Final ID: Sa4148
Unraveling the potential receptors involved in mediating globular CTRP9's protective effects in the cardiovascular system
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Improved reperfusion strategies have significantly reduced mortality rates after acute myocardial infarction. However, chronic heart failure cases are rising. Cardiokines and adipokines, as paralog family members, share similarities in multiple aspects and play critical roles in protecting against heart failure by blocking its progression. It has been debated and remains elusive whether the CTRP family has its own receptors or shares them with other family members during disease conditions. Our previous research has indicated that globular CTRP9 (gCTRP9) plays a vital role in protecting the cardiovascular system by promoting cell proliferation and energy production in ischemic-injured hearts. However, the signal transduction mechanisms are not yet fully understood.
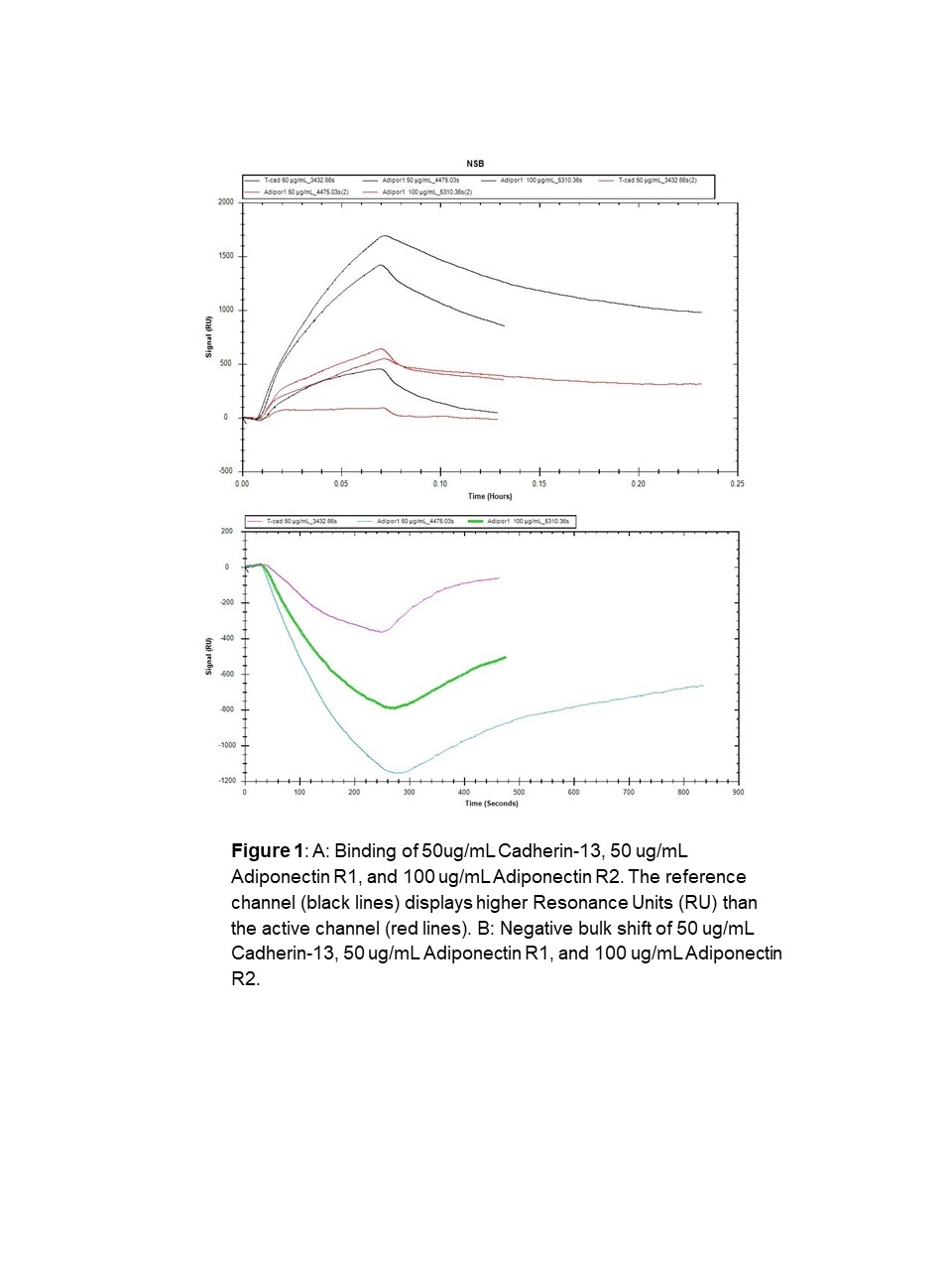
To address this gap in knowledge, we aimed to identify the potential cell membrane receptor for CTRP9 by analyzing the interaction between CTRP9 and three candidate receptors, namely Cadherin-13, adiponectin receptor 2, and adiponectin receptor 1. We utilized Surface Plasmon Resonance to examine the binding specificity, kinetics, and affinity of CTRP9 at a concentration of 50 µg/ml with varying levels of Cadherin-13 and Adiponectin Receptor 1, ranging from 0.1 to 100 µg/ml.
