Final ID: 4122301
The Role of Hepatic CDS2 in Phosphatidylinositol Homeostasis and Lipid Metabolism
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Recent studies in both human genetics and mouse models have highlighted the significance of phosphatidylinositol (PI) in the progression of fatty liver disease (FLD). Despite this, the precise mechanisms underlying PI's role remain elusive.
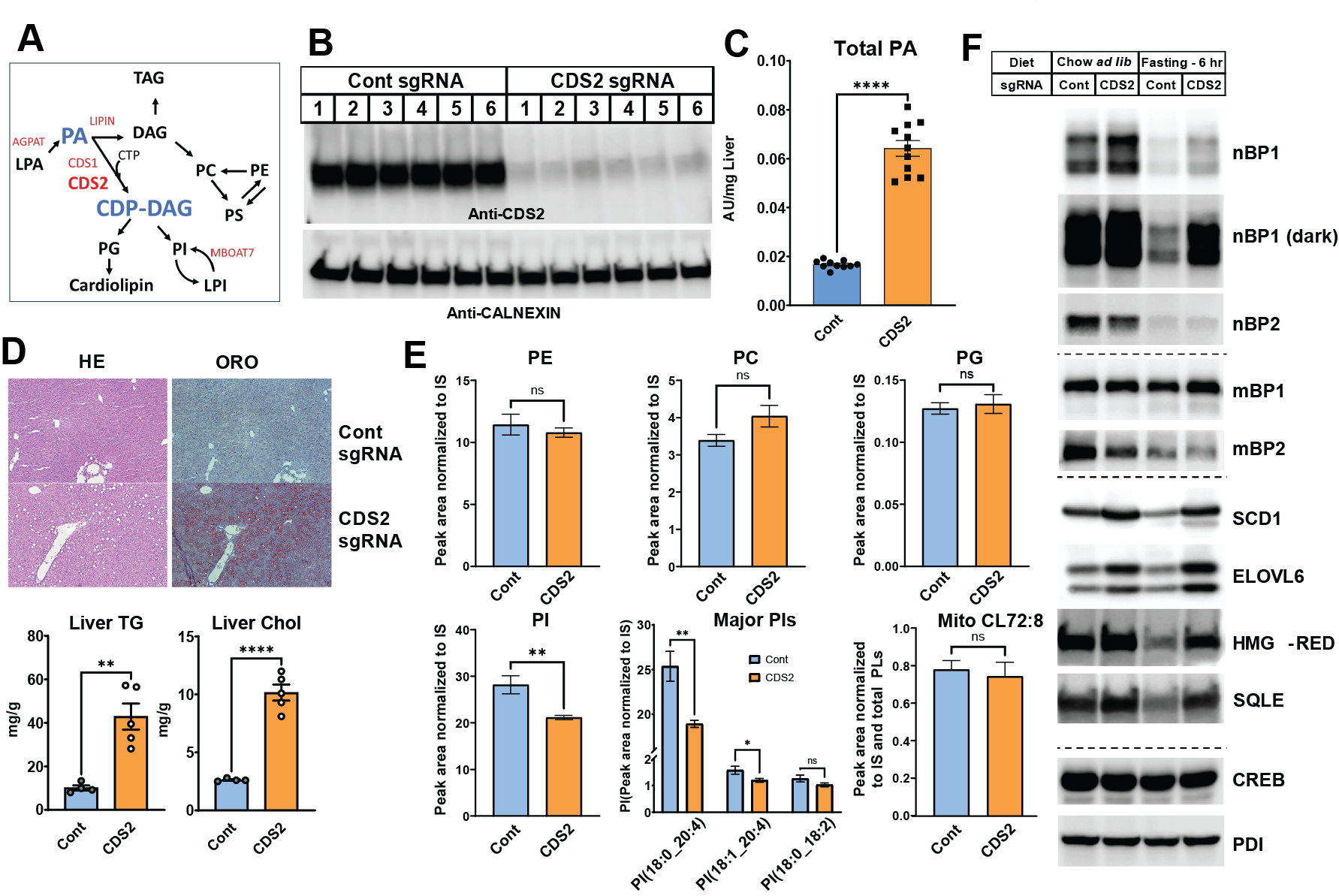
Aims: This study aimed to elucidate the involvement of PI in FLD by disrupting hepatic PI biosynthesis through modulation of CDP-diacylglycerol synthase 2 (CDS2) expression, the primary enzyme in PI biosynthesis (A).
