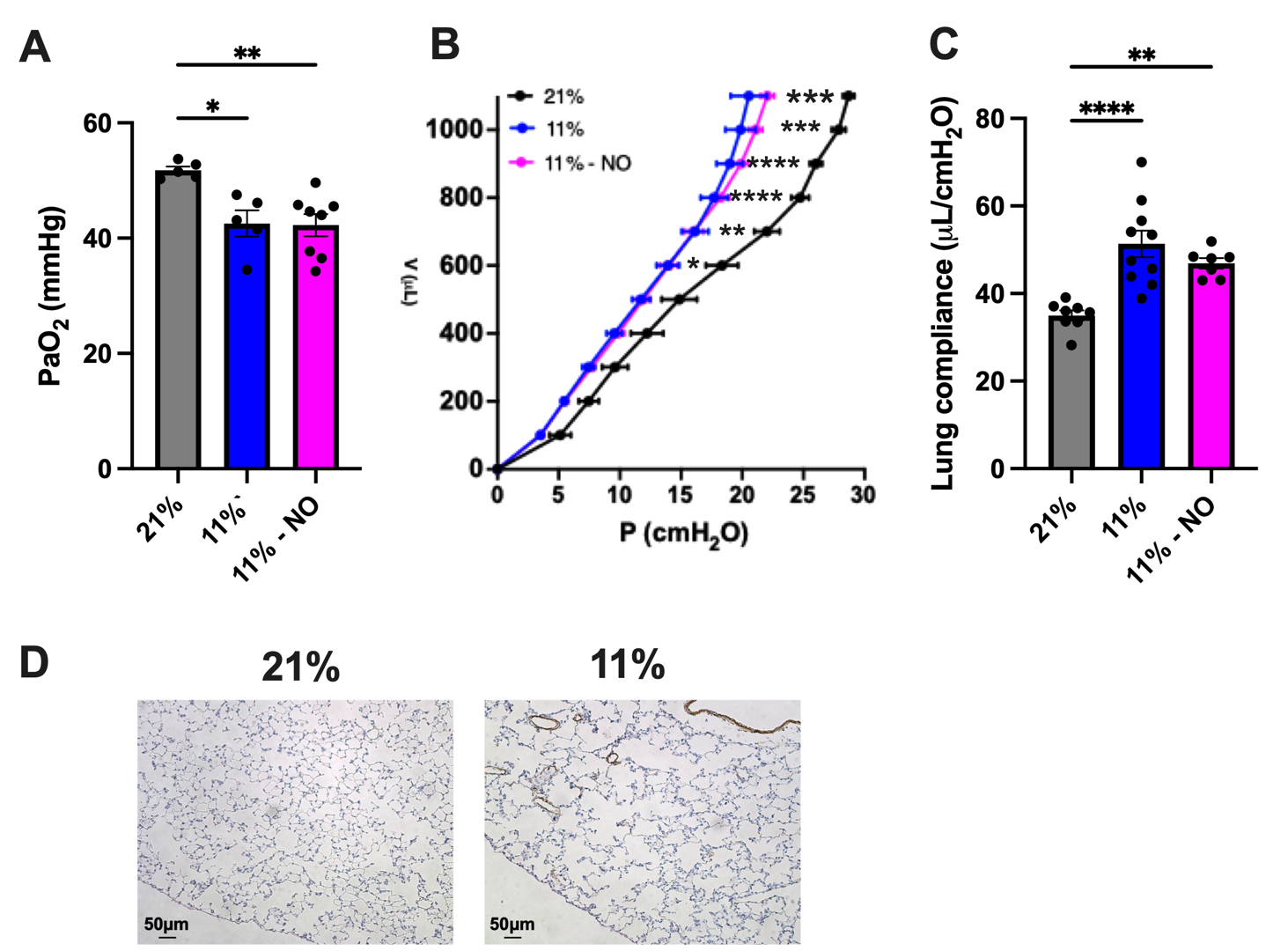
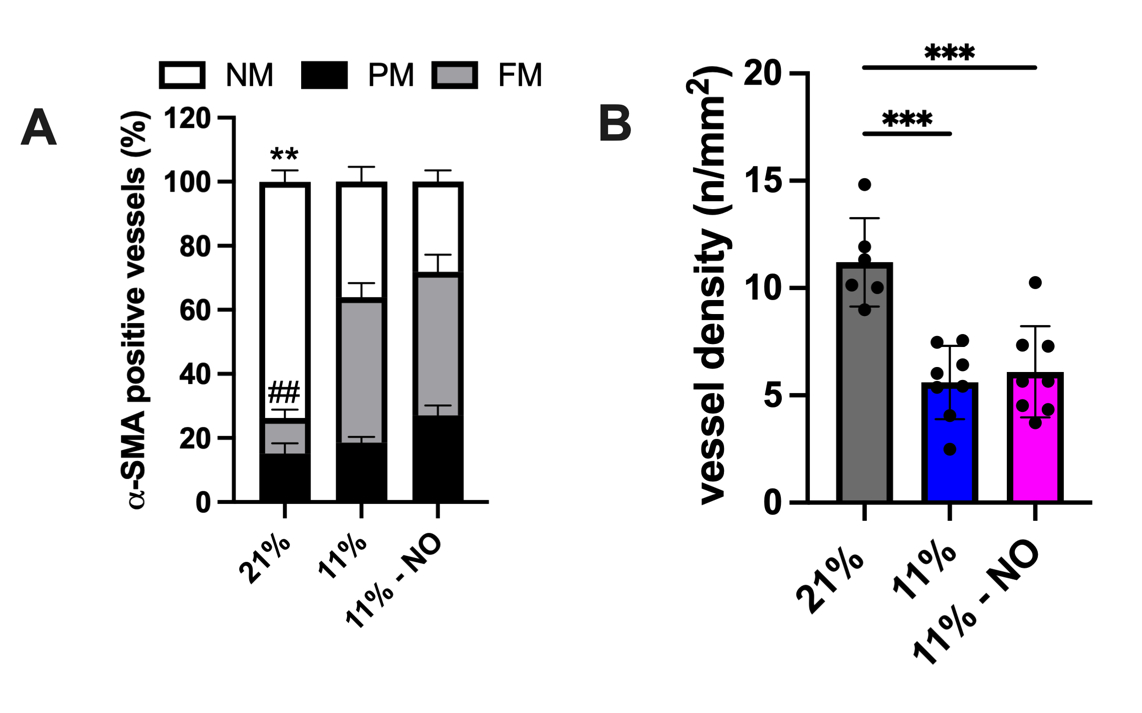
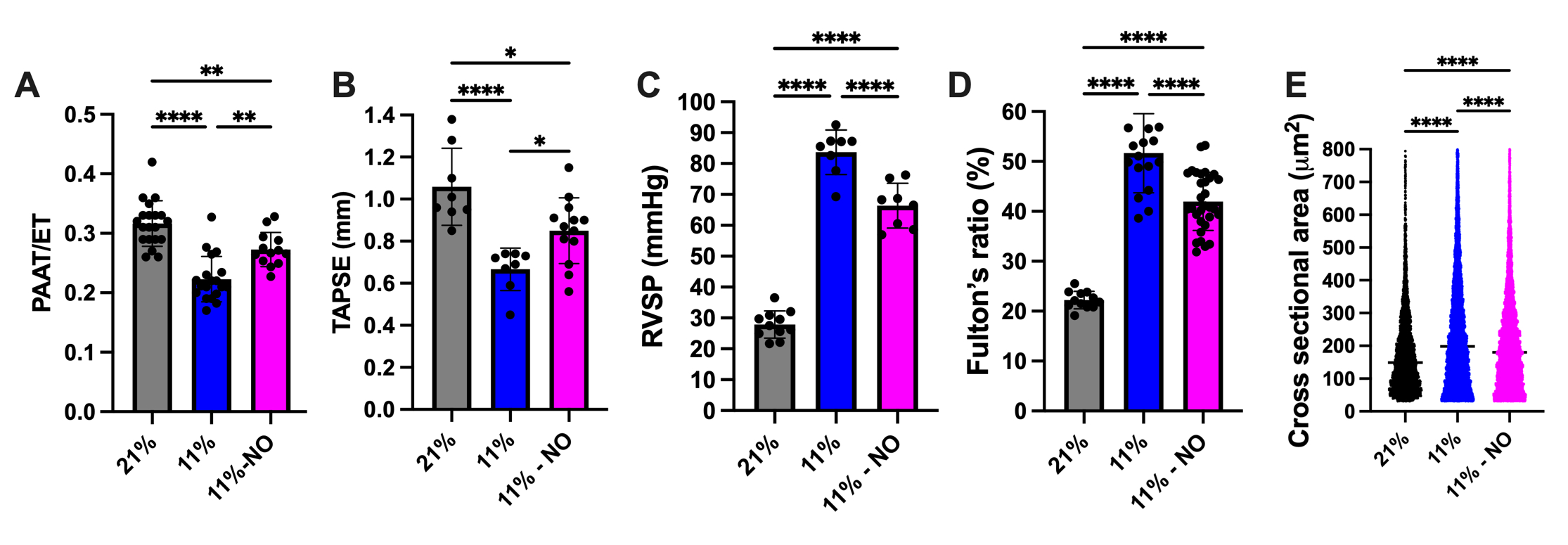
Results: 11% and 11%-NO mice compared to controls had lower PaO2 (42.5±5.1 vs. 42.3±5.4 vs. 51.8±1.4 mmHg, p<0.01), increased lung compliance (51.3±9.6 vs. 46.9±3.2 vs. 35.0±3.3 mL/cmH2O, p<0.001), reduced alveolarization, severe small vessel muscularization and vascular rarefaction (Fig. 1 and 2). Treatment with NO ameliorated the reduction in PAAT/ET and TAPSE that was observed in 11% mice compared to controls (11%-NO vs. 11% vs. 21%: PAAT/ET 0.27±0.03 vs. 0.22±0.04 vs. 0.32±0.04, p<0.0001, TAPSE: (0.85±0.16vs. 0.67±0.10 vs.1.1±0.2 mm, p<0.0001). Similarly, the RVSP of 11% mice was significantly elevated compared to control mice and diminished by NO treatment (11% vs. 21% vs. 11%-NO: 84±7 vs. 28±4 vs. 66±7 mmHg p<0.0001). RV hypertrophy in 11% mice was more severe than in 11%-NO mice compared to controls (Fulton’s ratio: 52±8% vs. 42±6% vs. 22±2%, p<0.0001). The median RV cardiomyocytes cross-sectional area significantly increased in both 11% and 11%-NO mice compared to controls but at a lesser extent in the 11%-NO mice (198[194-201 vs.181[178-183] vs.149[87-240] mm2, p<0.0001) (Fig. 3).
