Final ID: MDP186
CASE MANAGERS AND PEER SUPPORT GROUPS (CAMPS) FOR PROPHYLAXIS ADHERENCE IN RHEUMATIC HEART DISEASE
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): BACKGROUND
Secondary antibiotic prophylaxis (SAP) is the only intervention known to prevent rheumatic heart disease (RHD) progression, but non-adherence to SAP undermines most global RHD programs.
RESEARCH QUESTION
We sought to determine whether enhanced SAP support administered through the public health system was feasible and a scalable model.
AIMS
Determine the difference in 1-year SAP adherence rates of children with RHD in Uganda randomized to either Usual Care or Enhanced Support.
Explore differences in patient-reported outcomes including treatment satisfaction and health-related quality of life (HRQoL).
METHODS
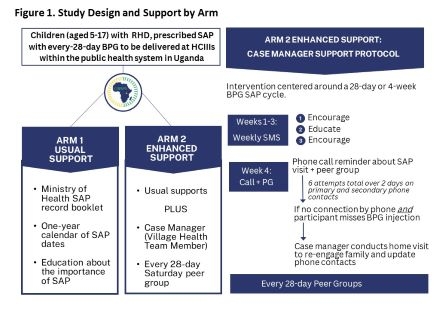
We conducted a pragmatic randomized trial of two support strategies for SAP integrated into routine care in Eastern Uganda. Children ages 5 to 17 years with RHD were randomized to either Usual Care or Enhanced Support. Outcome measures at the end of 12 months included SAP adherence, health related quality of life, and treatment satisfaction. See Figure 1.
RESULTS
In total, 208 participants were included in the analysis (103 from Usual Care and 105 from Enhanced Support) from 11 participating health centers. Mean age between the groups was the same (13.2 years), with 62.1% and 54.3% female participants in Usual Care and Enhanced Support, respectively. Most participants had only mild disease, with only 11.7% in Usual Care and 8.6% in Enhanced Support having moderate/severe disease. Mean WAMI scores between the two groups were the same, 0.49.
After 12 months, mean adherence was 80.0% for those receiving Usual Care, compared to 98.2% for those receiving Enhanced Support (estimated mean difference 18.2% days of coverage; 95% CI 14.4; 22.1, p<0.001). Treatment satisfaction and HRQoL scores were not statistically significantly different between the groups.
CONCLUSION
Although further research is needed to understand the minimum elements needed to achieve ideal SAP adherence and to understand implementation and dissemination at scale, the integration of community health workers into RHD supports may provide an effective and scalable model to improve outcomes for children with RHD in low-resource settings.
Secondary antibiotic prophylaxis (SAP) is the only intervention known to prevent rheumatic heart disease (RHD) progression, but non-adherence to SAP undermines most global RHD programs.
RESEARCH QUESTION
We sought to determine whether enhanced SAP support administered through the public health system was feasible and a scalable model.
AIMS
Determine the difference in 1-year SAP adherence rates of children with RHD in Uganda randomized to either Usual Care or Enhanced Support.
Explore differences in patient-reported outcomes including treatment satisfaction and health-related quality of life (HRQoL).
METHODS
We conducted a pragmatic randomized trial of two support strategies for SAP integrated into routine care in Eastern Uganda. Children ages 5 to 17 years with RHD were randomized to either Usual Care or Enhanced Support. Outcome measures at the end of 12 months included SAP adherence, health related quality of life, and treatment satisfaction. See Figure 1.
RESULTS
In total, 208 participants were included in the analysis (103 from Usual Care and 105 from Enhanced Support) from 11 participating health centers. Mean age between the groups was the same (13.2 years), with 62.1% and 54.3% female participants in Usual Care and Enhanced Support, respectively. Most participants had only mild disease, with only 11.7% in Usual Care and 8.6% in Enhanced Support having moderate/severe disease. Mean WAMI scores between the two groups were the same, 0.49.
After 12 months, mean adherence was 80.0% for those receiving Usual Care, compared to 98.2% for those receiving Enhanced Support (estimated mean difference 18.2% days of coverage; 95% CI 14.4; 22.1, p<0.001). Treatment satisfaction and HRQoL scores were not statistically significantly different between the groups.
CONCLUSION
Although further research is needed to understand the minimum elements needed to achieve ideal SAP adherence and to understand implementation and dissemination at scale, the integration of community health workers into RHD supports may provide an effective and scalable model to improve outcomes for children with RHD in low-resource settings.
More abstracts on this topic:
Barriers to Research Participation: The Impact of Race, Education, and Socioeconomic Status in a Diverse Urban Population
Mueller Anna Sophie, Berman Brandon, Jafri Komail, Bonilla Harrison, Contreras Johanna
Performance of a Novel Rheumatic Heart Disease Screening Protocol Led by Non-Expert Frontline Nurses in UgandaWirth Scott, Warren Paul, Nakagaayi Doreen, Pulle Jafesi, Sable Craig, Okello Emmy, Watkins David, Danforth Kristen, Beaton Andrea