Final ID: 4122249
Deletion of macrophage dynamin-related protein 1 exacerbates left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction by impairing mitochondrial quality maintenance machinery
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Macrophage-mediated inflammation plays an important role in the healing process after myocardial infarction (MI). We have previously reported in macrophages that inhibition of dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1), which induces mitochondrial fission, restrains skewing toward inflammatory phenotype. It is, however, obscure whether macrophage Drp1 promotes left ventricular (LV) remodeling after MI.
Aims: The aim of this study is to elucidate the role of macrophage Drp1 in the mechanisms of LV remodeling after MI.
Methods: C57Bl/6J mice specifically deficient Drp1 in Lysozyme-M+ macrophages (Drp1KO) were created by Cre/loxP technology and underwent ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery at 8 to 12 weeks of age.
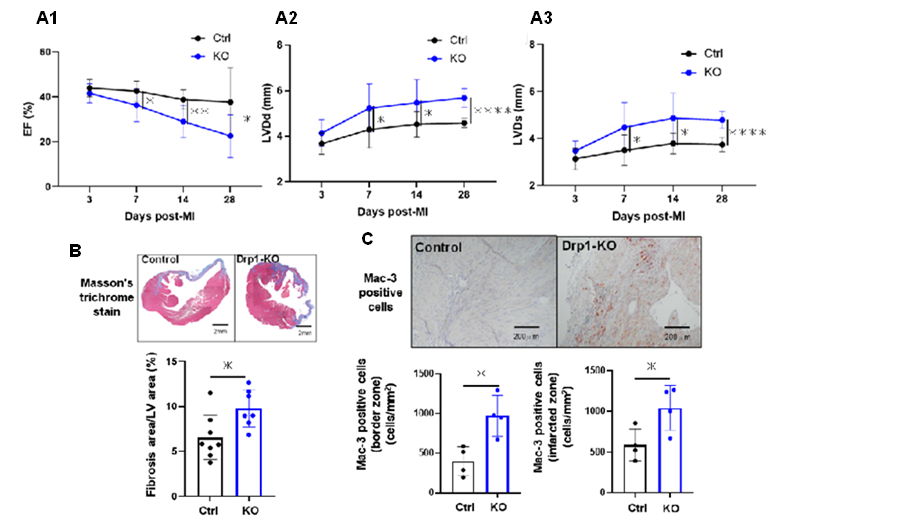
Results: Deletion of macrophage Drp1 decreased LV ejection fraction (38±14 vs. 23±9% at day 28. N=9, p<0.05) and increased LV diameter (LVDd/Ds 5.7±0.4/4.8±0.3 vs. 4.6±0.2/3.7±0.3mm at day 28, N=9, p<0.05) (Figure). Survival rates until 28 days after MI were significantly lower in Drp1KO mice (25 vs. 64%. N=24 and 33, p<0.05). Deletion of Drp1 led to sustained macrophage accumulation and fibrosis of infarcted tissues. TEM revealed that mitophagosomes are decreased in Drp1-deficient macrophages in infarcted hearts. In ex vivo cultured macrophages, siRNA-mediated knockdown of Drp1 impaired mitochondrial fission and LC3-dependent mitophagy. In these macrophages, inhibition of Drp1 by Mdivi-1 for 96 hr, but not for 24 hr, induced mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) leakage to the cytosol accompanied by increased expression of inflammatory cytokines. Hypoxia and starvation, in addition to Mdivi-1, induced leakage of mtDNA and expression of inflammatory cytokines at 24 hr. These results suggest that impairment of mitochondrial quality maintenance machinery causes leakage of mtDNA that induces inflammation.
Conclusions: Macrophage Drp1 protects the heart from sustained inflammation and adverse cardiac remodeling after MI. Drp1-LC3-mediated mitophagy could be a mechanism that maintains mitochondrial quality and prevents excessive inflammation after MI.
Aims: The aim of this study is to elucidate the role of macrophage Drp1 in the mechanisms of LV remodeling after MI.
Methods: C57Bl/6J mice specifically deficient Drp1 in Lysozyme-M+ macrophages (Drp1KO) were created by Cre/loxP technology and underwent ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery at 8 to 12 weeks of age.
Results: Deletion of macrophage Drp1 decreased LV ejection fraction (38±14 vs. 23±9% at day 28. N=9, p<0.05) and increased LV diameter (LVDd/Ds 5.7±0.4/4.8±0.3 vs. 4.6±0.2/3.7±0.3mm at day 28, N=9, p<0.05) (Figure). Survival rates until 28 days after MI were significantly lower in Drp1KO mice (25 vs. 64%. N=24 and 33, p<0.05). Deletion of Drp1 led to sustained macrophage accumulation and fibrosis of infarcted tissues. TEM revealed that mitophagosomes are decreased in Drp1-deficient macrophages in infarcted hearts. In ex vivo cultured macrophages, siRNA-mediated knockdown of Drp1 impaired mitochondrial fission and LC3-dependent mitophagy. In these macrophages, inhibition of Drp1 by Mdivi-1 for 96 hr, but not for 24 hr, induced mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) leakage to the cytosol accompanied by increased expression of inflammatory cytokines. Hypoxia and starvation, in addition to Mdivi-1, induced leakage of mtDNA and expression of inflammatory cytokines at 24 hr. These results suggest that impairment of mitochondrial quality maintenance machinery causes leakage of mtDNA that induces inflammation.
Conclusions: Macrophage Drp1 protects the heart from sustained inflammation and adverse cardiac remodeling after MI. Drp1-LC3-mediated mitophagy could be a mechanism that maintains mitochondrial quality and prevents excessive inflammation after MI.
More abstracts on this topic:
Aminoacylase-1 Regulates Hepatic Mitochondrial Respiration and Whole-Body Metabolism
Guan Yuntian, Banks Alexander, Gerszten Robert, Benson Mark, Jonas Zachary, Wang Alissa, Tendoh Foje-geh, Manish Mahesh, Shah Radhe, Hofmann Alissa, Shen Dongxiao, Cortopassi Marissa
A New Analytical Approach for Noninvasive Reconstruction of the Entire Left Ventricular Pressure Waveform in Myocardial Ischemia and InfarctionBilgi Coskun, Li Jiajun, Alavi Rashid, Dai Wangde, Matthews Ray, Kloner Robert, Pahlevan Niema