Conclusions: we developed a new mouse model of BPD with associated severe PH and RV dysfunction. Continuous inhaled NO did not improve neonatal hypoxia-induced lung injury but ameliorated PH, RV hypertrophy and function. Translation of this therapy to children with BPD and PH may improve clinical outcomes.
Aim: to develop an animal model of BPD and PH and examine the effects of chronic nitric oxide (NO) inhalation.
Methods: We exposed C57bl/6J mouse pups to 11% FiO2 starting on post-natal day 2-4 with (11%-NO) or without (11%) continuous inhalation of 10 ppm NO for 8 weeks. Control mice breathed air (21%). At age 8 weeks we evaluated the degree of lung injury by measuring arterial PO2 while breathing 11% FiO2, by obtaining lung pressure-volume curves and by pathological evaluation; on transthoracic echocardiography we evaluated the degree of PH by assessing the ratio between the pulmonary artery acceleration time and the ejection time (PAAT/ET), and the RV function by assessing the tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE). We measured RV systolic pressure (RVSP) and RV hypertrophy with the Fulton’s ratio.
Results: 11% and 11%-NO mice compared to controls had lower PaO2 (42.5±5.1 vs. 42.3±5.4 vs. 51.8±1.4 mmHg, p<0.01), increased lung compliance (51.3±9.6 vs. 46.9±3.2 vs. 35.0±3.3 mL/cmH2O, p<0.001), reduced alveolarization, severe small vessel muscularization and vascular rarefaction (Fig. 1 and 2). Treatment with NO ameliorated the reduction in PAAT/ET and TAPSE that was observed in 11% mice compared to controls (11%-NO vs. 11% vs. 21%: PAAT/ET 0.27±0.03 vs. 0.22±0.04 vs. 0.32±0.04, p<0.0001, TAPSE: (0.85±0.16vs. 0.67±0.10 vs.1.1±0.2 mm, p<0.0001). Similarly, the RVSP of 11% mice was significantly elevated compared to control mice and diminished by NO treatment (11% vs. 21% vs. 11%-NO: 84±7 vs. 28±4 vs. 66±7 mmHg p<0.0001). RV hypertrophy in 11% mice was more severe than in 11%-NO mice compared to controls (Fulton’s ratio: 52±8% vs. 42±6% vs. 22±2%, p<0.0001). The median RV cardiomyocytes cross-sectional area significantly increased in both 11% and 11%-NO mice compared to controls but at a lesser extent in the 11%-NO mice (198[194-201 vs.181[178-183] vs.149[87-240] mm2, p<0.0001) (Fig. 3).
Conclusions: we developed a new mouse model of BPD with associated severe PH and RV dysfunction. Continuous inhaled NO did not improve neonatal hypoxia-induced lung injury but ameliorated PH, RV hypertrophy and function. Translation of this therapy to children with BPD and PH may improve clinical outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 as Potential Indicator for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus-Induced Fetal Endothelial Dysfunction
Villar Ballesteros Maria De Leyre, Taylor Paul, Morawietz Henning, Brendel Heike, Hengst Clara, Carstens Philine Sophie, Effenberger Deborah, Mittag Jennifer, Giebe Sindy, Fruehauf Alexander, Birdir Cahit
A Dangerous Right Turn: Primary Right Heart Failure in Mechanically Ventilated Patients—-Prevalence, Inpatient Outcomes, and High Use of Advanced ICU Therapies— A Nationwide AnalysisKhan Dawlat, Chaudhry Hammad, Shehzad Dawood, Riaz Muhammad Faisal, Ahmed Mamoon