Methods: We generated liver-specific knockouts of CDS2 and SCAP (SREBP cleavage-activating protein) using adeno-associated virus (AAV) expressing sgRNA against each gene. Phospholipid species were analyzed and quantified by LC/MS.
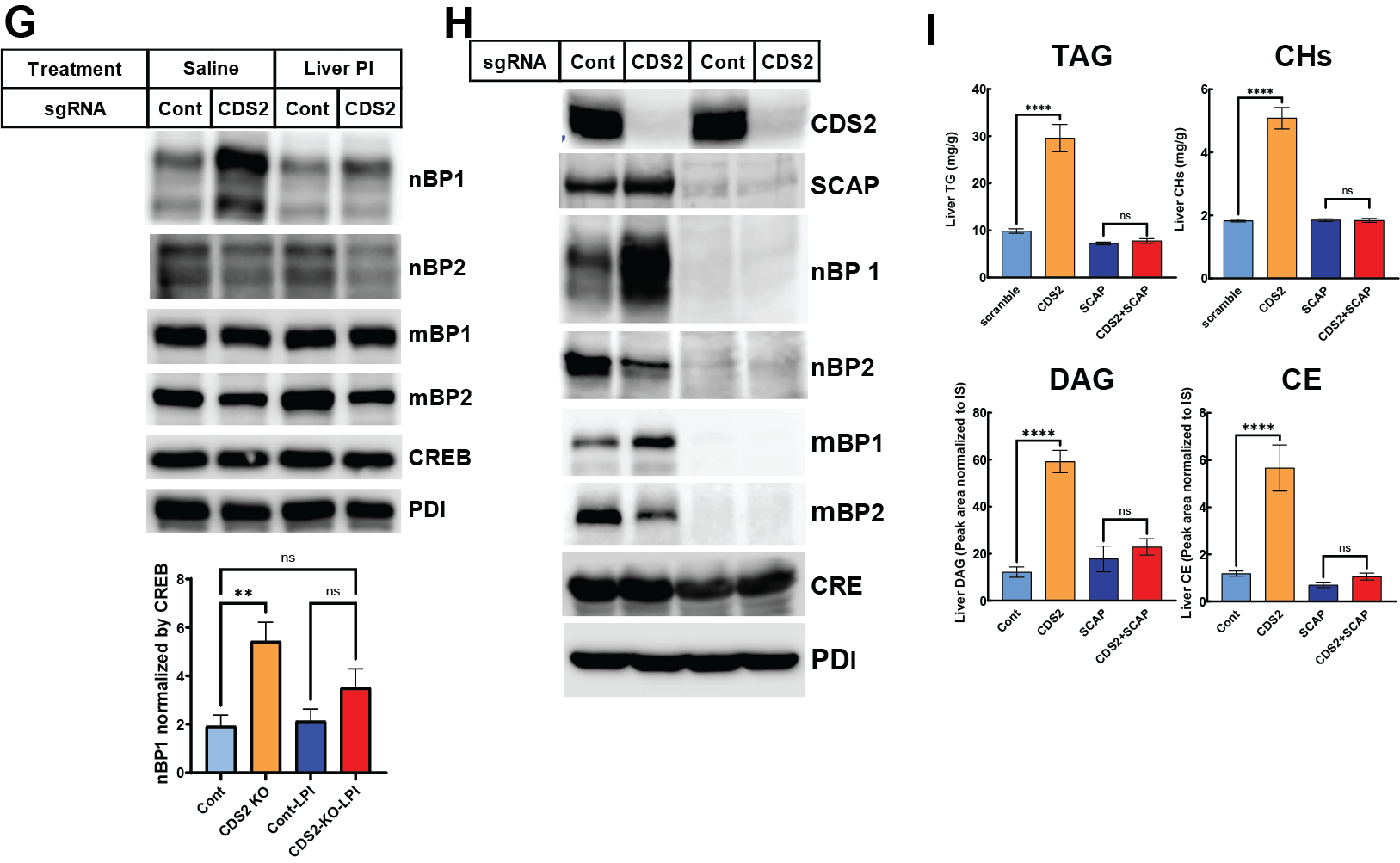
Results: CDS2 liver-specific knockout mice (B, C) exhibited a pronounced development of fatty liver, characterized by elevated triglyceride and cholesterol levels (C). Notably, liver PI levels were significantly reduced in CDS2 knockout mice (E), accompanied by dysregulated activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) even during fasting conditions (F), leading to increased de novo lipogenesis. Intraperitoneal administration of exogenous PI effectively normalized SREBP cleavage (G), highlighting PI's critical role in SREBP regulation. Furthermore, simultaneous knockout of SCAP with CDS2 restored the normal liver phenotype, implicating SREBP activation as a central mechanism underlying fatty liver development in CDS2 knockout mice (H, I).
Conclusion: Deletion of CDS2 in the liver reduced PI levels, subsequently inducing significant fatty liver due to dysregulated SREBP activation. This study underscores the importance of CDS2 in maintaining PI homeostasis, which in turn regulates SREBP activity and lipid metabolism. Our findings provide valuable insights into the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders and offer potential therapeutic strategies for targeting FLD.
Aims: This study aimed to elucidate the involvement of PI in FLD by disrupting hepatic PI biosynthesis through modulation of CDP-diacylglycerol synthase 2 (CDS2) expression, the primary enzyme in PI biosynthesis (A).
Methods: We generated liver-specific knockouts of CDS2 and SCAP (SREBP cleavage-activating protein) using adeno-associated virus (AAV) expressing sgRNA against each gene. Phospholipid species were analyzed and quantified by LC/MS.
