Final ID: MDP1296
Inflammation-related 5-hydroxymethylation signatures as markers for clinical presentations of coronary artery disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Coronary angiography, an invasive method, remains the gold standard technique for coronary artery disease (CAD) diagnosis in clinical practice. However, due to its invasive nature, it cannot be used for mass population screening. There is an urgent need in the clinical to identify new liquid biopsy molecular markers for screening patients with CAD.
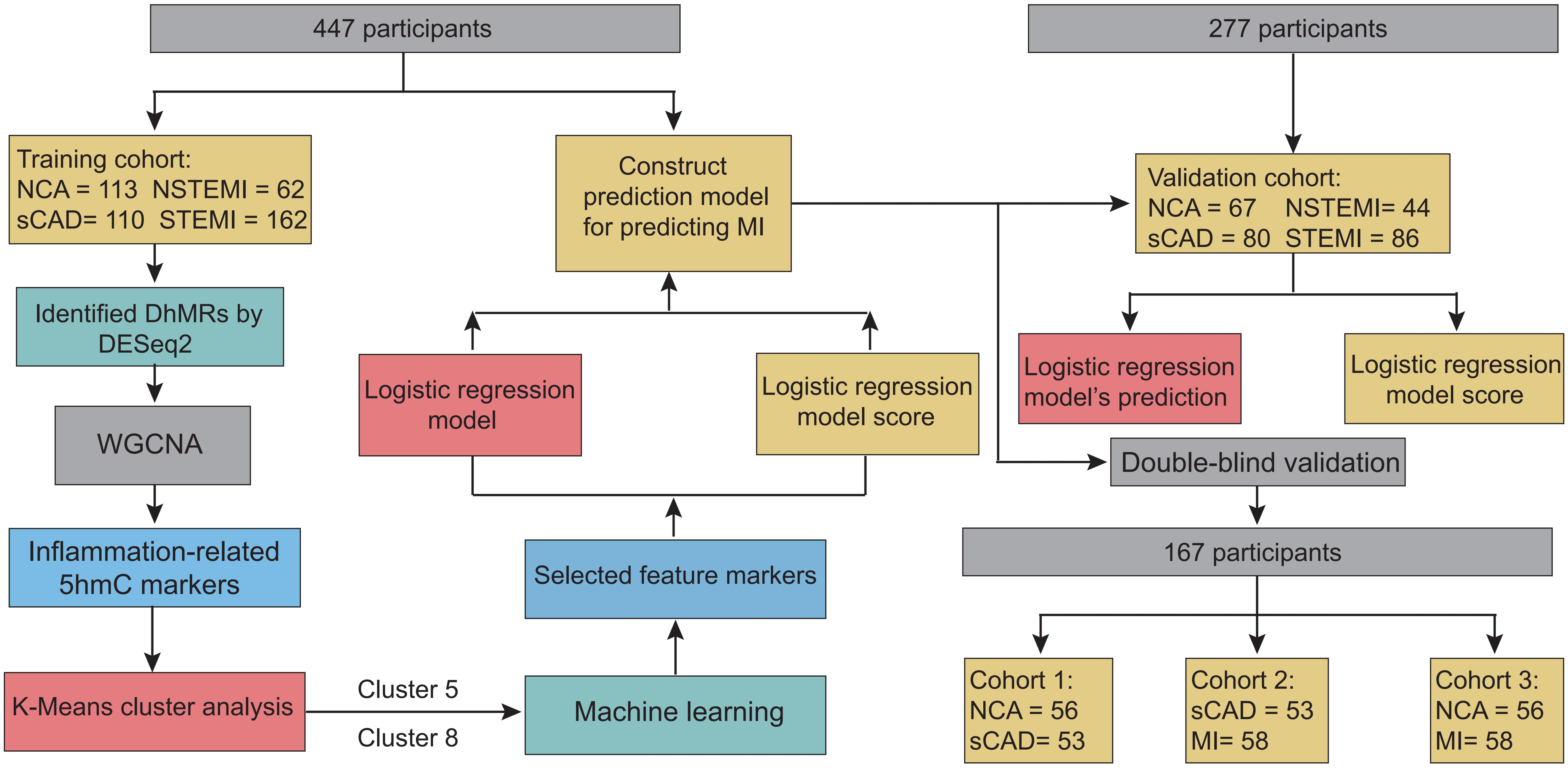
Methods: We utilized 5hmC-Seal to generate genome-wide 5hmC profiles in plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from 724 CAD patients. To investigate the correlation between 5hmC modifications and CAD, we separated patients into training and validation cohorts and developed a 5hmC-based logistic regression model from the training cohort to predict CAD patients in the validation cohort. Furthermore, we incorporated an external cohort comprising 167 samples to validate the reliability of our model.
