Final ID: Sa3016
High Visceral-to-Subcutaneous Fat Ratio is Correlated with Increased Coronary Artery Disease Severity Based on Computed Tomography-derived SYNTAX Score Regardless of Physique Stratified by Waist Circumference
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Waist circumference (WC) has been recognized as a significant factor of metabolic syndrome and is closely associated with the amounts of abdominal visceral and subcutaneous fats. Although abdominal fat distribution (AFD) is indicated using the ratio of the visceral fat area (VFA) to the subcutaneous fat area (SFA), i.e., V/S ratio, which is possibly related to an increased risk of coronary artery disease (CAD), few studies have shown the impact of the AFD and physique on CAD. A computed tomography (CT)-derived SYNTAX score (CT-SX score) has been suggested as a feasible method of assessing CAD severity based on coronary CT angiography (CCTA). We aimed to evaluate the effect of AFD based on the V/S ratio and physique classified by WC on CAD complexity using the CT-SX score.
Methods: CCTA was conducted on 931 consecutive patients suspected of CAD. Furthermore, a plain abdominal CT was also performed to measure VFA and SFA. To evaluate the AFD, V/S ratios were also determined. CAD severity was assessed using CCTA. Significant stenosis was defined as ≥50% diameter stenosis. The CT-SX score was calculated in patients with ≥1 significant stenosis. Finally, patients were classified into low and high WC groups based on their median value (84.79 cm).
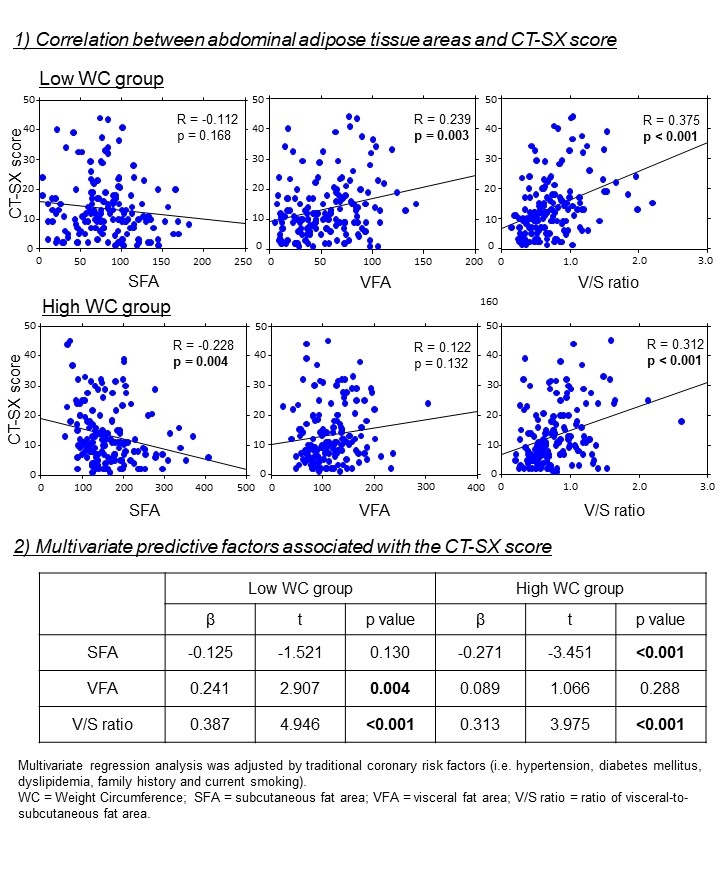
Results: Of the 931 patients enrolled, 308 (33.1%) had ≥1 significant stenosis. There was a positive correlation between the V/S ratio and CT-SX score regardless of the WC. Although VFA positively correlated with the CT-SX score in the low WC group, SFA negatively correlated with the CT-SX score in the high WC group. In a multivariate analysis adjusted for traditional coronary risks, same results were observed (Figure).
Conclusions: The AFD indicated by the V/S ratio appears to be an effective index to determine CAD severity regardless of the physique based on WC. However, factors that increase the V/S ratio vary depending on the physique; therefore, interventional treatment tailored to each physique may help mitigate CAD progression.
Methods: CCTA was conducted on 931 consecutive patients suspected of CAD. Furthermore, a plain abdominal CT was also performed to measure VFA and SFA. To evaluate the AFD, V/S ratios were also determined. CAD severity was assessed using CCTA. Significant stenosis was defined as ≥50% diameter stenosis. The CT-SX score was calculated in patients with ≥1 significant stenosis. Finally, patients were classified into low and high WC groups based on their median value (84.79 cm).
Results: Of the 931 patients enrolled, 308 (33.1%) had ≥1 significant stenosis. There was a positive correlation between the V/S ratio and CT-SX score regardless of the WC. Although VFA positively correlated with the CT-SX score in the low WC group, SFA negatively correlated with the CT-SX score in the high WC group. In a multivariate analysis adjusted for traditional coronary risks, same results were observed (Figure).
Conclusions: The AFD indicated by the V/S ratio appears to be an effective index to determine CAD severity regardless of the physique based on WC. However, factors that increase the V/S ratio vary depending on the physique; therefore, interventional treatment tailored to each physique may help mitigate CAD progression.
More abstracts on this topic:
Associations between Triglyceride-glucose-obesity Indicators with Cardiovascular Disease Across Combination of Body Mass Index and Central Obesity Categories: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
Zhang Ruolin, Wang Yaojie, Zhou Huiyuan, Li Juyuan, Zhu Junke, Ding Xiong
Advanced maternal age and association with major adverse cardiovascular events from NHANES from 1999 to 2018Mehta Adhya, Honigberg Michael, Kennedy Jamie, Spitz Jared, Sharma Garima, Agboola Olayinka, Satti Danish Iltaf, Harrington Colleen, Scott Nandita, Sarma Amy, Saad Antonio, Sullivan Scott, Epps Kelly