Final ID: Mo2141
Notched P-wave by digital ECG analysis was associated with new-onset atrial fibrillation onset and ischemic stroke
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: A bimodal P wave in lead II reflects left atrial remodeling and is described as a notched P wave. A notched P wave is usually defined as a dip over the smallest unit of electrocardiography (ECG) recording paper, 40 ms, but automated analysis of ECGs has shown that even a notch of 20 ms is associated with cardiovascular events. A notched P wave is also known to predict atrial fibrillation (AF) after catheter ablation. However, the relationship between automatically assessed notched P waves and new-onset AF and ischemic stroke in patients without documented AF has not been clarified.
Hypothesis: A notched P-wave by digital ECG analysis was associated with both new-onset AF and ischemic stroke.
Methods: We enrolled 4,216 subjects from the Cardiovascular Prognostic Coupling Study in Japan (Coupling Registry) who had one or more cardiovascular risk factors. Twelve-lead electrocardiography was conducted, and the peak-to-peak distance in the M shape was calculated automatically using a 12-lead ECG analysis system. We compared two definitions: P-waves defined as “notched” at the the peak-to-peak (“M shape”) distance in lead II of ≥20 ms or ≥40 ms. New-onset AF was confirmed through routine medical care as well as annual ECGs. We defined the primary endpoint as new-onset AF and the secondary endpoint as ischemic stroke.
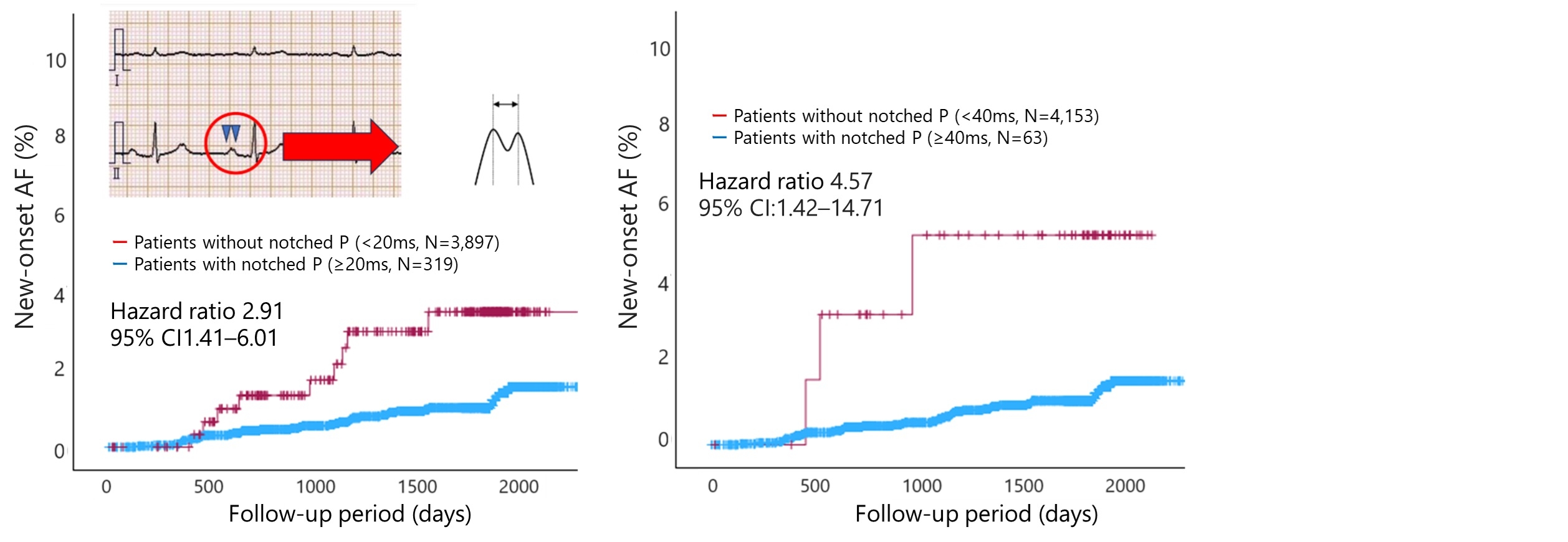
Results: The mean follow-up period was 53 ± 17 months, during which 17 AF cases developed. When a notched P-wave was defined as ≥20 ms (n = 319), it was a significant predictor of both new-onset AF (hazard ratio [HR] 2.91, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.41–6.01, p=0.004) and ischemic stroke (HR 3.02, 95% CI 1.56–5.83, P=0.001). A notched P-wave defined as ≥40 ms (n = 63) was also a predictor of new-onset AF (HR 4.57; 95% CI:1.42–14.71, p = 0.011) and ischemic stroke (HR 3.84, 95% CI 1.20–12.29, P=0.024).
Conclusions: A notched P-wave by digital ECG analysis was associated with ischemic stroke as well as the new-onset AF.
Hypothesis: A notched P-wave by digital ECG analysis was associated with both new-onset AF and ischemic stroke.
Methods: We enrolled 4,216 subjects from the Cardiovascular Prognostic Coupling Study in Japan (Coupling Registry) who had one or more cardiovascular risk factors. Twelve-lead electrocardiography was conducted, and the peak-to-peak distance in the M shape was calculated automatically using a 12-lead ECG analysis system. We compared two definitions: P-waves defined as “notched” at the the peak-to-peak (“M shape”) distance in lead II of ≥20 ms or ≥40 ms. New-onset AF was confirmed through routine medical care as well as annual ECGs. We defined the primary endpoint as new-onset AF and the secondary endpoint as ischemic stroke.
Results: The mean follow-up period was 53 ± 17 months, during which 17 AF cases developed. When a notched P-wave was defined as ≥20 ms (n = 319), it was a significant predictor of both new-onset AF (hazard ratio [HR] 2.91, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.41–6.01, p=0.004) and ischemic stroke (HR 3.02, 95% CI 1.56–5.83, P=0.001). A notched P-wave defined as ≥40 ms (n = 63) was also a predictor of new-onset AF (HR 4.57; 95% CI:1.42–14.71, p = 0.011) and ischemic stroke (HR 3.84, 95% CI 1.20–12.29, P=0.024).
Conclusions: A notched P-wave by digital ECG analysis was associated with ischemic stroke as well as the new-onset AF.
More abstracts on this topic:
A novel risk score predicts the prevalence of left atrial low-voltage areas and rhythm outcome in patients undergoing long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation ablation
Ooka Hirotaka, Nakao Sho, Kusuda Masaya, Ariyasu Wataru, Kudo Satoshi, Fujii Subaru, Mano Toshiaki, Matsuda Yasuhiro, Masuda Masaharu, Okamoto Shin, Ishihara Takayuki, Nanto Kiyonori, Tsujimura Takuya, Hata Yosuke, Uematsu Hiroyuki
A distinct clot transcriptomic signature is associated with atrial fibrillation-derived ischemic stroke in the INSIGHT RegistrySeah Carina, Rivet Dennis, Fraser Justin, Kellner Christopher, Devarajan Alex, Vicari James, Dabney Alan, Baltan Selva, Sohrabji Farida, Pennypacker Keith, Nanda Ashish, Woodward Britton