Our results showed that gCTRP9 exhibited saturation on the carboxyl chip, indicating its ability to bind to specific mobile receptors on the surface. Notably, we observed a significant binding affinity between CTRP9 and Adiponectin Receptor 1 in a dose-dependent, suggesting a stronger interaction between Adiponectin Receptor 1 and CTRP9. In contrast, Cadherin-13 also exhibited some binding affinity with CTRP9, although the response was comparatively lower. Importantly, no binding signals were detected between CTRP9 and Adiponectin Receptor 2.
In conclusion, our study provides evidence that Adiponectin Receptor 1 is a potential cell membrane receptor for gCTRP9, playing a crucial role in transmitting signals that protect injured or diabetic cardiomyocytes. Further research is needed to fully understand the downstream signaling pathways and mechanisms by which gCTRP9 and Adiponectin Receptor 1 interact to exert their protective effects on the cardiovascular system.
To address this gap in knowledge, we aimed to identify the potential cell membrane receptor for CTRP9 by analyzing the interaction between CTRP9 and three candidate receptors, namely Cadherin-13, adiponectin receptor 2, and adiponectin receptor 1. We utilized Surface Plasmon Resonance to examine the binding specificity, kinetics, and affinity of CTRP9 at a concentration of 50 µg/ml with varying levels of Cadherin-13 and Adiponectin Receptor 1, ranging from 0.1 to 100 µg/ml.
Our results showed that gCTRP9 exhibited saturation on the carboxyl chip, indicating its ability to bind to specific mobile receptors on the surface. Notably, we observed a significant binding affinity between CTRP9 and Adiponectin Receptor 1 in a dose-dependent, suggesting a stronger interaction between Adiponectin Receptor 1 and CTRP9. In contrast, Cadherin-13 also exhibited some binding affinity with CTRP9, although the response was comparatively lower. Importantly, no binding signals were detected between CTRP9 and Adiponectin Receptor 2.
In conclusion, our study provides evidence that Adiponectin Receptor 1 is a potential cell membrane receptor for gCTRP9, playing a crucial role in transmitting signals that protect injured or diabetic cardiomyocytes. Further research is needed to fully understand the downstream signaling pathways and mechanisms by which gCTRP9 and Adiponectin Receptor 1 interact to exert their protective effects on the cardiovascular system.
More abstracts on this topic:
ADAR1 inhibiting ZBP1-driven neuronal necroptosis to improve secondary injury after intracerebral hemorrhage
Wang Shuoyang, Zhao Shoucai, Wu Xiaodong, Chu Zhaohu, Xu Yang
Leptin Upregulates Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptor-2 (BMPR2) and Suppresses Growth Differentiation Factor 15 in an Endothelial Model of Pulmonary Arterial HypertensionKonja Daniels, Awad Keytam S., Wang Shuibang, Knight Colin, Ferreyra Gabriela, Hersi Kadija, Elinoff Jason, Danner Robert