Final ID: MDP530
Identifying atrial fibrillation symptom clusters and examining associations with major adverse cardiovascular events following catheter ablation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with a heavy burden of symptoms that frequently co-occur. Patterns of co-occurring symptoms and improvements after AF treatments are poorly understood. Disentangling AF symptoms can support better clinical management.
Objective: This study aims to (1) identify co-occurring symptoms, or clusters, of patients undergoing catheter ablation for AF and (2) determine associations between symptom clusters and post-ablation AF-related major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective secondary analysis of electronic health record (EHR) data for adults who underwent catheter ablation for treatment of AF at one academic medical center from 2010-2020. We used a natural language processing algorithm developed by our team (F-score=0.81) to extract ten symptoms from clinical notes: anxiety, chest pain, dizziness, dyspnea, edema, fatigue, malaise, palpitations, syncope, and weakness. To conduct symptom clustering, we used an unsupervised machine learning approach, Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering, to identify subgroups of patients representing different clusters. The composite AF-related MACE variable included AF-specific ED visit, AF-specific hospitalization, stroke, and/or death within one year post-ablation documented in EHRs. We used logistic regression models to examine associations between the six symptom clusters and the AF-related MACE outcome, adjusting for age, sex, and race.
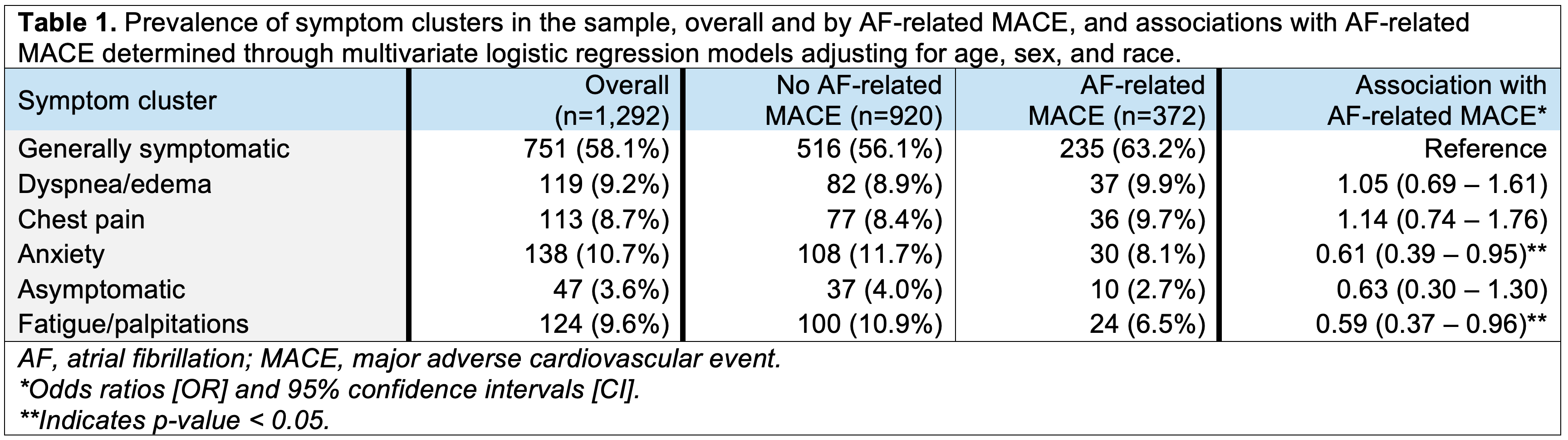
Results: The mean age of the sample (n=1,292) was 65.5 (standard deviation 12.6) years, 35% were female, and 58% were White. We identified six distinct clusters from notes (n=13,416), labeled using the most prevalent symptoms in each cluster: generally symptomatic, dyspnea and edema, chest pain, anxiety, asymptomatic, and fatigue and palpitations. One-third (n= 372; 29%) had an AF-related MACE within one year of ablation. The prevalence of symptom clusters within the sample and associations with MACE are shown in Table 1.
Conclusions: AF patients’ pre-ablation symptoms vary widely and correlate with post-ablation MACE. It is possible symptom clusters signify latent biological differences with implications for the clinical care of AF.
Objective: This study aims to (1) identify co-occurring symptoms, or clusters, of patients undergoing catheter ablation for AF and (2) determine associations between symptom clusters and post-ablation AF-related major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective secondary analysis of electronic health record (EHR) data for adults who underwent catheter ablation for treatment of AF at one academic medical center from 2010-2020. We used a natural language processing algorithm developed by our team (F-score=0.81) to extract ten symptoms from clinical notes: anxiety, chest pain, dizziness, dyspnea, edema, fatigue, malaise, palpitations, syncope, and weakness. To conduct symptom clustering, we used an unsupervised machine learning approach, Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering, to identify subgroups of patients representing different clusters. The composite AF-related MACE variable included AF-specific ED visit, AF-specific hospitalization, stroke, and/or death within one year post-ablation documented in EHRs. We used logistic regression models to examine associations between the six symptom clusters and the AF-related MACE outcome, adjusting for age, sex, and race.
Results: The mean age of the sample (n=1,292) was 65.5 (standard deviation 12.6) years, 35% were female, and 58% were White. We identified six distinct clusters from notes (n=13,416), labeled using the most prevalent symptoms in each cluster: generally symptomatic, dyspnea and edema, chest pain, anxiety, asymptomatic, and fatigue and palpitations. One-third (n= 372; 29%) had an AF-related MACE within one year of ablation. The prevalence of symptom clusters within the sample and associations with MACE are shown in Table 1.
Conclusions: AF patients’ pre-ablation symptoms vary widely and correlate with post-ablation MACE. It is possible symptom clusters signify latent biological differences with implications for the clinical care of AF.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comprehensive Study on Machine Learning Models Combining with Oversampling for One-year Persistent Coronary Artery Aneurysm in Kawasaki Disease
Liang Kaizhi, Pang Yusheng, Su Danyan
A Machine Learning Approach to Simplify Risk Stratification of Patients with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseLi Hsin Fang, Gluckman Ty, Nute Andrew, Weerasinghe Roshanthi, Wendt Staci, Wilson Eleni, Sidelnikov Eduard, Kathe Niranjan, Swihart Charissa, Jones Laney