Final ID: MDP691
Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy Rates in Patients with Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection increases the risk of heart failure, particularly Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF). Guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT), including beta-blockers (BB), renin-angiotensin system inhibitors (RASi), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2i), has been shown to decrease morbidity and mortality in patients with HFrEF.
Hypothesis: Lower GDMT prescription rates would be associated with higher 30-day readmission or mortality rates in patients with HIV and HFrEF
Aims: To assess GDMT prescription rates and their impact on short-term morbidity and mortality in patients with HIV and HFrEF.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with HIV and HFrEF who were admitted with acute heart failure within Emory Healthcare from 2010 to 2020 were identified using ICD codes. Diagnoses were confirmed by physician review. Baseline demographics, CD4 count, viral load (VL), prescriptions for GDMT and antiretroviral medications at the time of admission were assessed. A simple GDMT score was created, assigning 1 point for each medication prescribed (0-3, excluding SGLT2i given the study timeframe). Multivariable logistic regression was used to determine the association of the GDMT score with 30-day readmission or death, adjusting for age, sex, race, hypertension, diabetes, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and VL.
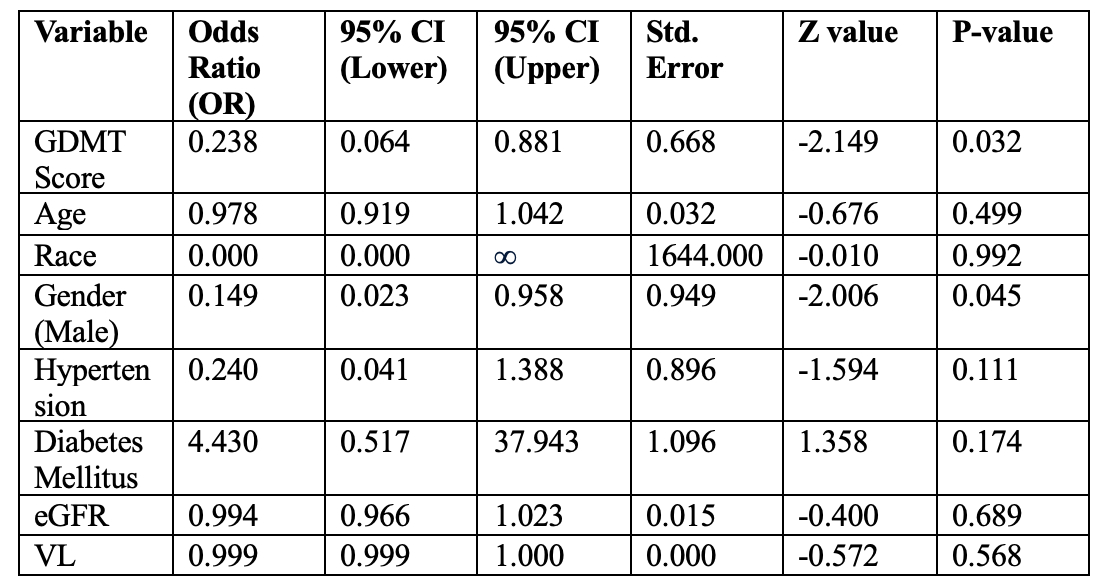
Results: The study included 161 patients (mean age 56 years, 22.9% women, 86.3% Black, 55% with VL <200 copies/ml). Of these, 96 (59.6%) were prescribed BB, 82 (50.9%) RASi, and 18 (11.1%) MRA. This distribution resulted in 38 patients (26.7%) with a GDMT score of 0, 62 patients (43.7%) with a score of 1, 49 patients (34.5%) with a score of 2, and 12 patients (8.5%) with a score of 3. During the 30-day follow-up period, 22 patients (13.7%) were re-hospitalized or died. After adjusting for risk factors, a higher GDMT score was associated with a lower risk of 30-day readmission or death (OR 0.24, CI 0.06 – 0.88, p = 0.032). Male sex was also associated with a lower risk of this endpoint (p = 0.045).
Conclusion: GDMT is under-prescribed in patients with HIV and HFrEF. Lower rates of GDMT prescription are associated with worse short-term outcomes in this population. Further efforts are required to ascertain reasons for under-prescription in these comorbid patients and to improve adherence to GDMT guidelines to enhance patient outcomes.
Hypothesis: Lower GDMT prescription rates would be associated with higher 30-day readmission or mortality rates in patients with HIV and HFrEF
Aims: To assess GDMT prescription rates and their impact on short-term morbidity and mortality in patients with HIV and HFrEF.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with HIV and HFrEF who were admitted with acute heart failure within Emory Healthcare from 2010 to 2020 were identified using ICD codes. Diagnoses were confirmed by physician review. Baseline demographics, CD4 count, viral load (VL), prescriptions for GDMT and antiretroviral medications at the time of admission were assessed. A simple GDMT score was created, assigning 1 point for each medication prescribed (0-3, excluding SGLT2i given the study timeframe). Multivariable logistic regression was used to determine the association of the GDMT score with 30-day readmission or death, adjusting for age, sex, race, hypertension, diabetes, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and VL.
Results: The study included 161 patients (mean age 56 years, 22.9% women, 86.3% Black, 55% with VL <200 copies/ml). Of these, 96 (59.6%) were prescribed BB, 82 (50.9%) RASi, and 18 (11.1%) MRA. This distribution resulted in 38 patients (26.7%) with a GDMT score of 0, 62 patients (43.7%) with a score of 1, 49 patients (34.5%) with a score of 2, and 12 patients (8.5%) with a score of 3. During the 30-day follow-up period, 22 patients (13.7%) were re-hospitalized or died. After adjusting for risk factors, a higher GDMT score was associated with a lower risk of 30-day readmission or death (OR 0.24, CI 0.06 – 0.88, p = 0.032). Male sex was also associated with a lower risk of this endpoint (p = 0.045).
Conclusion: GDMT is under-prescribed in patients with HIV and HFrEF. Lower rates of GDMT prescription are associated with worse short-term outcomes in this population. Further efforts are required to ascertain reasons for under-prescription in these comorbid patients and to improve adherence to GDMT guidelines to enhance patient outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Steroid-Refractory Immune-checkpoint-inhibitor Induced Myocarditis Responsive to Mycophenolate and Anti-thymocyte globulin
Dabdoub Jorge, Wilson Michael, Gottbrecht Matthew, Salazar Ryan, Shih Jeffrey
β1-adrenergic autoantibodies (β1-AA) augment macropinocytosis in CD4+ T cells, leading to the expansion of CD4+CD28− T cell subsets in heart failure.Sun Fei, Yao Junyan, Li Bingjie, Zhang Suli, Liu Huirong