Results: CDS2 liver-specific knockout mice (B, C) exhibited a pronounced development of fatty liver, characterized by elevated triglyceride and cholesterol levels (C). Notably, liver PI levels were significantly reduced in CDS2 knockout mice (E), accompanied by dysregulated activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) even during fasting conditions (F), leading to increased de novo lipogenesis. Intraperitoneal administration of exogenous PI effectively normalized SREBP cleavage (G), highlighting PI's critical role in SREBP regulation. Furthermore, simultaneous knockout of SCAP with CDS2 restored the normal liver phenotype, implicating SREBP activation as a central mechanism underlying fatty liver development in CDS2 knockout mice (H, I).
Conclusion: Deletion of CDS2 in the liver reduced PI levels, subsequently inducing significant fatty liver due to dysregulated SREBP activation. This study underscores the importance of CDS2 in maintaining PI homeostasis, which in turn regulates SREBP activity and lipid metabolism. Our findings provide valuable insights into the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders and offer potential therapeutic strategies for targeting FLD.
More abstracts on this topic:
Adherence to Lipid Lowering Therapy among US Veterans with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Ward Rachel, Gaziano Michael, Wellman Helen, Yel Nedim, Young Melissa, Coleman-lopez Mason, Niu Xiaoli, Mcelligott Sean, Gagnon David, Djousse Luc
Association of Triglyceride Glucose-Related Parameters with All-cause mortality and Cardiovascular Disease in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease PatientsChen Yaqin, Zhang Yusha, Wang Fengjiao