Final ID: Mo2004
Stethoscopes to Sequencers: How Next Generation Sequencing Aids Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Diagnosis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Despite a high burden of rare genetic diseases among children admitted to cardiac intensive care units (CICUs), comprehensive guidelines for genetic testing in children with heart disease, particularly those that are critically ill, are lacking. Traditional testing methods, such as karyotype, chromosomal microarray (CMA) and candidate gene panels, are often employed based on suspected diagnoses. Rapid advancements in next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies allow for more comprehensive genetic evaluation which is already recommended for patients with ventricular dysfunction, primary arrhythmias, and pulmonary hypertension (PH). Broad application of NGS in intensive care settings for pediatric heart disease has not been extensively investigated.
Aims: Evaluate diagnostic efficacy of NGS in critically ill pediatric patients with cardiac disease.
Methods: Retrospective cohort of patients who underwent exome or genome sequencing in a pediatric CICU between January 2020 and August 2023.
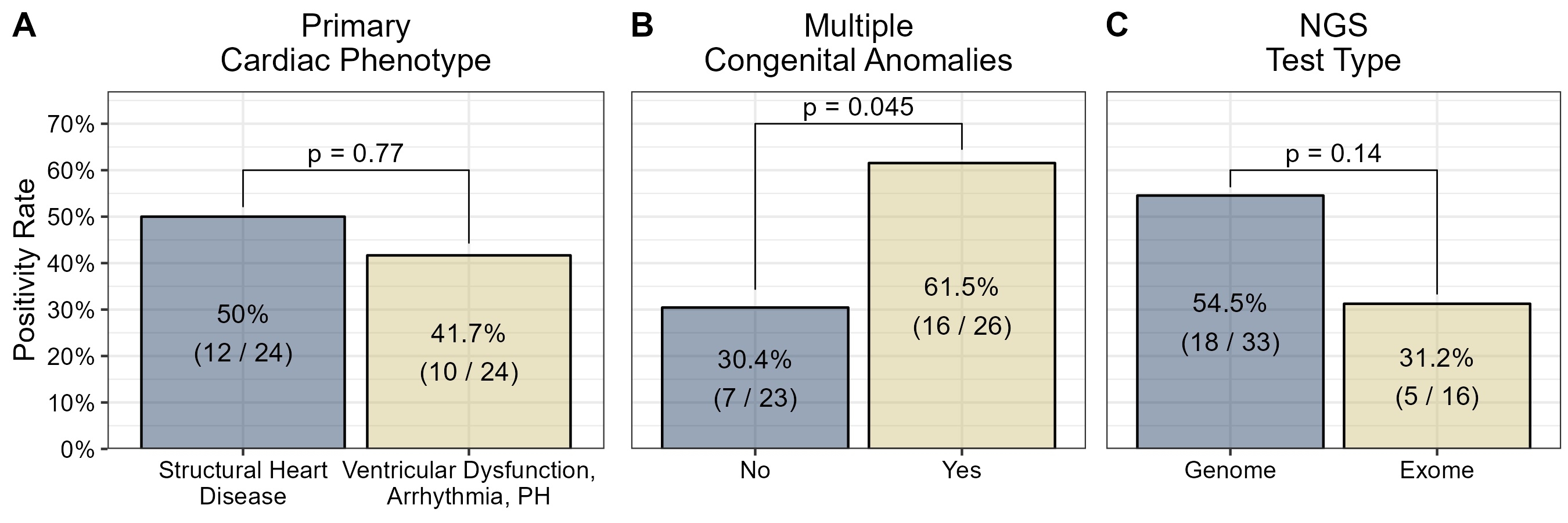
Results: Exome or genome sequencing was performed on 49 patients with median testing age of 46 days (IQR 7-609). Primary cardiac phenotypes included congenital heart disease, ventricular dysfunction, arrhythmia, and PH. Forty-two pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants were identified and 23 (46.9%) resulted in a genetic diagnosis, of those, 16 (69.6%) were associated with a cardiac phenotype. Positivity rate did not differ between primary cardiac phenotypes but was significantly higher when the patient had associated multiple congenital anomalies (Fig. 1). Genome sequencing trended towards a higher positivity rate (54.5%) than exome (31.3%), though did not meet statistical significance (Fig. 1). Notably, 84.6% and 38.5% of the identified pathogenic variants would have remained undetectable by CMA and many commercially available gene panels, respectively.
Conclusion: Exome and genome sequencing demonstrate high diagnostic yield across isolated and non-isolated cardiac disease and various cardiac phenotypes with diagnostic efficacy surpassing CMA and many commercial gene panels. As NGS technologies evolve, they promise to streamline diagnoses and enhance therapeutic decision-making for this patient population.
Aims: Evaluate diagnostic efficacy of NGS in critically ill pediatric patients with cardiac disease.
Methods: Retrospective cohort of patients who underwent exome or genome sequencing in a pediatric CICU between January 2020 and August 2023.
Results: Exome or genome sequencing was performed on 49 patients with median testing age of 46 days (IQR 7-609). Primary cardiac phenotypes included congenital heart disease, ventricular dysfunction, arrhythmia, and PH. Forty-two pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants were identified and 23 (46.9%) resulted in a genetic diagnosis, of those, 16 (69.6%) were associated with a cardiac phenotype. Positivity rate did not differ between primary cardiac phenotypes but was significantly higher when the patient had associated multiple congenital anomalies (Fig. 1). Genome sequencing trended towards a higher positivity rate (54.5%) than exome (31.3%), though did not meet statistical significance (Fig. 1). Notably, 84.6% and 38.5% of the identified pathogenic variants would have remained undetectable by CMA and many commercially available gene panels, respectively.
Conclusion: Exome and genome sequencing demonstrate high diagnostic yield across isolated and non-isolated cardiac disease and various cardiac phenotypes with diagnostic efficacy surpassing CMA and many commercial gene panels. As NGS technologies evolve, they promise to streamline diagnoses and enhance therapeutic decision-making for this patient population.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Rare Association of Darier’s Disease and Dilated Cardiomyopathy: A Case Report Exploring the Cardiac Implications of ATP2A2 Mutation
Jacob Nidhi
Aberrant Regulation of endMT in Turner Syndrome: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Congenital Cardiovascular DiseaseGarcia Huitron Eric Ivan, Zhang Xiaoying, Babcock Lance, Grande-allen Kathryn, Prakash Siddharth