Final ID: MDP469
Traditional Risk Factors, Cardiovascular Health, and Elevated Lipoprotein(a): The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: One in five individuals have elevated lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)], an inheritable risk factor that is causally associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Whether individuals with elevated Lp(a) derive similar benefit from control of ASCVD risk factors has not been well-studied.
Hypothesis: The magnitude of benefit associated with optimal cardiovascular health will be similar across the spectrum of Lp(a).
Aim: To assess the association of traditional risk factor burden and Life’s Simple 7 (LS7) score with incident ASCVD across Lp(a) values.
Methods: We studied 6,676 participants from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis who underwent Lp(a) testing and were followed for incident ASCVD events (coronary heart disease and stroke). Elevated Lp(a) was defined as >50 mg/dL. As defined by the American Heart Association, LS7 metrics included smoking, physical activity, body mass index, diet, total cholesterol, blood pressure, and glucose. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression assessed the association of traditional risk factor burden and LS7 score (poor: 0-8, average: 9-10, optimal: 11-14) with incident ASCVD for individuals with and without elevated Lp(a) during a median follow-up of 17.7 years.
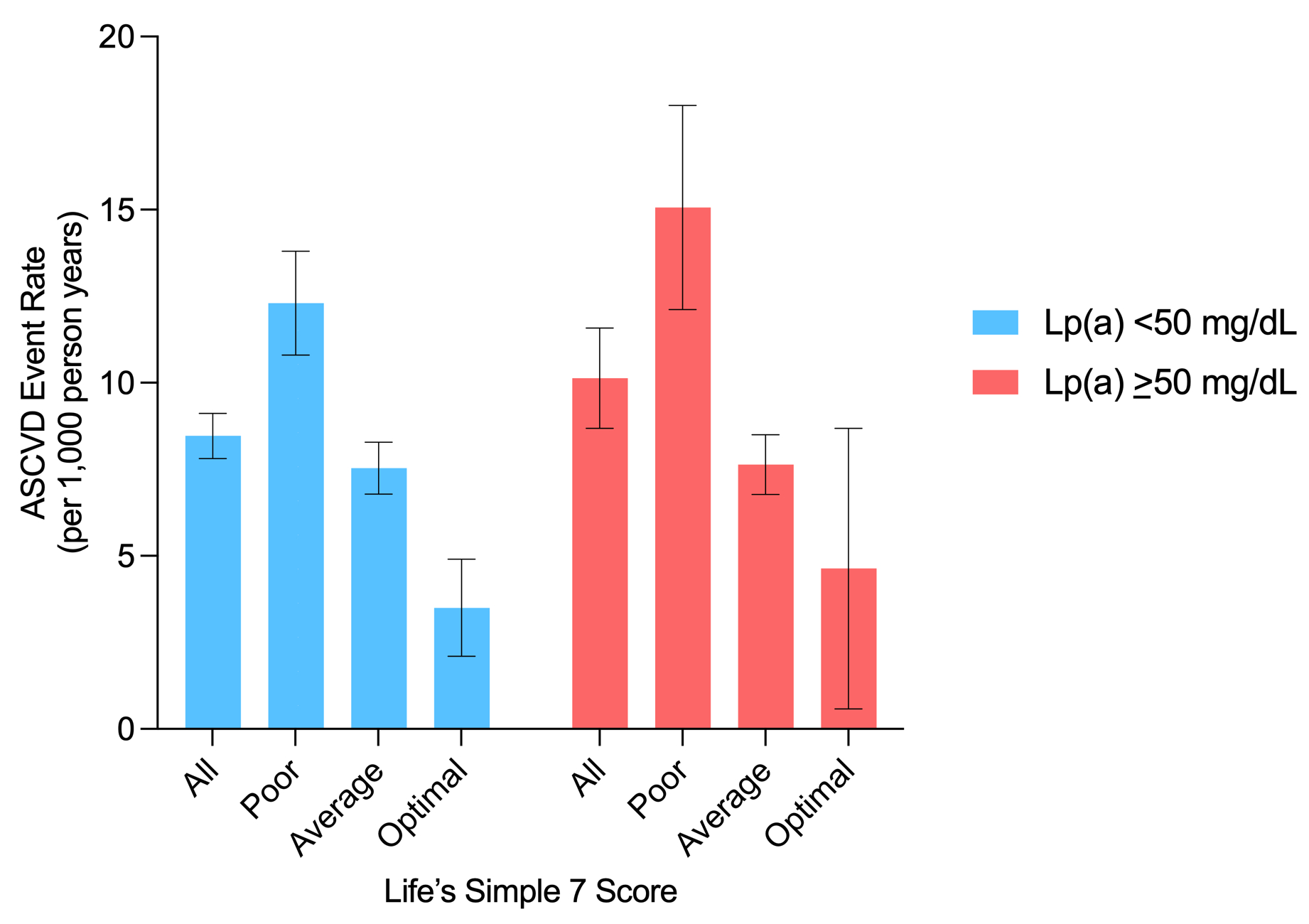
Results: The mean age was 62.1 years, 53% were women, and 61% were non-white. The median Lp(a) was 17 mg/dL and 20% had Lp(a) >50 mg/dL. Individuals with Lp(a) >50 mg/dL had the highest burden of traditional risk factors except cigarette smoking. Compared to those with a poor LS7 score, those with an optimal LS7 score had a lower ASCVD risk that was significant for participants with Lp(a) <50 mg/dL (HR=0.37, 95% CI: 0.25-0.55), but borderline significant for participants with Lp(a) >50 mg/dL (HR=0.41, 95% CI: 0.16-1.02). Individuals with Lp(a) >50 mg/dL had the highest absolute event rates across all LS7 categories, and there was no significant interaction between Lp(a) and LS7 score on incident ASCVD (p-interaction=0.64, Figure).
Conclusions: Participants with an optimal LS7 score had similar reduction in ASCVD risk regardless of their Lp(a) burden. These results emphasize the importance of a healthy lifestyle and ASCVD risk factor control among patients with elevated Lp(a).
