Final ID: MDP1259
SIRTUIN5 Modulates Na+/Ca2+ Handling Via Oxidative Stress Dependent Manner In Mouse Heart
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background: The cardiac Na+ channel NaV1.5 (encoded by SCN5A) governs cardiac inward Na+ current (INa) and the fast upstroke and plateau phases of the cardiac action potential. Mutations in NaV1.5 can cause acquired or inherited arrhythmias and conduction diseases, including ~20% of cases of Brugada Syndrome (BrS). Changes in INa can impact Ca2+ handling and cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. We have previously shown that SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of NaV1.5 increased INa. Recently, potential mutations (including P114T) in SIRT5, another NAD+-dependent deACYLase in the Sirtuin family localized to mitochondria, were identified in small families with BrS.
Hypothesis: Sirt5 dysfunction evokes arrhythmias via Na+ and Ca2+ mishandling in an oxidative stress-dependent manner in mouse hearts.
Aims: To explore the potential role of SIRT5 in BrS using heterologous expression systems and homozygous P114T-Sirt5 knock-in (P114T-KI) mice.
Methods: Protein expression and physical interactions were detected by immunoprecipitation and immunoblot. The effects of SIRT5 on Na+ current was measured using patch clamp in HEK cells and mouse cardiac myocytes. Confocal microscopy was used to measure reactive oxygen species (ROS) and for Ca2+ imaging.
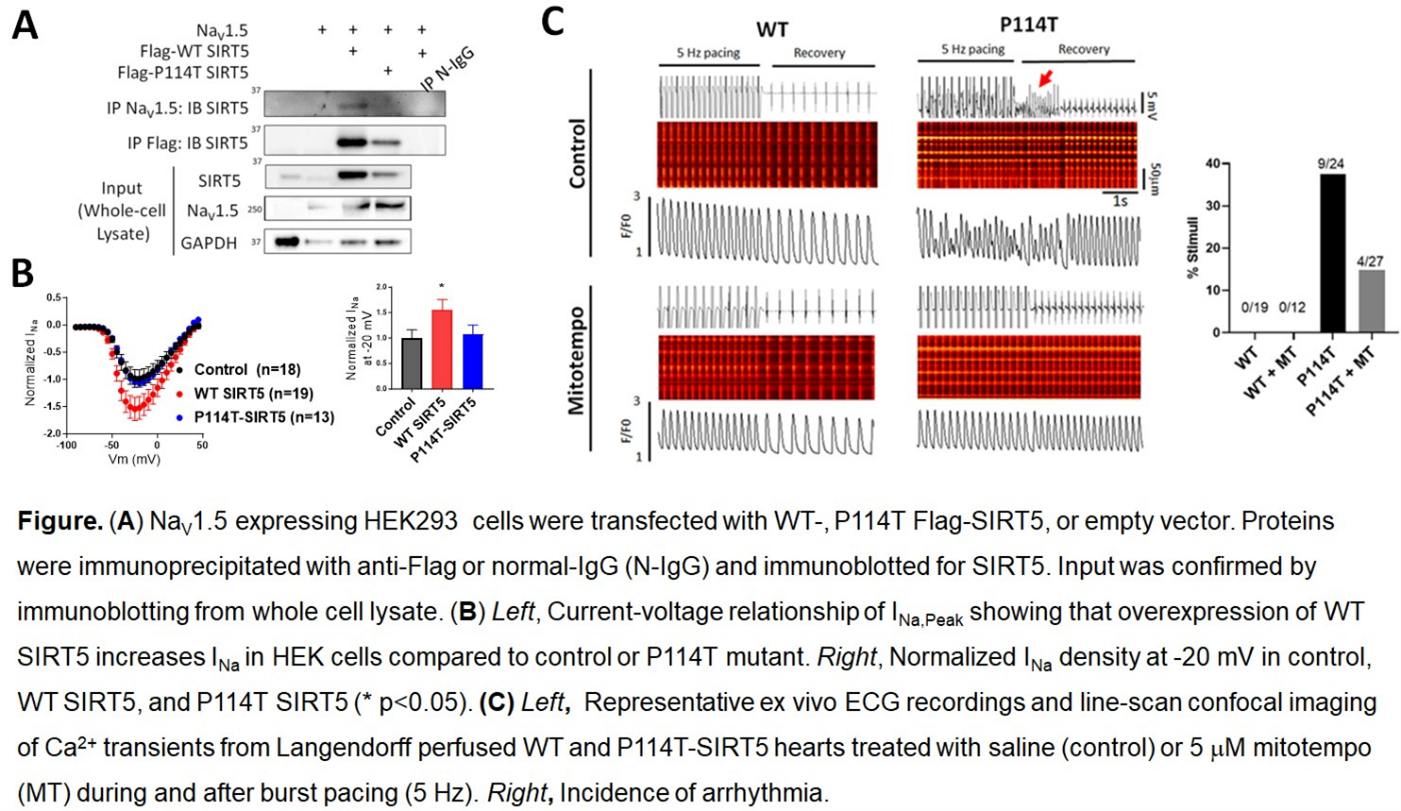
Results: Both WT and P114T-SIRT5 co-immunoprecipitate with NaV1.5, but WT increased peak INa in HEK cells while P114T did not (Fig A,B). Live-cell staining using DCFDA or mitoSOX showed that P114T-KI hearts had increased basal ROS and were more sensitive to oxidative stress induced by H2O2 than WT littermates. P114T-KI hearts had increased Na+/Ca2+ exchange protein 1 (NCX1) expression, and Langendorff-perfused hearts displayed abnormal Ca2+ handling and arrhythmias (Fig C). Notably, treatment with the mitochondrial ROS scavenger mitotempo mitigated the aberrant Ca2+ handling and arrhythmias.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that the P114T-SIRT5 causes abnormal Na+ and Ca2+ handling and arrhythmias in a ROS-dependent manner, highlighting potential mechanisms underlying BrS. This finding may pave the way for the use of SIRT5 or its activators as novel anti-arrhythmic therapies in the future.