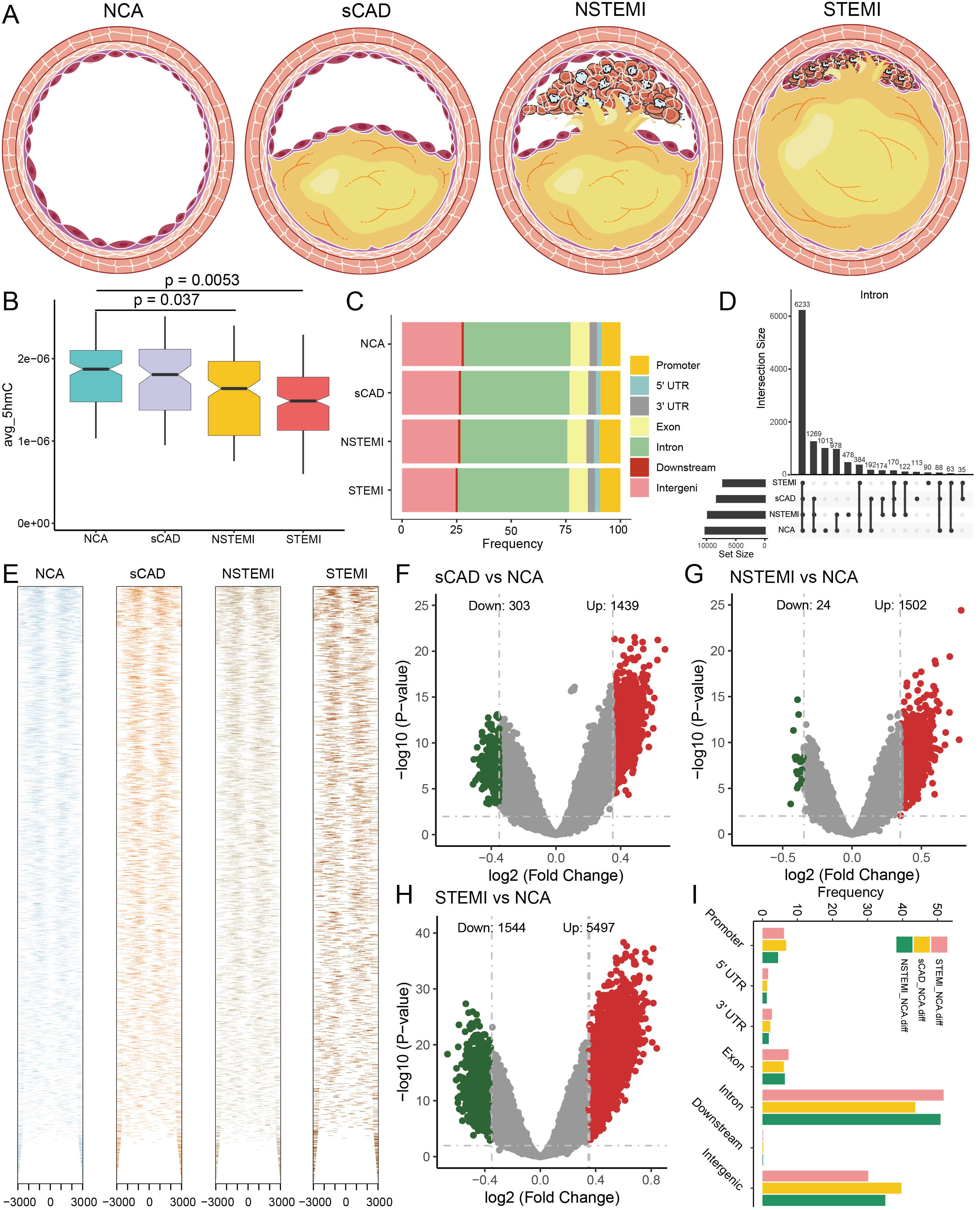
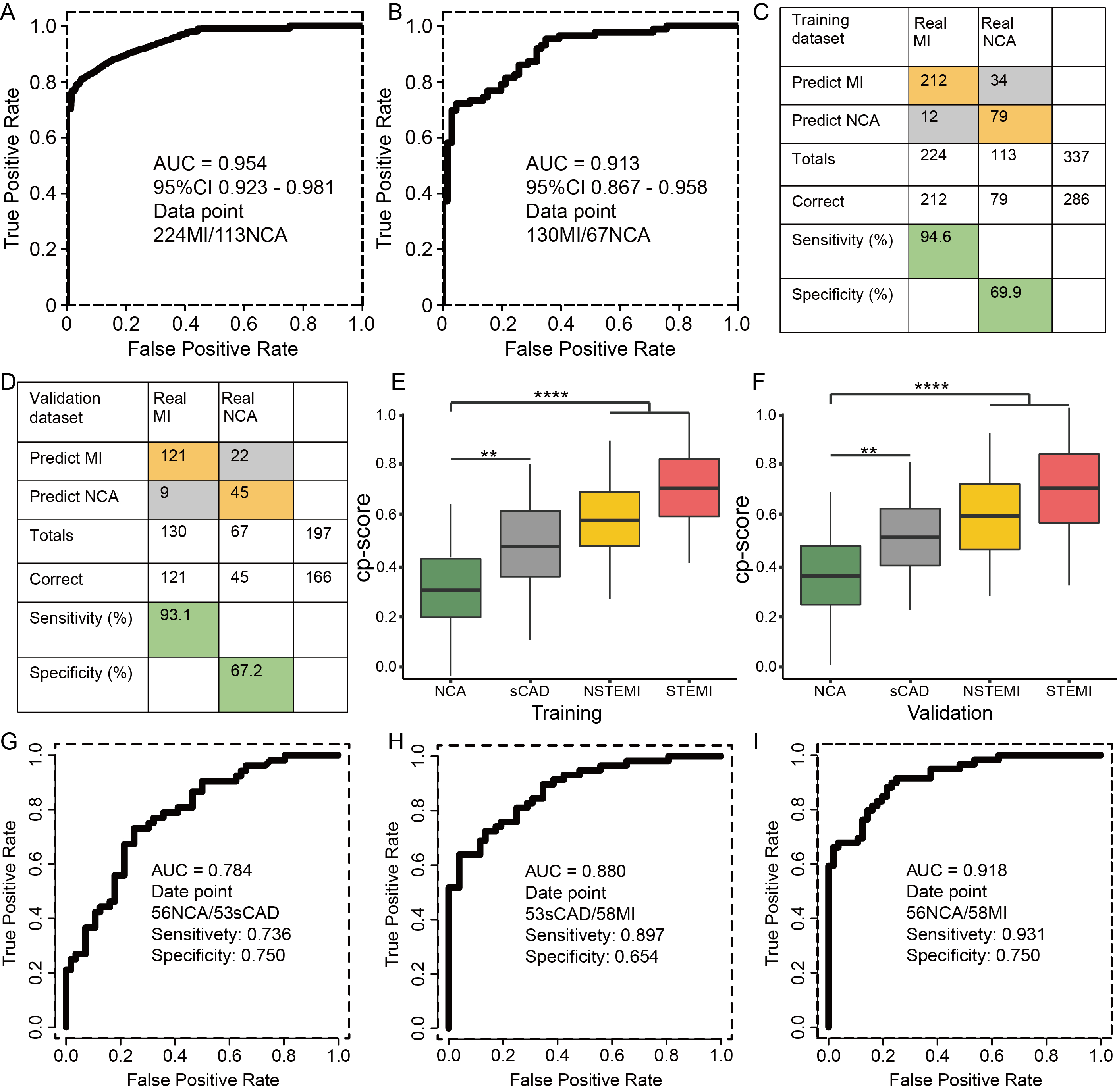
Results: We found that the differentially hydroxymethylated genes (DhMGs) in people with the normal coronary artery (NCA), nonfatal stable CAD (sCAD), non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), as well as ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) enriched in neutrophil-mediated inflammatory response pathways, and inflammation-related DhMGs can reflect the progression of atherosclerotic plaque. Furthermore, we used machine learning algorithms to develop a predictive model for predicting the occurrence of myocardial infarction (MI) based on 19 inflammatory markers, and the predictive model could effectively predict MI (NSTEMI and STEMI) (AUC = 0.913). Simultaneously, our model has demonstrated strong performance in external validation.
Conclusions: We have identified a novel biomarker, the inflammation-associated 5hmC markers, which can reflect the clinical manifestations of CAD and can effectively predict the occurrence of MI.
Methods: We utilized 5hmC-Seal to generate genome-wide 5hmC profiles in plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from 724 CAD patients. To investigate the correlation between 5hmC modifications and CAD, we separated patients into training and validation cohorts and developed a 5hmC-based logistic regression model from the training cohort to predict CAD patients in the validation cohort. Furthermore, we incorporated an external cohort comprising 167 samples to validate the reliability of our model.
