Final ID: Mo4043
Shifting in the settings of stroke fatalities during the COVID-19 pandemic
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Stroke-related mortality poses significant challenges in the US. Increased at-home deaths since COVID-19 pandemic prompted changes in the provision of end-of-life care.
Question: What were the settings of stroke deaths in the US during COVID-19 pandemic?
Methods: Decedent-level mortality data from death certificates in CDC repository were obtained for the year 2020 (pandemic) and 2019 (comparison). Demographic data include age, sex, race/ethnicity, education, marital status, and place of stroke death, including inpatient, outpatient/emergency room (ER), hospice/nursing facilities (H/NF), and at-home. Multivariable logistic regression models assessed demographic impact on stroke mortality by place-of-death, yielding odds ratios (OR) with significance threshold of p<0.05.
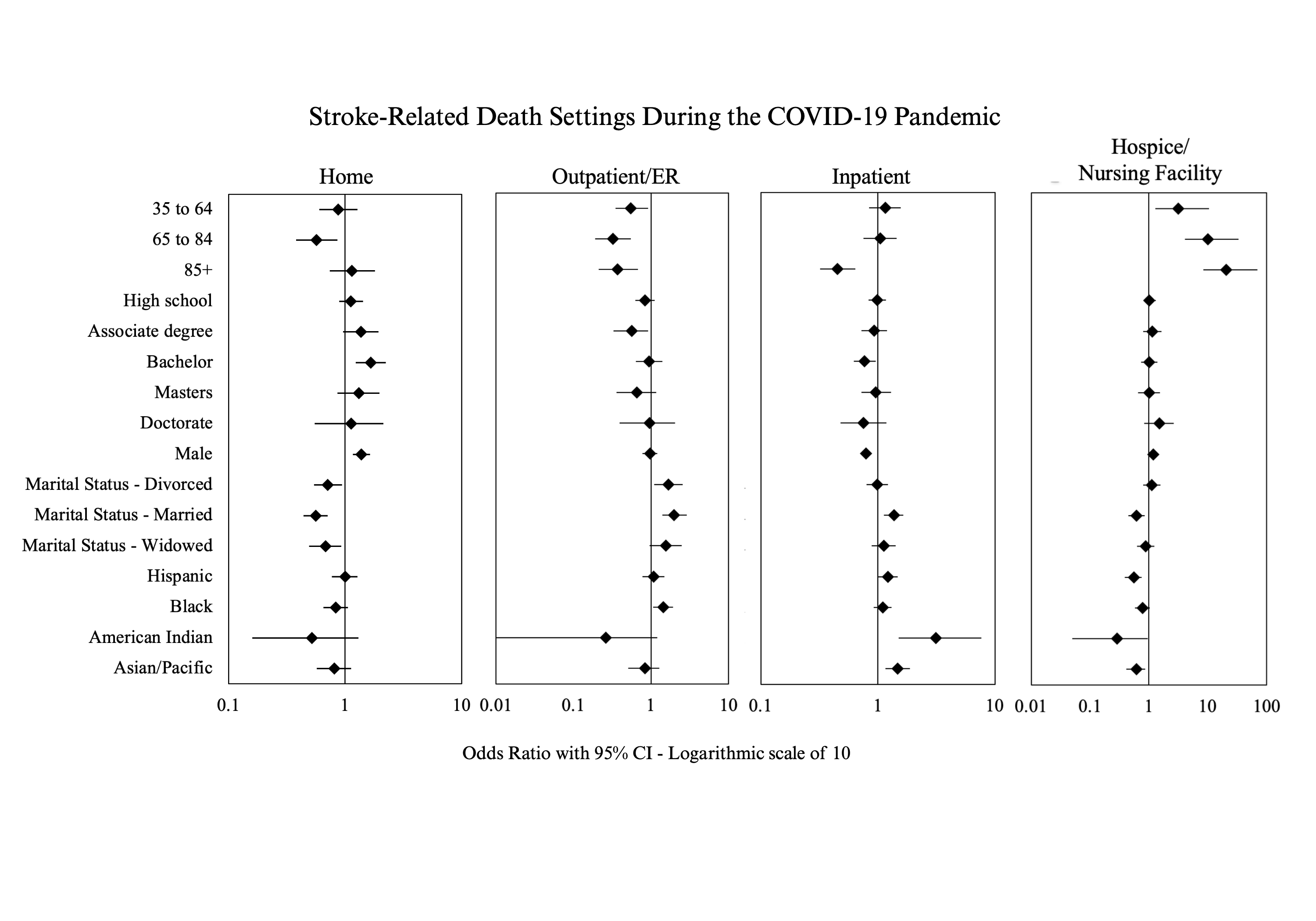
Results: A total of 5,400 and 5,712 stroke-related deaths occurred in 2019 and 2020, respectively. During COVID-19, decedents >65 years were more likely to die in H/NF (OR 10.05, p<0.001) but less likely in outpatient/ER (OR 0.32, p<0.001) or at home (OR 0.57, p=0.007) compared to those <35 years. High education level did not significantly influence the place of death than having high school diploma or less (p>0.05). Males were more likely to die at home (OR 1.38, p<0.001) but less likely as inpatient (OR 0.79, p<0.001) than females. Hispanic decedents had a higher likelihood of inpatient death (OR 1.22, p=0.041) but less likely to die in H/NF (OR 0.55, p<0.001) compared to non-Hispanic decedents. Compared to White decedents, Black decedents were more likely to die in outpatient/ER (OR 1.44, p=0.018), while American Indian decedents were more likely to die as inpatient (OR 3.12, p=0.005). Asian/Pacific Islander decedents had a higher chance of inpatient death (OR 1.47, p=0.002) but a lower likelihood of dying in H/NF (OR 0.61, p=0.010). Married decedents were more likely than singles to die as inpatient (OR 1.37, p=0.001) or in outpatient/ER (OR 1.99, p<0.001), but less likely to die in H/NF (OR 0.61, p=0.002) or at home (OR 0.56, p<0.001).
Conclusion: Our analysis revealed the influence of demographics on the settings of stroke fatalities during the COVID-19 pandemic. Further investigation is needed to determine contributing factors.
