Final ID: 4137846
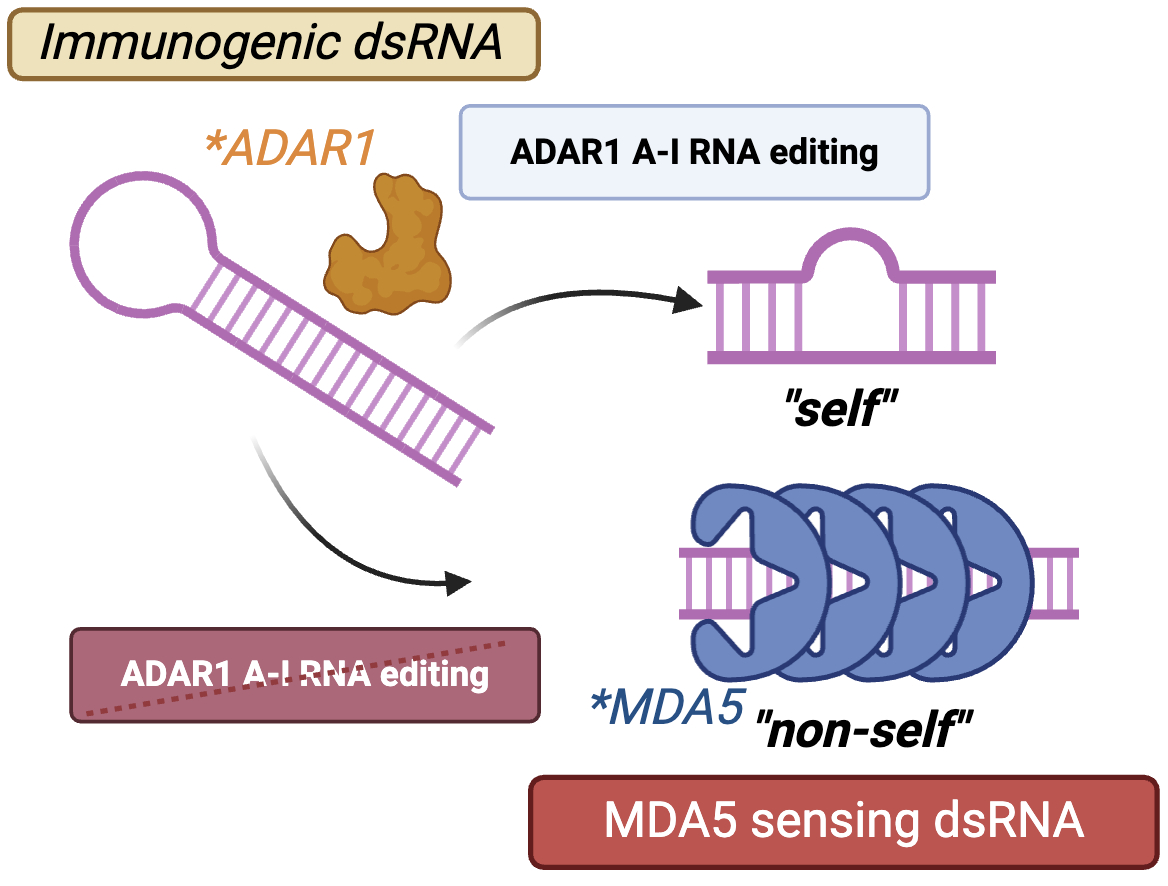
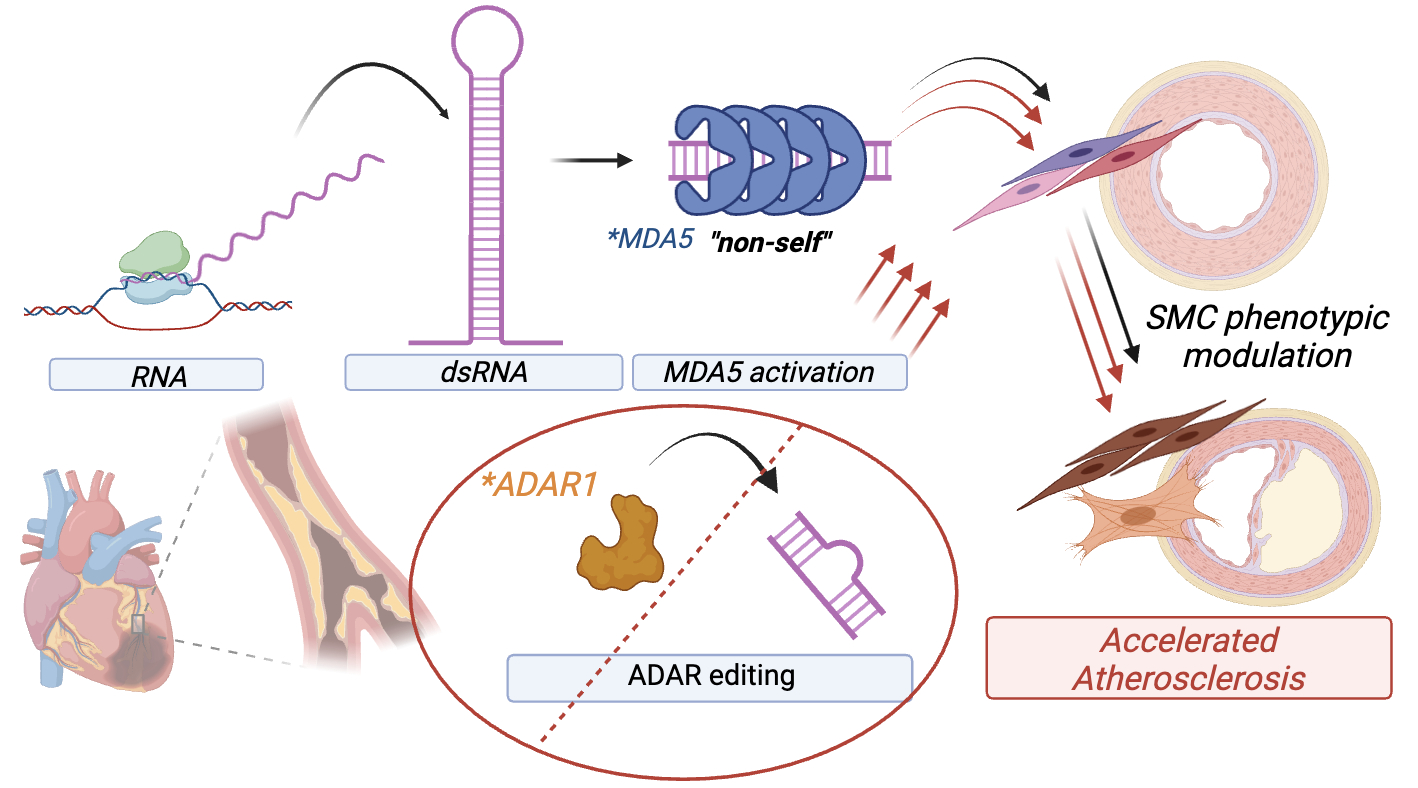
Smooth muscle expression of RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 controls vascular integrity and progression of atherosclerosis
- Weldy, Chad ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Palmisano, Brian ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Sharma, Disha ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Worssam, Matthew ( Stanford University , Palo Alto , California , United States )
- Zhao, Quanyi ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Bhate, Amruta ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Kundu, Ramendra ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Nguyen, Trieu ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Li, Jin Billy ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Quertermous, Thomas ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Li, Qin ( University of Pennsylvania , Philadelphia , Pennsylvania , United States )
- Monteiro, Joao ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Guo, Hongchao ( University of Utah , Salt Lake , Utah , United States )