Hypothesis: The magnitude of benefit associated with optimal cardiovascular health will be similar across the spectrum of Lp(a).
Aim: To assess the association of traditional risk factor burden and Life’s Simple 7 (LS7) score with incident ASCVD across Lp(a) values.
Methods: We studied 6,676 participants from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis who underwent Lp(a) testing and were followed for incident ASCVD events (coronary heart disease and stroke). Elevated Lp(a) was defined as >50 mg/dL. As defined by the American Heart Association, LS7 metrics included smoking, physical activity, body mass index, diet, total cholesterol, blood pressure, and glucose. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression assessed the association of traditional risk factor burden and LS7 score (poor: 0-8, average: 9-10, optimal: 11-14) with incident ASCVD for individuals with and without elevated Lp(a) during a median follow-up of 17.7 years.
Results: The mean age was 62.1 years, 53% were women, and 61% were non-white. The median Lp(a) was 17 mg/dL and 20% had Lp(a) >50 mg/dL. Individuals with Lp(a) >50 mg/dL had the highest burden of traditional risk factors except cigarette smoking. Compared to those with a poor LS7 score, those with an optimal LS7 score had a lower ASCVD risk that was significant for participants with Lp(a) <50 mg/dL (HR=0.37, 95% CI: 0.25-0.55), but borderline significant for participants with Lp(a) >50 mg/dL (HR=0.41, 95% CI: 0.16-1.02). Individuals with Lp(a) >50 mg/dL had the highest absolute event rates across all LS7 categories, and there was no significant interaction between Lp(a) and LS7 score on incident ASCVD (p-interaction=0.64, Figure).
Conclusions: Participants with an optimal LS7 score had similar reduction in ASCVD risk regardless of their Lp(a) burden. These results emphasize the importance of a healthy lifestyle and ASCVD risk factor control among patients with elevated Lp(a).
More abstracts on this topic:
A Quarter Century of Mortality Trends in Hypertension and Sick Sinus Syndrome Among Elderly in the United States
Eltawansy Sherif, Khan Muhammad, Iqbal Asad, Sharif Aleena, Hossain Mohammad, Ali Muhammad Faizan, Ahmad Husnain, Faizan Muhammad, Ahmed Ashraf, Abdul Malik Mohammad Hamza Bin, Pahwani Ritesh, Patel Rahul, Mehdi Hassan
A Blood(y) Pressure Crisis: Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage as a Rare Manifestation of Severely Uncontrolled HypertensionNandyal Shreyas, Amdetsion Gedion Yilma, Varma Revati, Kohli Saksham, Hammo Hasan