Final ID: MDP813
The Histone Methyltransferase MLL1 Regulates Notch Signaling and T Cell Phenotype During Pathologic Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Development
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Objective: Abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) are characterized by pathological vascular remodeling and an imbalance between anti-inflammatory regulatory TH cells (Tregs) and pro-inflammatory TH17 cells within the aortic wall. The mechanisms regulating CD4+TH cell differentiation during AAA development remain unknown. Recently, the histone methyltransferase, mixed lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1), has been shown to influence TH cell phenotype by directly altering key transcription factors for TH17 (RORγ) and Treg (FOXp3) differentiation in varying disease states. As such the objective of this study was to evaluate the role of MLL1 in promoting TH17 activity within AAA development and to determine key TH17 cell signaling pathways that are altered
Methods: Single-cell sequencing was conducted on human AAAs and control tissue samples. For our murine model, C57BL/6 mice were injected with an AAV encoding a PCSK9 gain-of-function mutation and fed a saturated fat diet followed by either AngII infusion to induce AAAs (1 µg/kg/min) or saline. Mice with T-cell specific deletion of Notch1 signaling (Notch1f/fCD4cre+) or MLL1 (Mll1f/fCD4cre+) were subjected to the AngII-induced AAA model and AAA diameters quantified. CD4+ T-cells were isolated by MACs and gene expression analyzed by qPCR as well as T-cell phenotype by flow cytometry. ChIP was used to evaluate histone 3 lysine trimethylation (H3K4me3).
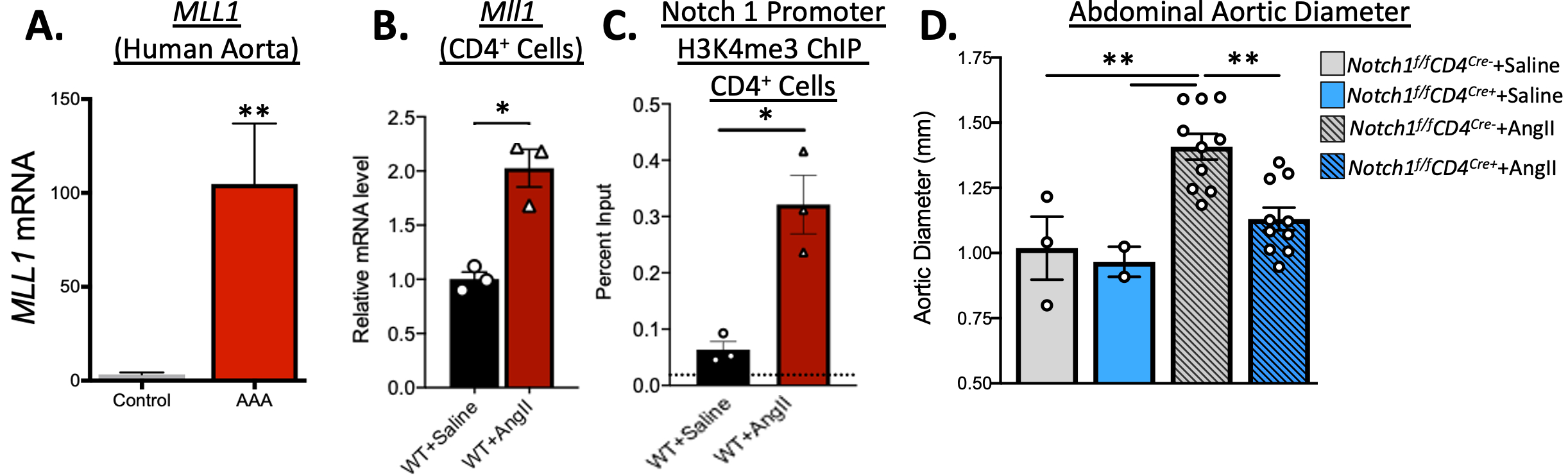
Results: Single-cell RNA sequencing of human aortic tissue revealed that the epigenetic enzyme MLL1 and Notch1 signaling were profoundly upregulated in human AAA CD4+ cells compared to non-aneurysmal control samples. Congruently, CD4+TH cells isolated from the murine AngII-induced AAA model displayed a predominance of TH17 phenotype and elevated expression of MLL1. Histone methylation was evaluated by ChIP in AngII-induced AAA CD4+ cells and demonstrated increased levels of the MLL1-mediated activation histone methylation mark, H3K4me3, on the Notch 1 promoter. Mice deficient in CD4+ TH cell Notch signaling (Notch1f/fCD4cre+) or MLL1 (Mll1f/fCD4cre+) subjected to the AngII-induced murine model displayed significant reduction AAA development (n=10/group, p<0.05) with decreased CD4+ TH17 cell activity and reciprocal increase in Treg expression.
