Final ID: Mo4014
The Usefulness of the Quick Forrester Classification with Respiratory Rate and Serum Lactate Levels for Predicting Decreased Left Ventricular Function in Patients with ST-elevation Myocardial Infarction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Although respiratory rate (RR) is one of the vital signs, few studies have evaluated the association between respiratory rate at hospital arrival and clinical outcomes in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Serum lactate levels, which can be rapidly measured in the emergency department, have been reported to be associated with prognosis in STEMI patients with or without cardiogenic shock. We hypothesized that profiling by RR, which reflects hypoxia or metabolic acidosis, and serum lactate level, which reflects tissue perfusion, at hospital arrival named the Quick Forrester Classification (QFC), would be associated with clinical outcomes in STEMI patients.
Methods: This is a retrospective analysis of STEMI patients between 2018 and 2023. Patients were divided into 4 classifications: RR <22/min and lactate <2.0mmol/L (Class-1), RR ≧22/min and lactate <2.0mmol/L (Class-2), RR <22/min and lactate ≧2.0mmol/L (Class-3), RR ≧22/min and lactate ≧2.0mmol/L (Class-4) as the QFC. The primary outcome was decreased cardiac function (left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF] less than 45% measured during hospitalization).
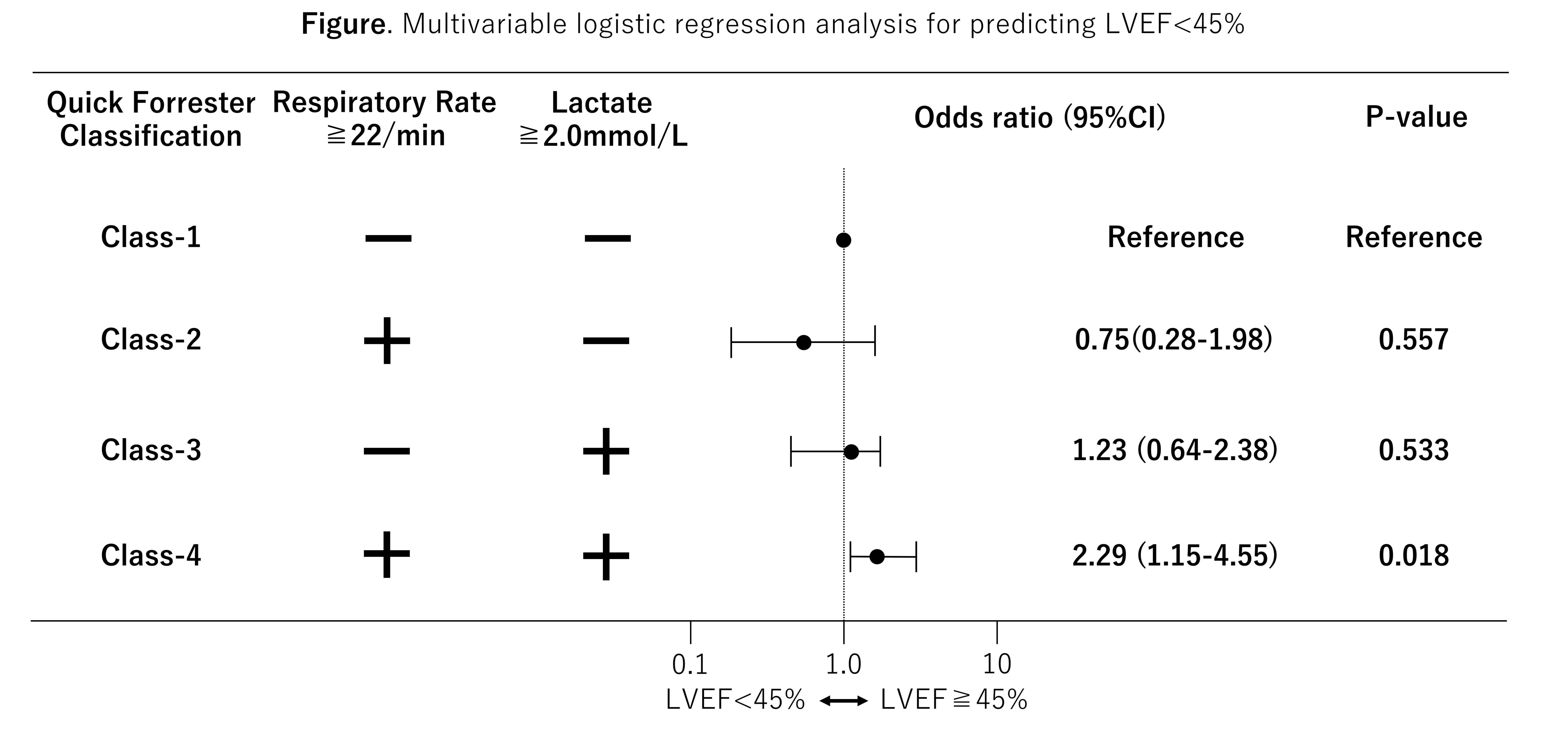
Results: Of 592 STEMI patients (age, 71±13 years; male, 72%), 569 patients were classified by QFC (Class-1, n=156; Class-2, n=52; Class-3, n=213; Class-4, n=148). The proportion of patients with decreased cardiac function increased from 15% in Class-1, 13% in Class-2, 16% in Class-3 to 30% in Class-4 (P=0.003 for trend). Multivariable analysis revealed that a patient in QFC Class-4 was a significantly predictor of decreased LVEF when compared with a patient in QFC Class-1(Odds ratio [OR] 2.29, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.15-4.55, p=0.018) as were age (OR 1.03, 95%CI 1.01-1.06, p=0.003), heart rate at hospital arrival (OR 1.03, 95%CI 1.02-1.05, p<0.001), and anterior wall infarction (OR 2.21, 95%CI 1.31-3.73, p=0.003).
