Final ID: Mo4087
Long term Safety and Efficacy of Ultrathin Bioabsorbable polymer sirolimus eluting Stents Versus Thin Durable polymer everolimus eluting Stents in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A systematic review and meta analysis
First generation drug eluting stents (DES) with thick polymers may contribute to local vascular inflammation and late stent thrombosis. Thinner-strut DES (ultrathin), particularly those with biodegradable polymers, aim to reduce this risk by minimizing flow disturbance and vascular injury. However, the long-term safety and efficacy of ultrathin biodegradable polymer sirolimus eluting stents (BP-SES) compared to durable polymer everolimus eluting stents (DP-EES) are still uncertain. Thus, we performed a meta analysis to compare outcomes of these two stents.
Methods:
Inclusion criteria comprised randomized controlled trials comparing ultrathin BP SES and thin DP EES in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions with long term follow-up of at least 3 years. We excluded cohort studies, case reports, editorials, conference abstracts, and animal studies. Primary outcomes were target lesion failure (TLF), cardiac death (CD), target-vessel myocardial infarction (TV-MI), and clinically indicated target lesion revascularization (CI-TLR). We systematically searched PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, and Scopus. Cochrane’s ROB 2.0 tool assessed trial quality, and RevMan software (5.4) performed the meta-analysis.
Results:
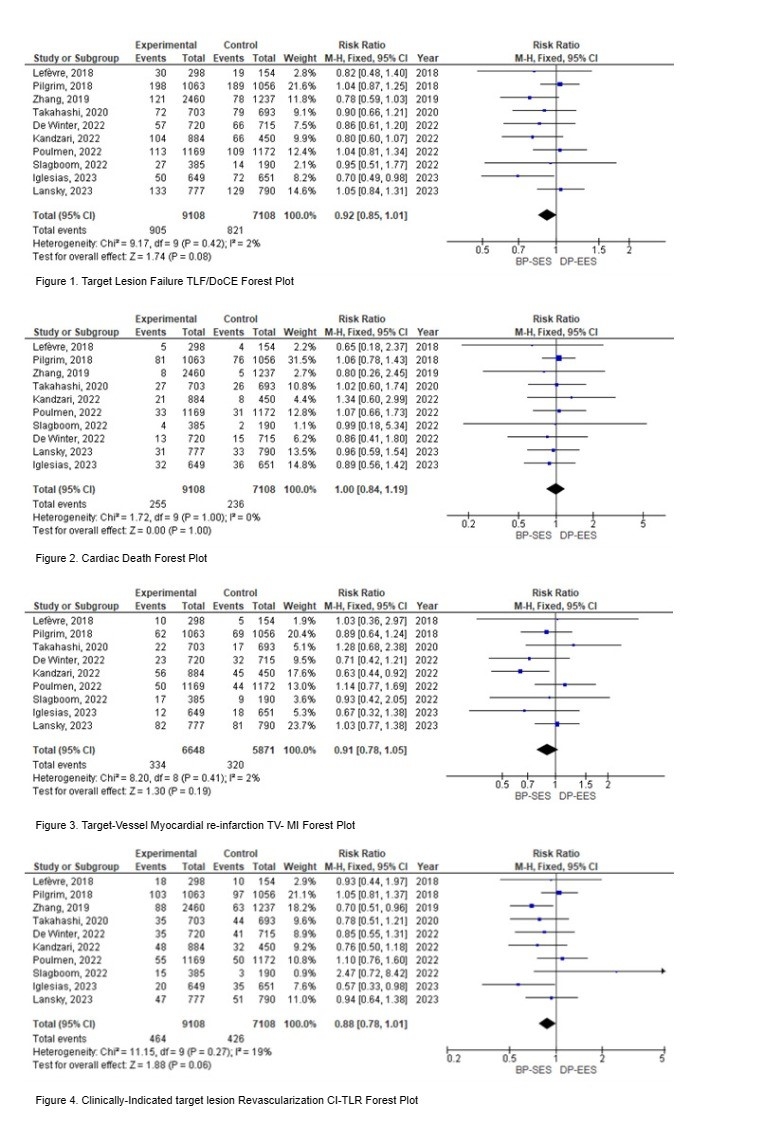
Our analysis included ten RCTs, totaling 16,216 patients, with 9,108 in the BP SES group and 7,108 in the DP EES group. TLF occurred in 905 patients (9.94%) in the BP-SES group and 821 patients (11.55%) in the DP-EES group, with no statistically significant differences between the groups (RR = 0.92, 95% CI = 0.85 to 1.01, p = 0.08). Additionally, there were no significant differences in cardiac death (RR = 1.00, 95% CI = 0.84 to 1.19, p = 1.00), TV-MI (RR = 0.91, 95% CI = 0.78 to 1.05, p = 0.19), and CI-TLR (RR = 0.88, 95% CI = 0.78 to 1.01, p = 0.06) between the two groups.
Conclusion:
The use of BP-SES did not result in higher rates of TLF, CD, TV-MI, or CI-TLR compared to DP-DES. These findings suggest that both BP-SES and DP-DES are viable options for PCI procedures, with comparable long-term safety profiles. However, some trials used strut thicknesses exceeding 70µm in cases requiring wider diameters, similar to the strut thickness in the DP-EES group. This makes it challenging to assess whether, in addition to biodegradable polymers, lower strut thickness contributes to reducing target lesion-related events. Further research may be needed to explore other relevant outcomes and to confirm these findings in diverse patient populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
Carvalho Pedro, Jalli Sandeep, Rangan Bavana, Mastrodemos Olga, Brilakis Emmanouil, Sandoval Yader, Belzer Will, Pollmann Daniel, Helseth Hans, Mutlu Deniz, Strepkos Dimitrios, Alexandrou Michaella, Kladou Eleni, Ser Ozgur
Comparison of clinical outcomes and complications in patients undergoing Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS) with or without pre and post-stent balloon angioplasty.Martucci Maria, Alaraj Ali, Niazi Muhammad, Mansour Ossama, Chen Michael, Bushnaq Saif, Tanweer Omar, Ezzeldin Rime, Zwein Mohammad, Mealer Leighann, Navpreet Bains, Hussain Shazam, Miller Samantha, Colina Gabriela, Rodriguez Gustavo, Maud Alberto, Almajali Mohammad, Barakat Benan, Edhayan Gautam, Froukh Musaab, Salah Walid, Nico Elsa, Hassan Ameer, Ashraf Shehab, Radaideh Yazan, Quispe-orozco Darko, Zaidat Osama, Ezzeldin Mohamad, Siddiq Farhan, Sheriff Faheem, Kan Peter, Janjua Nazli, Asif Kaiz, Grandhi Ramesh