- Galls, Drew ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Gu, Wenduo ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Cheng, Paul ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Ramste, Markus ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
- Li, Daniel ( Stanford University , Stanford , California , United States )
Meeting Info:
Session Info:
Louis N. and Arnold M. Katz Basic Science Research Prize for Early Career Investigators Competition
Saturday, 11/16/2024 , 01:30PM - 02:45PM
Abstract Oral Session
More abstracts on this topic:
Dai Zhiyu, Yi Dan, Zhao Hanqiu, Hong Jason, Fallon Michael
A Loss of Function Polymorphism in the Propeptide of Lysyl Oxidase Exacerbates AtherosclerosisJung In-hyuk, Amrute Junedh, Luna Sophia, Wagoner Ryan, Lee Paul, Burks Kendall, Holloway Karyn, Alisio Arturo, Stitziel Nathan
More abstracts from these authors:
Weldy Chad, Zhao Quanyi, Sharma Disha, Nguyen Trieu, Kundu Ramendra, Fischbein Michael, Engreitz Jesse, Kundaje Anshul, Cheng Paul, Quertermous Thomas, Kundu Soumya, Monteiro Joao, Gu Wenduo, Pedroza Albert, Dalal Alex, Worssam Matthew, Li Daniel, Palmisano Brian
Discrete Population of Rare SMC Progenitors Gives Rise Exclusively to the Fibrous CapGu Wenduo, Monteiro Joao, Kumar Maya, Quertermous Thomas, Cheng Paul, Jackson William, Zhu Ashley, Li Daniel, Zhao Quanyi, Nguyen Trieu, Worssam Matthew, Ramste Markus, Weldy Chad