Results: We found that the differentially hydroxymethylated genes (DhMGs) in people with the normal coronary artery (NCA), nonfatal stable CAD (sCAD), non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), as well as ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) enriched in neutrophil-mediated inflammatory response pathways, and inflammation-related DhMGs can reflect the progression of atherosclerotic plaque. Furthermore, we used machine learning algorithms to develop a predictive model for predicting the occurrence of myocardial infarction (MI) based on 19 inflammatory markers, and the predictive model could effectively predict MI (NSTEMI and STEMI) (AUC = 0.913). Simultaneously, our model has demonstrated strong performance in external validation.
Conclusions: We have identified a novel biomarker, the inflammation-associated 5hmC markers, which can reflect the clinical manifestations of CAD and can effectively predict the occurrence of MI.
More abstracts on this topic:
Apabetalone Protects Against Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction by Suppressing Myocardial Inflammation
Costantino Sarah, Nazha Hamdani, Paneni Francesco, Gorica Era, Mohammed Shafeeq, Telesca Marialucia, Mongelli Alessia, Masciovecchio Valeria, Herwig Melissa, Ambrosini Samuele, Ruschitzka Frank
A Nationwide Italian Network for the Clinical and Genetic Diagnosis of Familial Dyslipidemias: The LIPIGEN registryCasula Manuela, Galimberti Federica, Olmastroni Elena, Arca Marcello, Averna Maurizio, Catapano Alberico