Background: The cardiac Na+ channel NaV1.5 (encoded by SCN5A) governs cardiac inward Na+ current (INa) and the fast upstroke and plateau phases of the cardiac action potential. Mutations in NaV1.5 can cause acquired or inherited arrhythmias and conduction diseases, including ~20% of cases of Brugada Syndrome (BrS). Changes in INa can impact Ca2+ handling and cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. We have previously shown that SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of NaV1.5 increased INa. Recently, potential mutations (including P114T) in SIRT5, another NAD+-dependent deACYLase in the Sirtuin family localized to mitochondria, were identified in small families with BrS.
Hypothesis: Sirt5 dysfunction evokes arrhythmias via Na+ and Ca2+ mishandling in an oxidative stress-dependent manner in mouse hearts.
Aims: To explore the potential role of SIRT5 in BrS using heterologous expression systems and homozygous P114T-Sirt5 knock-in (P114T-KI) mice.
Methods: Protein expression and physical interactions were detected by immunoprecipitation and immunoblot. The effects of SIRT5 on Na+ current was measured using patch clamp in HEK cells and mouse cardiac myocytes. Confocal microscopy was used to measure reactive oxygen species (ROS) and for Ca2+ imaging.
Results: Both WT and P114T-SIRT5 co-immunoprecipitate with NaV1.5, but WT increased peak INa in HEK cells while P114T did not (Fig A,B). Live-cell staining using DCFDA or mitoSOX showed that P114T-KI hearts had increased basal ROS and were more sensitive to oxidative stress induced by H2O2 than WT littermates. P114T-KI hearts had increased Na+/Ca2+ exchange protein 1 (NCX1) expression, and Langendorff-perfused hearts displayed abnormal Ca2+ handling and arrhythmias (Fig C). Notably, treatment with the mitochondrial ROS scavenger mitotempo mitigated the aberrant Ca2+ handling and arrhythmias.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that the P114T-SIRT5 causes abnormal Na+ and Ca2+ handling and arrhythmias in a ROS-dependent manner, highlighting potential mechanisms underlying BrS. This finding may pave the way for the use of SIRT5 or its activators as novel anti-arrhythmic therapies in the future.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Beta Tubulin Mutation Suppresses Arrhythmias and Improves Connexin 43 Localization in Heart of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Mice
Zhou Delong, Liu Tong, Yehia Ghassan, Romanienko Peter, Rodney George, Wehrens Xander, Lampe Paul, Gourdie Robert, Xie Lai-hua, Fraidenraich Diego, Nouet Julie, Mesa Elam, Yegneshwaran Vasisht, Geukgeuzian Geovanni, Adibemma Ifeanyichukwu, Nandakumar Swetha, Ramirez Edwin, Li Hong
Admission and Discharge B-Natriuretic Peptide Profiles Are Predictive of 1-Year Mortality Above Intermountain Risk Score in Heart Failure PhenotypesSanchez Pablo, Odonnell Christian, Bagherzadeh Shadi, Celestin Bettia, Santana Everton, Bair Tami, Haddad Francois, Horne Benjamin