Final ID: Su1014
Lipoprotein(a) Local Sybthesis And Plasma Uptake Via MDFS5 in Human Calcified Valve
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
High circulating levels of lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] are associated with increased risk of calcific aortic stenosis (CAS). Targeting Lp(a) metabolism holds promise for therapeutic interventions. However, the precise mechanisms by which Lp(a) accumulates on aortic valves still not fully understood.
Hypothesis
Lp(a) could be synthesized in situ in human aortic valves under specific stimuli, such as calcification, in addition to being taken up from plasma via membrane receptors, including the newly identified receptor Major Facilitator Superfamily Domain Containing 5 (MFSD5).
Methods
Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the Lp(a) and its receptor MFSD5 in human aortic valves from CAS patients or controls, which were non-CAS patients. Plasma Lp(a) levels were measured in individuals undergoing aortic valve resection. Human valvular interstitial cells (VICs) were cultured in procalcifying medium, with or without Lp(a) (10uM) for 14 and 21 days. Von-kossa or Alizarin Red staining were used to assess valve calcification. Expression of Lp(a) and MFSD5 was analyzed with quantitative RT-PCR and western blot.
Results
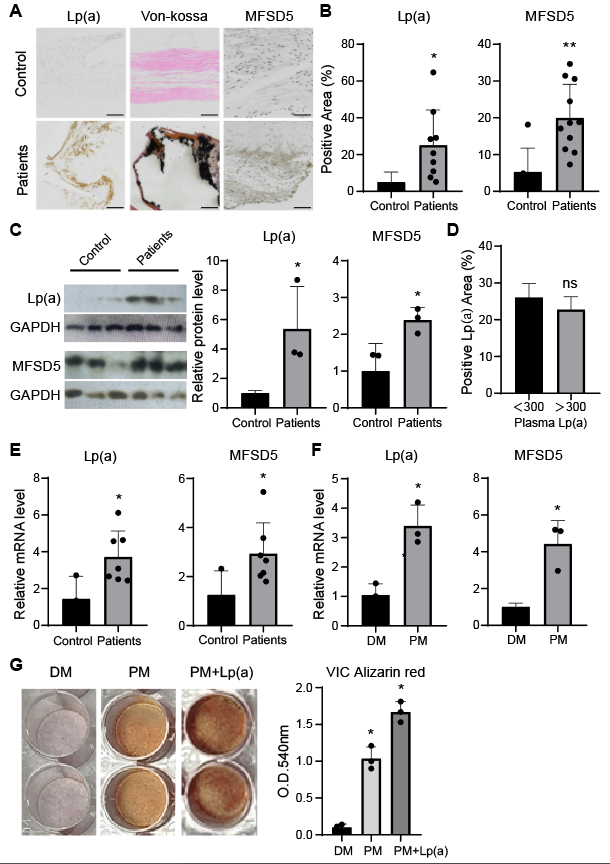
Lp(a) was nearly absent in control valve site, whereas it was abundantly present in valve site from CAS patients (p<0.05). The higher the level of Lp(a) detected, the greater the extent of calcification noted in valve site. The mRNA and protein levels of Lp(a) extracted from calcified human valves were significantly higher compared to controls. However, the concentration of plasma Lp(a) did not affect the expression of Lp(a) in valve site (p>0.05). In vitro studies showed that Lp(a) mRNA was minimally detectable in normal VICs, but was significantly upregulated following exposure to procalcifying medium (p < 0.05). Lp(a) incubation led to severer calcification than that induced by procalcifying medium alone (p < 0.05). As MFSD5 was a newly identified receptor of Lp(a), we also test its expression. MDFS5 was increased in human calcified valve (p<0.05) and calcified VICs (p<0.05). These results showed that the Lp(a) in valve could be increased by either uptake from serum or by synthesized locally by proper stimuli.
Conclusion
Our study has shown that the degree of aortic valve calcification is correlated with the level of Lp(a) in the valve site rather than in serum. We also verified MFSD5 was the receptor of Lp(a) on human valve. Targeting Lp(a) accumulation at the valve site may offer a more effective strategy for the prevention or treatment of CAS.
High circulating levels of lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] are associated with increased risk of calcific aortic stenosis (CAS). Targeting Lp(a) metabolism holds promise for therapeutic interventions. However, the precise mechanisms by which Lp(a) accumulates on aortic valves still not fully understood.
Hypothesis
Lp(a) could be synthesized in situ in human aortic valves under specific stimuli, such as calcification, in addition to being taken up from plasma via membrane receptors, including the newly identified receptor Major Facilitator Superfamily Domain Containing 5 (MFSD5).
Methods
Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the Lp(a) and its receptor MFSD5 in human aortic valves from CAS patients or controls, which were non-CAS patients. Plasma Lp(a) levels were measured in individuals undergoing aortic valve resection. Human valvular interstitial cells (VICs) were cultured in procalcifying medium, with or without Lp(a) (10uM) for 14 and 21 days. Von-kossa or Alizarin Red staining were used to assess valve calcification. Expression of Lp(a) and MFSD5 was analyzed with quantitative RT-PCR and western blot.
Results
Lp(a) was nearly absent in control valve site, whereas it was abundantly present in valve site from CAS patients (p<0.05). The higher the level of Lp(a) detected, the greater the extent of calcification noted in valve site. The mRNA and protein levels of Lp(a) extracted from calcified human valves were significantly higher compared to controls. However, the concentration of plasma Lp(a) did not affect the expression of Lp(a) in valve site (p>0.05). In vitro studies showed that Lp(a) mRNA was minimally detectable in normal VICs, but was significantly upregulated following exposure to procalcifying medium (p < 0.05). Lp(a) incubation led to severer calcification than that induced by procalcifying medium alone (p < 0.05). As MFSD5 was a newly identified receptor of Lp(a), we also test its expression. MDFS5 was increased in human calcified valve (p<0.05) and calcified VICs (p<0.05). These results showed that the Lp(a) in valve could be increased by either uptake from serum or by synthesized locally by proper stimuli.
Conclusion
Our study has shown that the degree of aortic valve calcification is correlated with the level of Lp(a) in the valve site rather than in serum. We also verified MFSD5 was the receptor of Lp(a) on human valve. Targeting Lp(a) accumulation at the valve site may offer a more effective strategy for the prevention or treatment of CAS.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Meta-Analysis Comparing Same-Day Discharge to Later-Day Discharge in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Jain Hritvik, Passey Siddhant, Jain Jyoti, Goyal Aman, Wasir Amanpreet, Ahmed Mushood, Patel Nandan, Yadav Ashish, Shah Janhvi, Mehta Aryan
Association of Elevated Serum Lipoprotein(a) with New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Study of 108930 PatientsKamel Moaz, Arsanjani Reza, Awad Kamal, Mahmoud Ahmed K., Farina Juan, Scalia Isabel, Pereyra Milagros, Abbas Mohammed Tiseer, Baba Nima, Ayoub Chadi