Final ID: MDP1310
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Unmasks High-Risk Atherosclerotic Features in Human Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Coronary plaque rupture remains the prominent mechanism of myocardial infarction. Accurate identification of rupture-prone plaque may improve clinical management. This study assessed the discriminatory performance of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in human cardiac explants to detect high-risk atherosclerotic features that portend rupture risk.
Methods
In this single-center, prospective study, n=26 cardiac explants were collected for EIS interrogation of the three major coronary arteries. Vessels in which advancement of the EIS catheter without iatrogenic plaque disruption was rendered impossible were not assessed. N=61 vessels underwent EIS measurement and histological analyses. Plaques were dichotomized according to previously established high rupture-risk parameter thresholds. Diagnostic performance was determined via receiver operating characteristic areas-under-the-curve (AUC).
Results
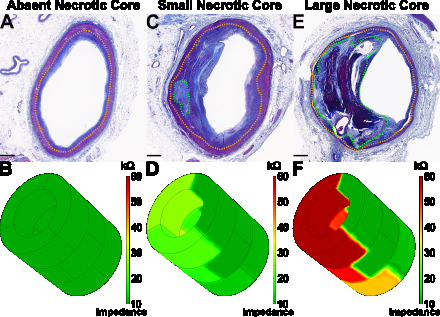
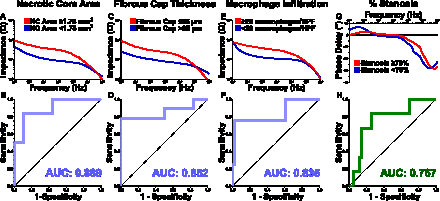
Necrotic cores were identified in n=19 vessels (median area 1.53 mm2) with median fibrous cap thickness of 62 μm. Impedance was significantly greater in plaques with necrotic core area ≥1.75 mm2 vs <1.75 mm2 (19.8±4.4 kΩ vs 7.2±1.0 kΩ, P=0.019), fibrous cap thickness ≤65 μm vs >65 μm (19.1±3.5 kΩ vs 6.5±0.9 kΩ, P=0.004), and ≥20 macrophages per 0.3 mm-diameter high-power field (HPF) vs <20 macrophages per HPF (19.8±4.1 kΩ vs 10.2±0.9 kΩ, P=0.002). Impedance identified necrotic core area ≥1.75 mm2, fibrous cap thickness ≤65 μm, and ≥20 macrophages per HPF with AUCs of 0.889 (95% CI: 0.716–1.000) (P=0.013), 0.852 (0.646—1.000) (P=0.025), and 0.835 (0.577—1.000) (P=0.028), respectively. Further, phase delay discriminated severe stenosis (≥70%) with an AUC of 0.767 (0.573—0.962) (P=0.035).
Conclusions
EIS discriminates high-risk atherosclerotic features that portend plaque rupture in human coronary artery disease and may serve as a complementary modality for angiography-guided atherosclerosis evaluation.
Coronary plaque rupture remains the prominent mechanism of myocardial infarction. Accurate identification of rupture-prone plaque may improve clinical management. This study assessed the discriminatory performance of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) in human cardiac explants to detect high-risk atherosclerotic features that portend rupture risk.
Methods
In this single-center, prospective study, n=26 cardiac explants were collected for EIS interrogation of the three major coronary arteries. Vessels in which advancement of the EIS catheter without iatrogenic plaque disruption was rendered impossible were not assessed. N=61 vessels underwent EIS measurement and histological analyses. Plaques were dichotomized according to previously established high rupture-risk parameter thresholds. Diagnostic performance was determined via receiver operating characteristic areas-under-the-curve (AUC).
Results
Necrotic cores were identified in n=19 vessels (median area 1.53 mm2) with median fibrous cap thickness of 62 μm. Impedance was significantly greater in plaques with necrotic core area ≥1.75 mm2 vs <1.75 mm2 (19.8±4.4 kΩ vs 7.2±1.0 kΩ, P=0.019), fibrous cap thickness ≤65 μm vs >65 μm (19.1±3.5 kΩ vs 6.5±0.9 kΩ, P=0.004), and ≥20 macrophages per 0.3 mm-diameter high-power field (HPF) vs <20 macrophages per HPF (19.8±4.1 kΩ vs 10.2±0.9 kΩ, P=0.002). Impedance identified necrotic core area ≥1.75 mm2, fibrous cap thickness ≤65 μm, and ≥20 macrophages per HPF with AUCs of 0.889 (95% CI: 0.716–1.000) (P=0.013), 0.852 (0.646—1.000) (P=0.025), and 0.835 (0.577—1.000) (P=0.028), respectively. Further, phase delay discriminated severe stenosis (≥70%) with an AUC of 0.767 (0.573—0.962) (P=0.035).
Conclusions
EIS discriminates high-risk atherosclerotic features that portend plaque rupture in human coronary artery disease and may serve as a complementary modality for angiography-guided atherosclerosis evaluation.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Loss of Function Polymorphism in the Propeptide of Lysyl Oxidase Exacerbates Atherosclerosis
Jung In-hyuk, Amrute Junedh, Luna Sophia, Wagoner Ryan, Lee Paul, Burks Kendall, Holloway Karyn, Alisio Arturo, Stitziel Nathan
A 50% or Greater Reduction in LDL-Cholesterol Is Associated with Improved Long-Term Outcomes and Lower Health Care Utilization After Myocardial Infarction - a SWEDEHEART studyReitan Christian, Watanabe Alexandre, Bash Lori, Galvain Thibaut, Arnet Urs, Jernberg Tomas