Final ID: Mo4128
Impact of Non-Culprit Chronic Total Occlusion in Patients with Infarct-Related Cardiogenic Shock: Results from the RESCUE Registry
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: About 25% of patients with acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock (AMI-CS) have chronic total occlusion (CTO) at non-culprit artery. However, the prognostic impact of CTO in these patients is still unclear.
Aims: We aimed to investigate the impact of CTO at non-culprit artery on 1-year mortality in patients with AMI-CS using the multicenter registry of cardiogenic shock.
Methods: A total of 1,247 patients presented with cardiogenic shock (CS) were enrolled in the SMART-RESCUE registry between January 2014 and December 2018. After exclusion of non-ischemic cause shock, ischemic cardiomyopathy, failed or no revascularization, vasospasm, and patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery, 695 patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Among these, we analyzed 536 patients with multivessel disease (MVD) according to the presence of CTO at non-culprit artery. The study endpoint was a 1-year all-cause mortality. We also examined the incidence of 1-year cardiac death, and in-hospital death or renal replacement therapy (RRT).
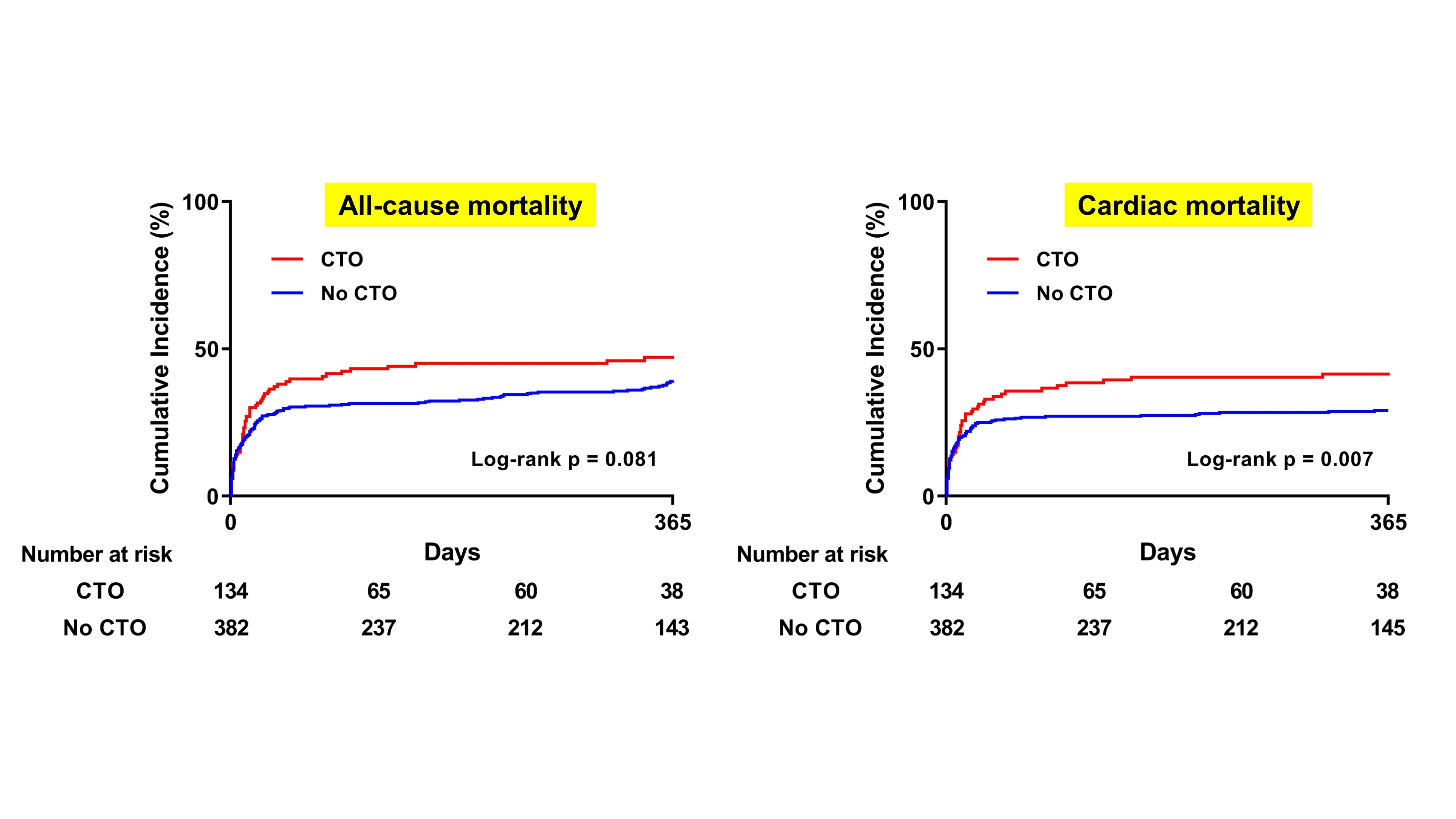
Results: A 141 patients (26.3%) of study population had CTO lesion at non-culprit artery. The CTO group had more patients with diabetes mellitus, and lesser patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Although initial left ventricular ejection fraction was lower in CTO group (28.5 vs. 34.1%, P=0.005), initial systolic blood pressure (73.8 vs. 73.2 mmHg, P=0.822) and the level of lactate (6.6 vs. 6.4 mmol/L, P=0.804) were similar in both groups. Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was applied in 206 patients (38.4%), and its use rate was comparable in 2 groups (40.4 vs. 37.7%, P=0.571). Pre- (32.9 vs. 22.9, P <0.001) and post-PCI SYNTAX score (16.7 vs. 5.3, P <0.001) was significantly higher in CTO group. In CTO group, 53 patients (37.6%) had CTO at left main or left anterior descending artery, and only 19 patients (13.5%) in CTO group received PCI for CTO. In multivariate analysis, all-cause mortality at 1-year was significantly higher in CTO group (51.8 vs. 40.5%, hazard ratio [HR] 1.44, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.09-1.90, P=0.011). The incidences of 1-year cardiac death (45.4 vs. 32.4%, HR 1.55, 95% CI 1.15-2.10, P=0.004) and in-hospital death or RRT (46.8 vs. 36.5%, P=0.031) were also higher in CTO group.
Conclusions: Non-culprit CTO lesion was associated with higher 1-year mortality in patients with AMI-CS and multivessel disease.
