Final ID: MDP496
Machine learning-based prediction of heart rate at anaerobic threshold from cardiopulmonary exercise testing - a large-scale study in cardiovascular and healthy population
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
For effective exercise prescription in cardiovascular patients, it is important to determine the target exercise heart rate (AT-HR) at the level of the anaerobic threshold. The AT-HR is usually obtained by cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPX).
Objectives
The aim of this study is to develop a machine learning (ML) approach to predict AT-HR without CPX.
Methods
We used data from 21,491 patients who underwent CPX between 2004 and 2023. The data consisted of 71 features including vital signs, blood tests, and echocardiography. We predicted AT-HR using an ML-based model based on gradient boosting. The study sample was randomly divided into training (64% of patients), validation (16%), and test (20%) cohorts. In addition, the features were ranked based on feature selection using the trained model in terms of importance for predicting AT-HR.
Results
The test mean absolute error of AT-HR by the ML-based model was 7.7±0.2, otherwise, Karvonen methods with coefficient 0.7 or 0.4 were 34.3±0.2, 11.9±0.1. The feature ranking method showed that hsCRP, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, creatine kinase, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and creatinine were important features for the prediction of AT-HR. The predictive performance with a limited number of features was comparable to that with all features.
Conclusions
The prediction of AT-HR by the ML-based model can improve the effectiveness of cardiac rehabilitation. We can reduce the required patient characteristics for AT-HR prediction by using the ranked features.
Clinical implementation
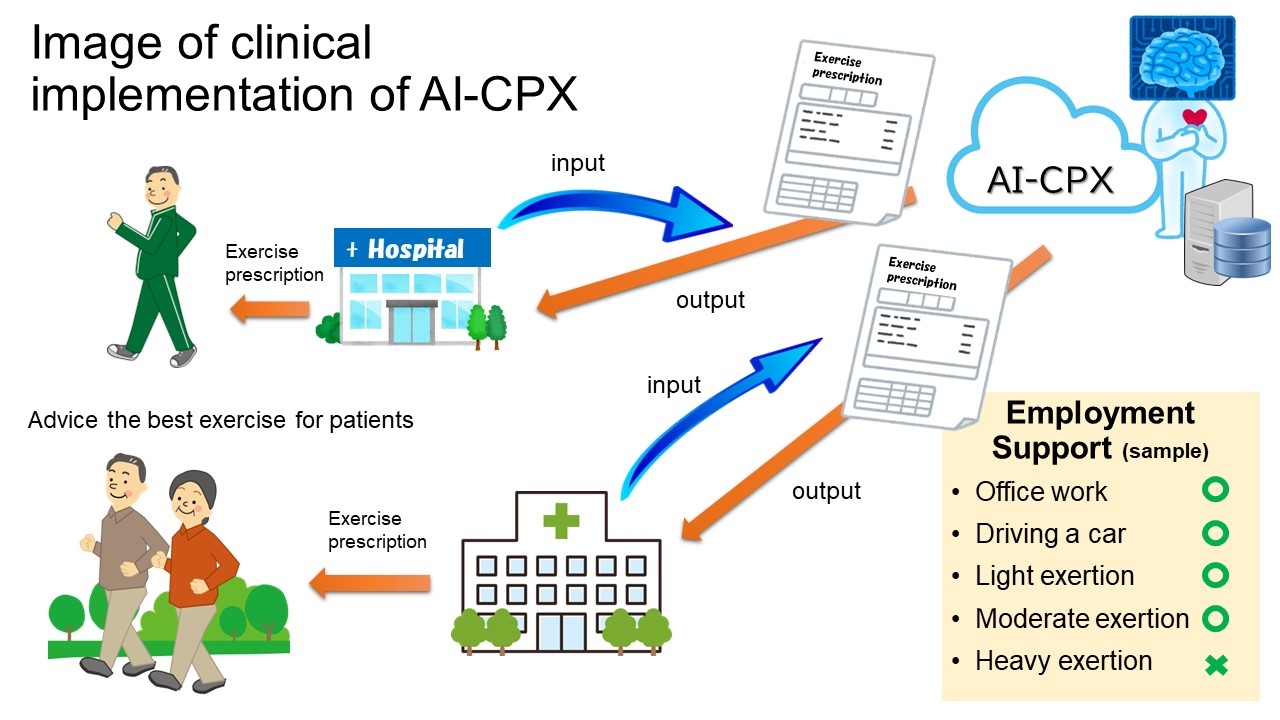
Our study showed that the prediction performance by the ML-based model with a limited number of features was comparable to that with all features. This result implies that we can reduce the cost and time to for obtaining patient characteristics to predict AT-HR for each patient. With this system, city hospitals and private clinics without CPX can obtain predicted AT-HR by entering basic information and provide aerobic exercise support to many patients based on the exercise prescription generated by the system. In addition, even in CPX facilities where frequent testing is not possible due to manpower and time constraints, this system can be used to frequently predict AT-HR and update exercise prescriptions in response to ever-changing cardiovascular conditions.
For effective exercise prescription in cardiovascular patients, it is important to determine the target exercise heart rate (AT-HR) at the level of the anaerobic threshold. The AT-HR is usually obtained by cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPX).
Objectives
The aim of this study is to develop a machine learning (ML) approach to predict AT-HR without CPX.
Methods
We used data from 21,491 patients who underwent CPX between 2004 and 2023. The data consisted of 71 features including vital signs, blood tests, and echocardiography. We predicted AT-HR using an ML-based model based on gradient boosting. The study sample was randomly divided into training (64% of patients), validation (16%), and test (20%) cohorts. In addition, the features were ranked based on feature selection using the trained model in terms of importance for predicting AT-HR.
Results
The test mean absolute error of AT-HR by the ML-based model was 7.7±0.2, otherwise, Karvonen methods with coefficient 0.7 or 0.4 were 34.3±0.2, 11.9±0.1. The feature ranking method showed that hsCRP, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, creatine kinase, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and creatinine were important features for the prediction of AT-HR. The predictive performance with a limited number of features was comparable to that with all features.
Conclusions
The prediction of AT-HR by the ML-based model can improve the effectiveness of cardiac rehabilitation. We can reduce the required patient characteristics for AT-HR prediction by using the ranked features.
Clinical implementation
Our study showed that the prediction performance by the ML-based model with a limited number of features was comparable to that with all features. This result implies that we can reduce the cost and time to for obtaining patient characteristics to predict AT-HR for each patient. With this system, city hospitals and private clinics without CPX can obtain predicted AT-HR by entering basic information and provide aerobic exercise support to many patients based on the exercise prescription generated by the system. In addition, even in CPX facilities where frequent testing is not possible due to manpower and time constraints, this system can be used to frequently predict AT-HR and update exercise prescriptions in response to ever-changing cardiovascular conditions.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Deep Learning Digital Biomarker for Mitral Valve Prolapse using Echocardiogram Videos
Al-alusi Mostafa, Khurshid Shaan, Sanborn Danita, Picard Michael, Ho Jennifer, Maddah Mahnaz, Ellinor Patrick, Lau Emily, Small Aeron, Reeder Christopher, Shnitzer Dery Tal, Andrews Carl, Kany Shinwan, Ramo Joel, Haimovich Julian
Effect of Mavacamten on Measures of Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing: An Analysis of the ODYSSEY-HCM Randomized TrialOwens Anjali, Desai Milind