Question: What were the settings of stroke deaths in the US during COVID-19 pandemic?
Methods: Decedent-level mortality data from death certificates in CDC repository were obtained for the year 2020 (pandemic) and 2019 (comparison). Demographic data include age, sex, race/ethnicity, education, marital status, and place of stroke death, including inpatient, outpatient/emergency room (ER), hospice/nursing facilities (H/NF), and at-home. Multivariable logistic regression models assessed demographic impact on stroke mortality by place-of-death, yielding odds ratios (OR) with significance threshold of p<0.05.
Results: A total of 5,400 and 5,712 stroke-related deaths occurred in 2019 and 2020, respectively. During COVID-19, decedents >65 years were more likely to die in H/NF (OR 10.05, p<0.001) but less likely in outpatient/ER (OR 0.32, p<0.001) or at home (OR 0.57, p=0.007) compared to those <35 years. High education level did not significantly influence the place of death than having high school diploma or less (p>0.05). Males were more likely to die at home (OR 1.38, p<0.001) but less likely as inpatient (OR 0.79, p<0.001) than females. Hispanic decedents had a higher likelihood of inpatient death (OR 1.22, p=0.041) but less likely to die in H/NF (OR 0.55, p<0.001) compared to non-Hispanic decedents. Compared to White decedents, Black decedents were more likely to die in outpatient/ER (OR 1.44, p=0.018), while American Indian decedents were more likely to die as inpatient (OR 3.12, p=0.005). Asian/Pacific Islander decedents had a higher chance of inpatient death (OR 1.47, p=0.002) but a lower likelihood of dying in H/NF (OR 0.61, p=0.010). Married decedents were more likely than singles to die as inpatient (OR 1.37, p=0.001) or in outpatient/ER (OR 1.99, p<0.001), but less likely to die in H/NF (OR 0.61, p=0.002) or at home (OR 0.56, p<0.001).
Conclusion: Our analysis revealed the influence of demographics on the settings of stroke fatalities during the COVID-19 pandemic. Further investigation is needed to determine contributing factors.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Contactless and Automated Approach to the Acute Stroke Assessment
Saadat Moh, Titus Ryan, Verkuilen Haley, Fleming Phil, Sur Sanjib, Sen Souvik
A ChatGLM-based stroke diagnosis and prediction toolSong Xiaowei, Wang Jiayi, Ma Weizhi, Wu Jian, Wang Yueming, Gao Ceshu, Wei Chenming, Pi Jingtao