Conclusion: In STEMI patients, the QFC with RR and serum lactate level at hospital arrival was significantly associated with decreased LVEF.
Methods: This is a retrospective analysis of STEMI patients between 2018 and 2023. Patients were divided into 4 classifications: RR <22/min and lactate <2.0mmol/L (Class-1), RR ≧22/min and lactate <2.0mmol/L (Class-2), RR <22/min and lactate ≧2.0mmol/L (Class-3), RR ≧22/min and lactate ≧2.0mmol/L (Class-4) as the QFC. The primary outcome was decreased cardiac function (left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF] less than 45% measured during hospitalization).
Results: Of 592 STEMI patients (age, 71±13 years; male, 72%), 569 patients were classified by QFC (Class-1, n=156; Class-2, n=52; Class-3, n=213; Class-4, n=148). The proportion of patients with decreased cardiac function increased from 15% in Class-1, 13% in Class-2, 16% in Class-3 to 30% in Class-4 (P=0.003 for trend). Multivariable analysis revealed that a patient in QFC Class-4 was a significantly predictor of decreased LVEF when compared with a patient in QFC Class-1(Odds ratio [OR] 2.29, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.15-4.55, p=0.018) as were age (OR 1.03, 95%CI 1.01-1.06, p=0.003), heart rate at hospital arrival (OR 1.03, 95%CI 1.02-1.05, p<0.001), and anterior wall infarction (OR 2.21, 95%CI 1.31-3.73, p=0.003).
Conclusion: In STEMI patients, the QFC with RR and serum lactate level at hospital arrival was significantly associated with decreased LVEF.
More abstracts on this topic:
An individual patient data meta-analysis of complete versus culprit-lesion only revascularization for acute myocardial infarction involving >8,800 individuals: The Complete Revascularization Trialists’ Collaboration
Mehta Shamir, Banning Amerjeet, Ramasundarahettige Chinthanie, Nguyen Helen, Wood David, Engstrom Thomas, Tiong Denise, Böhm Felix, James Stefan, Biscaglia Simone, Campo Gianluca, Smits Pieter, Giacoppo Daniele, Mccann Gerry
Airway Opening Index is Associated with Return of Spontaneous Circulation in Swine and Humans with Cardiac ArrestBhandari Shiv, Coult Jason, Sharpe Zachary, Rea Thomas, Neumar Robert, Hsu Cindy, Counts Catherine, Sayre Michael, Johnson Nicholas