Final ID: Su4015
Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Mortality Risk in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease (CAD). SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) are effective in reducing cardiovascular mortality in T2DM patients, but their benefits for those with both CAD and T2DM are uncertain.
Objective: The primary outcome was to evaluate the efficacy of SGLT2i compared to other hypoglycemic agents or placebo in reducing the risk of all-cause mortality in patients with T2DM and CAD. Secondary outcomes included cardiovascular death, fatal or non-fatal stroke, and fatal or non-fatal myocardial infarction. We hypothesize that SGLT2i are more effective in mortality risk reduction in patients with T2DM and concomitant CAD.
Methods: A systematic review following PRISMA-2020 guidelines was conducted across four databases to evaluate the efficacy of SGLT2i in reducing mortality risk in diabetic patients with CAD. Quantitative analysis using Stata v18 employed a random-effects model (Restricted Maximum Likelihood) with Hazard Ratios (HR) as the measure of association.
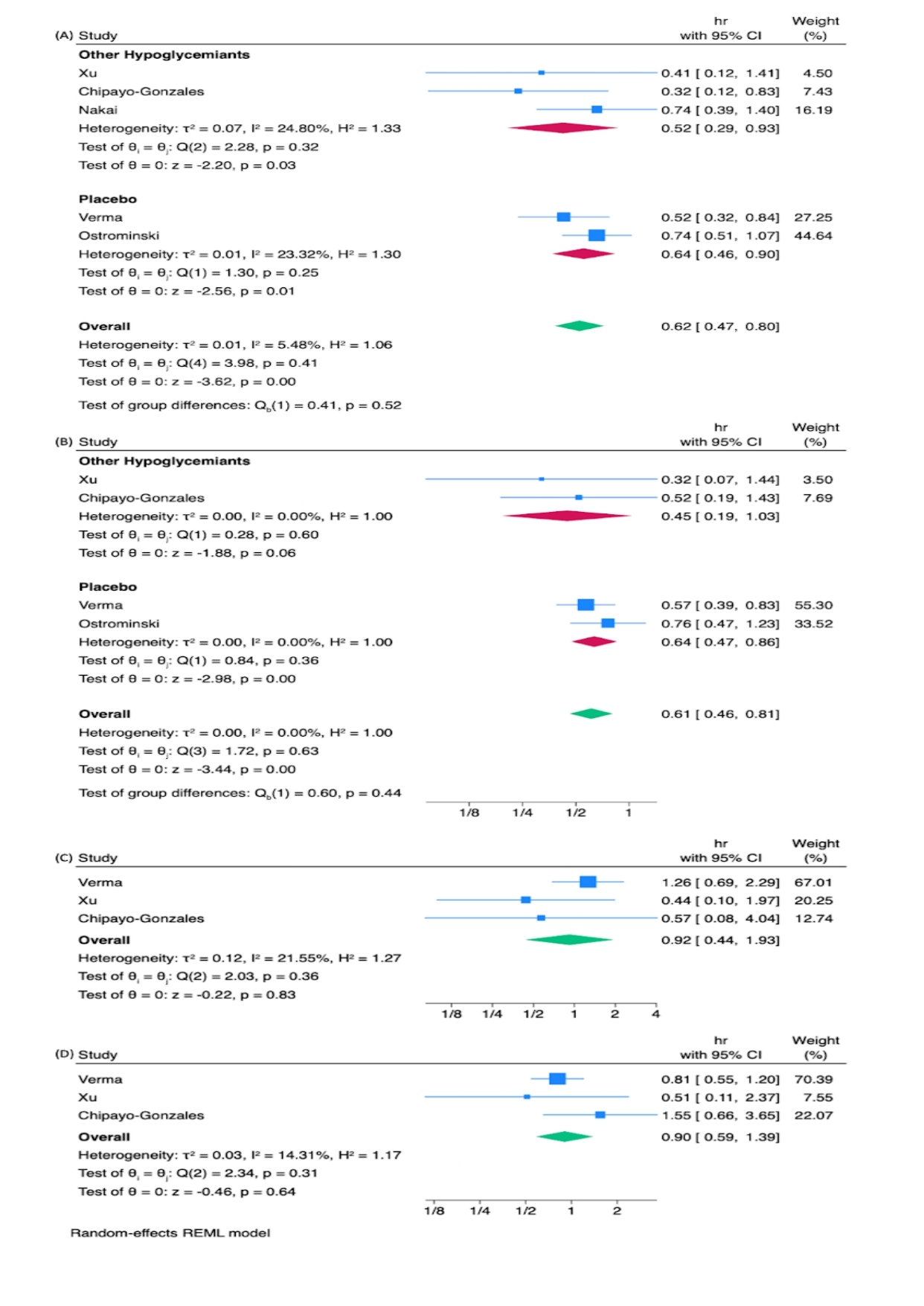
Results: Out of 853 studies identified, 5 publications were included in the final quantitative analysis, which included 5225 patients. The Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Form showed all included cohort studies had a low risk of bias. Those patients taking SGLT2i had a significant reduction in 38% the risk of all-cause mortality (HR 0.62 [0.47, 0.80]), this same effect was observed when compared with each subgroup vs. other hypoglycemic agents, HR 0.52 [0.29, 0.93]; vs. placebo, HR 0.64 [0.46, 0.90]. Results show very low heterogeneity. In overall cardiovascular death analysis, a significantly greater reduction was observed with SGLT2i (HR 0.61 [0.46, 0.81]), as well as when compared with placebo (HR 0.64 [0.47, 0.86]). In contrast, when compared with other hypoglycemic agents, there was a reduction, but this was not significant (HR 0.45 [0.19, 1.03]). No statistically significant decrease in the risk of fatal or non-fatal stroke and myocardial infarction was found with SGLT2i.
Conclusion: SGLT2i demonstrates a greater significant benefit in reducing all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with T2DM and CAD.
Introduction: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease (CAD). SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) are effective in reducing cardiovascular mortality in T2DM patients, but their benefits for those with both CAD and T2DM are uncertain.
