Final ID: MDP338
Systemic Sirolimus Therapy is Associated with Reduced Intervention Frequency in Pediatric Pulmonary Vein Stenosis
Hypothesis: We hypothesized patients undergo PVS interventions less frequently while receiving SST compared to pre-SST.
Aims: The principal aim was to determine the impact of systemic sirolimus therapy on PVS intervention frequency.
Methods: We retrospectively identified 45 patients treated at Texas Children’s Hospital who completed >1 month of SST for PVS between 2015-2022. First course of SST was analyzed. Primary endpoint was PVS intervention frequency (number of surgical or transcatheter PVS interventions/year), calculated for two intervals per patient: pre-SST (PVS diagnosis until start of SST) and on-SST (start of SST until cessation or follow-up if no interruptions >1 month). Generalized Poisson mixed linear models were fit to test the impact of SST on intervention frequency, accounting for paired intervals within each patient. A multivariable model also included age at interval start, PVS type (primary/post-repair), sex, prematurity, and concurrent antiproliferative medications. Mean cumulative functions were also compared.
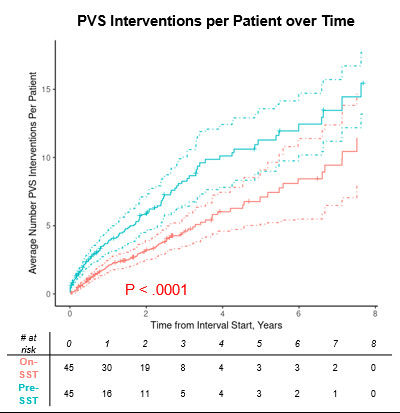
Results: Median per-patient PVS intervention rate (interventions/year) was 5 (IQR 2.3-10.6) pre-SST and 1.7 (0.8-2.8) on-SST. PVS intervention rate was significantly lower on-SST compared to pre-SST by the univariable and multivariable Poisson models (P<.0001, both). Patients accrued an increased mean cumulative number of interventions over time pre-SST compared to on-SST (P<.0001, Figure). Median duration of SST was 1.7 years and follow-up time from SST initiation was 2.7 years. There were 6 mortalities with 90% (95% CI 75-96%) Kaplan-Meier estimated survival 2 years from SST initiation.
Conclusions: SST was associated with a reduction in PVS intervention frequency. Prospective studies are warranted to determine potential causality, delineate patient and vein-level outcomes, and determine optimal therapeutic duration.
- Kalustian, Alyssa ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Bansal, Manish ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Gowda, Srinath ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Eilers, Lindsay ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Khan, Asra ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Sandoval-jones, Juan Pablo ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Imamura, Michiaki ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Orr, Yishay ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Caldarone, Chris ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Qureshi, Athar ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Hagan, Joseph ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Brlecic, Paige ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Iacobas, Ionela ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Vanderlaan, Rachel ( Hospital for Sick Children , Toronto , Ontario , Canada )
- Burns, Joseph ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Wu, Thao ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Birla, Ravi ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
- Gowda, Sharada ( Texas Children's Hospital , Houston , Texas , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Pediatric Surgery, Cath, and EP
Saturday, 11/16/2024 , 12:50PM - 02:15PM
Moderated Digital Poster Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Atasi Montaser, Dankar Razan, Barakat Salim, Wehbi Jad, Refaat Marwan
22q11 Deletion Syndrome: A Potenitial Risk Factor For Left Pulmonary Artery Hypoplasia and Need For Intervention in Patients With Congeital Heart DiseaseOliver Shannon, Ward Cameron
More abstracts from these authors:
Burns Joseph, Stephens Sara, Kyle William, Cai Yu, Morris Shaine
UPDATED OUTCOMES OF ADULTS WITH CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE AND HETEROTAXYUppalapati Lakshmi, Tinsay Maria Andrea Francesca, Ermis Peter, Lam Wilson, Qureshi Athar, Heinle Jeffrey, Hickey Edward, Broda Christopher