Aims: We aimed to investigate the impact of CTO at non-culprit artery on 1-year mortality in patients with AMI-CS using the multicenter registry of cardiogenic shock.
Methods: A total of 1,247 patients presented with cardiogenic shock (CS) were enrolled in the SMART-RESCUE registry between January 2014 and December 2018. After exclusion of non-ischemic cause shock, ischemic cardiomyopathy, failed or no revascularization, vasospasm, and patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery, 695 patients underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Among these, we analyzed 536 patients with multivessel disease (MVD) according to the presence of CTO at non-culprit artery. The study endpoint was a 1-year all-cause mortality. We also examined the incidence of 1-year cardiac death, and in-hospital death or renal replacement therapy (RRT).
Results: A 141 patients (26.3%) of study population had CTO lesion at non-culprit artery. The CTO group had more patients with diabetes mellitus, and lesser patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Although initial left ventricular ejection fraction was lower in CTO group (28.5 vs. 34.1%, P=0.005), initial systolic blood pressure (73.8 vs. 73.2 mmHg, P=0.822) and the level of lactate (6.6 vs. 6.4 mmol/L, P=0.804) were similar in both groups. Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was applied in 206 patients (38.4%), and its use rate was comparable in 2 groups (40.4 vs. 37.7%, P=0.571). Pre- (32.9 vs. 22.9, P <0.001) and post-PCI SYNTAX score (16.7 vs. 5.3, P <0.001) was significantly higher in CTO group. In CTO group, 53 patients (37.6%) had CTO at left main or left anterior descending artery, and only 19 patients (13.5%) in CTO group received PCI for CTO. In multivariate analysis, all-cause mortality at 1-year was significantly higher in CTO group (51.8 vs. 40.5%, hazard ratio [HR] 1.44, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.09-1.90, P=0.011). The incidences of 1-year cardiac death (45.4 vs. 32.4%, HR 1.55, 95% CI 1.15-2.10, P=0.004) and in-hospital death or RRT (46.8 vs. 36.5%, P=0.031) were also higher in CTO group.
Conclusions: Non-culprit CTO lesion was associated with higher 1-year mortality in patients with AMI-CS and multivessel disease.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Transient Cortical Blindness occurring during Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angiography for Acute Coronary Syndrome.
Adelakun Adeniyi, Farouji Iyad, Haddad Ahmad, Szwed Stanley
A New Analytical Approach for Noninvasive Reconstruction of the Entire Left Ventricular Pressure Waveform in Myocardial Ischemia and InfarctionBilgi Coskun, Li Jiajun, Alavi Rashid, Dai Wangde, Matthews Ray, Kloner Robert, Pahlevan Niema