Conclusions: MLL1, a histone methyltransferase, regulates Notch1 signaling and T-cell differentiation in AAA development, causing pathologic inflammation. This pathway may serve as a potential therapeutic target to prevent aortic dilation.
Methods: Single-cell sequencing was conducted on human AAAs and control tissue samples. For our murine model, C57BL/6 mice were injected with an AAV encoding a PCSK9 gain-of-function mutation and fed a saturated fat diet followed by either AngII infusion to induce AAAs (1 µg/kg/min) or saline. Mice with T-cell specific deletion of Notch1 signaling (Notch1f/fCD4cre+) or MLL1 (Mll1f/fCD4cre+) were subjected to the AngII-induced AAA model and AAA diameters quantified. CD4+ T-cells were isolated by MACs and gene expression analyzed by qPCR as well as T-cell phenotype by flow cytometry. ChIP was used to evaluate histone 3 lysine trimethylation (H3K4me3).
Results: Single-cell RNA sequencing of human aortic tissue revealed that the epigenetic enzyme MLL1 and Notch1 signaling were profoundly upregulated in human AAA CD4+ cells compared to non-aneurysmal control samples. Congruently, CD4+TH cells isolated from the murine AngII-induced AAA model displayed a predominance of TH17 phenotype and elevated expression of MLL1. Histone methylation was evaluated by ChIP in AngII-induced AAA CD4+ cells and demonstrated increased levels of the MLL1-mediated activation histone methylation mark, H3K4me3, on the Notch 1 promoter. Mice deficient in CD4+ TH cell Notch signaling (Notch1f/fCD4cre+) or MLL1 (Mll1f/fCD4cre+) subjected to the AngII-induced murine model displayed significant reduction AAA development (n=10/group, p<0.05) with decreased CD4+ TH17 cell activity and reciprocal increase in Treg expression.
Conclusions: MLL1, a histone methyltransferase, regulates Notch1 signaling and T-cell differentiation in AAA development, causing pathologic inflammation. This pathway may serve as a potential therapeutic target to prevent aortic dilation.
More abstracts on this topic:
Comparative Outcomes of Local-Regional Versus General Anesthesia in Endovascular Aortic Aneurysm Repair: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Queiroz Ivo, Mulatti Grace, Mesquita Cynthia, Barbosa Lucas, Fernandez Miguel, Diaz Braiana, Pimentel Junior Dilson, Monteiro Mastra Fontoura Milena, Bertolino Enrico, Tavares Arthur
A multi-proteomic Risk Score Predicts Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Angina and Non-obstructive Coronary Artery DiseaseHuang Jingwen, Lodhi Rafia, Lodhi Saleha, Eldaidamouni Ahmed, Hritani Wesam, Hasan Muhammet, Haroun Nisreen, Quyyumi Arshed, Mehta Puja, Leon Ana, Ko Yi-an, Yang Huiying, Medina-inojosa Jose, Ahmed Taha, Harris Kristen, Alkhoder Ayman, Al Kasem Mahmoud