Final ID: MDP812
Valvular oxidized phospholipids correlate with severity of human aortic valvular stenosis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Aortic valve stenosis (AVS) is a degenerative disease characterized by progressive calcification and stenosis, driven by a multifactorial inflammatory process. Oxidized phospholipids (OxPL) have been implicated in this process, yet their presence in aortic valve tissue remains unexplored. This study aims to fill this gap by developing a sensitive method to identify and quantify OxPL in the plasma and tissue of patients with severe AVS.
Methods: We obtained aortic valve tissue from 70 patients undergoing aortic valve replacement surgery. The tissue samples were subjected to derivatization with DNPH, followed by LC/MS/MS analysis, enabling the identification and quantification of 60 individual OxPL across five different phospholipid classes.
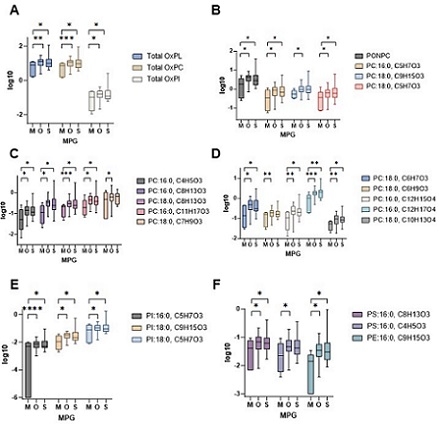
Results: Our analysis identified 34 OxPL species across five phospholipid classes in human valvular tissue, including oxidized phosphatidylcholine (OxPC), phosphatidylethanolamine (OxPE), phosphatidylinositol (OxPI), and phosphatidylserine (OxPS). OxPC was the most abundant class, with PONPC being the most prevalent molecule, constituting 35% of total OxPL. We observed a significant increase (p<0.05) in 20 OxPL species in valvular tissue when comparing mild to moderate to severe valve stenosis based on pressure gradient. The most significant change occurred between mild and moderate AVS as PONPC increased by 90% (p=0.012) and total OxPC increased by 83% (p=0.004). Compared to plasma, valvular tissue had more OxPS species present and an increase in longer chain fatty acid aldehydes in the SN-2 position of OxPCs.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that OxPL infiltration of the valve tissue is an early event in the progression of AVS. This suggests that early intervention with OxPL-lowering therapies may prove beneficial in managing AVS.
Methods: We obtained aortic valve tissue from 70 patients undergoing aortic valve replacement surgery. The tissue samples were subjected to derivatization with DNPH, followed by LC/MS/MS analysis, enabling the identification and quantification of 60 individual OxPL across five different phospholipid classes.
Results: Our analysis identified 34 OxPL species across five phospholipid classes in human valvular tissue, including oxidized phosphatidylcholine (OxPC), phosphatidylethanolamine (OxPE), phosphatidylinositol (OxPI), and phosphatidylserine (OxPS). OxPC was the most abundant class, with PONPC being the most prevalent molecule, constituting 35% of total OxPL. We observed a significant increase (p<0.05) in 20 OxPL species in valvular tissue when comparing mild to moderate to severe valve stenosis based on pressure gradient. The most significant change occurred between mild and moderate AVS as PONPC increased by 90% (p=0.012) and total OxPC increased by 83% (p=0.004). Compared to plasma, valvular tissue had more OxPS species present and an increase in longer chain fatty acid aldehydes in the SN-2 position of OxPCs.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that OxPL infiltration of the valve tissue is an early event in the progression of AVS. This suggests that early intervention with OxPL-lowering therapies may prove beneficial in managing AVS.
More abstracts on this topic:
Aortic Stenosis is Promoted by Ferroptosis via 5-Lipoxygenase
Qin Zihan, Haftbaradaran Esfahani Payam, Pawelzik Sven-christian, Bosman Matthias, Bergstrom Goran, Guns Pieter-jan, Franco-cereceda Anders, Back Magnus
A human cardiomyocyte model of CD36 haploinsufficiency uncovers fatty acid oxidation deficits driving dilated cardiomyopathyAl Sayed Zeina, Klattenhoff Carla, Aragam Krishna, Ellinor Patrick, Willcox Jon, Zheng Alice, Koledova Vera, Srivastava Salil, Yin Xiaofei, Chaffin Mark, Rigaud Vagner, Kovacs-bogdan Erika