Objective: The primary outcome was to evaluate the efficacy of SGLT2i compared to other hypoglycemic agents or placebo in reducing the risk of all-cause mortality in patients with T2DM and CAD. Secondary outcomes included cardiovascular death, fatal or non-fatal stroke, and fatal or non-fatal myocardial infarction. We hypothesize that SGLT2i are more effective in mortality risk reduction in patients with T2DM and concomitant CAD.
Methods: A systematic review following PRISMA-2020 guidelines was conducted across four databases to evaluate the efficacy of SGLT2i in reducing mortality risk in diabetic patients with CAD. Quantitative analysis using Stata v18 employed a random-effects model (Restricted Maximum Likelihood) with Hazard Ratios (HR) as the measure of association.
Results: Out of 853 studies identified, 5 publications were included in the final quantitative analysis, which included 5225 patients. The Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Form showed all included cohort studies had a low risk of bias. Those patients taking SGLT2i had a significant reduction in 38% the risk of all-cause mortality (HR 0.62 [0.47, 0.80]), this same effect was observed when compared with each subgroup vs. other hypoglycemic agents, HR 0.52 [0.29, 0.93]; vs. placebo, HR 0.64 [0.46, 0.90]. Results show very low heterogeneity. In overall cardiovascular death analysis, a significantly greater reduction was observed with SGLT2i (HR 0.61 [0.46, 0.81]), as well as when compared with placebo (HR 0.64 [0.47, 0.86]). In contrast, when compared with other hypoglycemic agents, there was a reduction, but this was not significant (HR 0.45 [0.19, 1.03]). No statistically significant decrease in the risk of fatal or non-fatal stroke and myocardial infarction was found with SGLT2i.
Conclusion: SGLT2i demonstrates a greater significant benefit in reducing all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with T2DM and CAD.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Systemic Thromboembolism in a Young Patient on Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Sabri Muhammad, Ijaz Naila, Nadeem Ramsha, Checchio Lucy, Riaz Faiza
A Clinical Trial of Healthy Food Subsidies and Behavioral Interventions to Increase Fruit and Vegetable Purchasing in an Online StoreHua Sophia, Klaiman Tamar, Dixon Erica, Volpp Kevin, Putt Mary, Coratti Samantha, White Jenna, Hossain Mohammad, Posner Hannah, Wang Erkuan, Zhu Jingsan, John Aileen