Final ID: MDP594
Trends in ACS-Related Mortality in Older Adults in the United States from 1999 to 2020: An Analysis of Gender, Race/Ethnicity, and Geographic Disparities
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background and Purpose
Specific populations of older adults in the United States are experiencing worsening trends in the incidence and prevalence of acute coronary syndrome (ACS). This study examined trends in ACS-related mortality among older adults in the United States.
Methods
The CDC-WONDER (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Wide-ranging OnLine Data for Epidemiologic Research) database was used to track deaths due to ACS in adults aged ≥ 65 years from 1999 to 2020. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) per 100,000 population were determined and stratified by year, sex, race/ethnicity, and geographic region. Joinpoint regression was used to analyze trends in AAMRs using annual percent change (APC).
Results
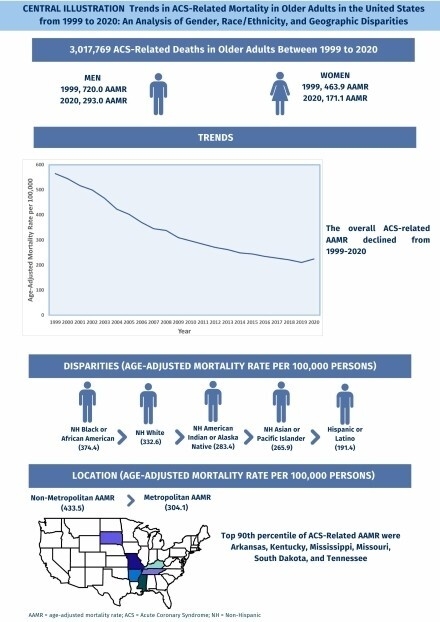
Altogether, 3,017,769 deaths occurred due to ACS and the overall ACS-related AAMR was 327.5 from 1999 to 2020. Following an initial period of rapid decrease in mortality rates from 1999 to 2011 (APC: -5.98; 95% CI: -6.40 to -5.65), the rate of decline halved from 2011 to 2020 (APC: -3.02; 95% CI: -3.62 to -2.19). Men had consistently higher AAMRs (410.6) than women (267.8). In racial and ethnic groups, the Non-Hispanic (NH) Black or African American population had both the highest total AAMR (374.4) and was one of the two ethnicities that displayed increasing trends from 2018-2020 (APC: 4.74; 95% CI: 0.30 to 7.10). The second ethnic group with increasing trends was Hispanic or Latino (2018-2020 APC: 9.27; 95% CI: 3.22 to 13.16). Significant geographic disparities were observed, with nonmetropolitan areas having consistently higher AAMRs (433.5) than metropolitan areas (304.1). States in the top 90th percentile (District of Arkansas, Kentucky, Mississippi, Missouri, South Dakota, and Tennessee) had almost double the AAMRs than states in the bottom 10th percentile (Alaska, Colorado, Hawaii, Minnesota, Montana, and Nevada).
Conclusion
Despite an overall decrease in mortality, the deceleration of decline since 2011is concerning. Men, NH Black/African American populations, and residents of nonmetropolitan areas displayed the highest burden of ACS-related mortality. Focused strategies are required to prevent and manage ACS in older adults to mitigate the rising levels of ACS-related mortality.
Specific populations of older adults in the United States are experiencing worsening trends in the incidence and prevalence of acute coronary syndrome (ACS). This study examined trends in ACS-related mortality among older adults in the United States.
Methods
The CDC-WONDER (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Wide-ranging OnLine Data for Epidemiologic Research) database was used to track deaths due to ACS in adults aged ≥ 65 years from 1999 to 2020. Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMRs) per 100,000 population were determined and stratified by year, sex, race/ethnicity, and geographic region. Joinpoint regression was used to analyze trends in AAMRs using annual percent change (APC).
Results
Altogether, 3,017,769 deaths occurred due to ACS and the overall ACS-related AAMR was 327.5 from 1999 to 2020. Following an initial period of rapid decrease in mortality rates from 1999 to 2011 (APC: -5.98; 95% CI: -6.40 to -5.65), the rate of decline halved from 2011 to 2020 (APC: -3.02; 95% CI: -3.62 to -2.19). Men had consistently higher AAMRs (410.6) than women (267.8). In racial and ethnic groups, the Non-Hispanic (NH) Black or African American population had both the highest total AAMR (374.4) and was one of the two ethnicities that displayed increasing trends from 2018-2020 (APC: 4.74; 95% CI: 0.30 to 7.10). The second ethnic group with increasing trends was Hispanic or Latino (2018-2020 APC: 9.27; 95% CI: 3.22 to 13.16). Significant geographic disparities were observed, with nonmetropolitan areas having consistently higher AAMRs (433.5) than metropolitan areas (304.1). States in the top 90th percentile (District of Arkansas, Kentucky, Mississippi, Missouri, South Dakota, and Tennessee) had almost double the AAMRs than states in the bottom 10th percentile (Alaska, Colorado, Hawaii, Minnesota, Montana, and Nevada).
Conclusion
Despite an overall decrease in mortality, the deceleration of decline since 2011is concerning. Men, NH Black/African American populations, and residents of nonmetropolitan areas displayed the highest burden of ACS-related mortality. Focused strategies are required to prevent and manage ACS in older adults to mitigate the rising levels of ACS-related mortality.
More abstracts on this topic:
ACS-Specific Gut Microbial and Metabolic Profiles Reveal Diagnostic and Recovery Markers
Xu Jing, Fu Jingyuan, Dai Die, Yang Yanan, Yang Jingang, Gao Shanshan, Wu Chongming, He Jiumin, Chen Weihua, Yang Yue-jin
A Body Shape Index at Age 25-64 Predicts Mortality and CHD HospitalizationShafran Itamar, Krakauer Nir, Krakauer Jesse, Cohen Gali, Gerber Yariv