Final ID: MDP318
Trend, Survival, and Disparity Analysis of Heart Transplantation in a Single Large Transplant Center
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
In the landscape of organ transplantation, heart transplantation stands as a life-saving procedure for patients with end-stage heart failure. Comprehensive analyses of transplant programs are imperative to optimize outcomes and understand the complexities.
Hypothesis
This study hypothesizes that an increasing trend of heart transplant service and short-term mechanical circulatory support (STMCS) is the bridge to transplant; the UNOS (United Network for Organ Sharing) guideline positively impacts STMCS utilization. Even with the standard of care, there might be a disparity in receiving care in terms of gender and race.
Goal/ Aims
By examining this center's collective experience, this research provides valuable insights into the evolving landscape of heart transplantation, ultimately contributing to advancements in patient care and transplant policy.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study includes heart transplant patients in a single large transplant center. For statistical analysis, Cox regression, Mann-Whitney test, Kruskal Wallis, and Chi-Square test were used in IBM SPSS 25.
Result
Trends
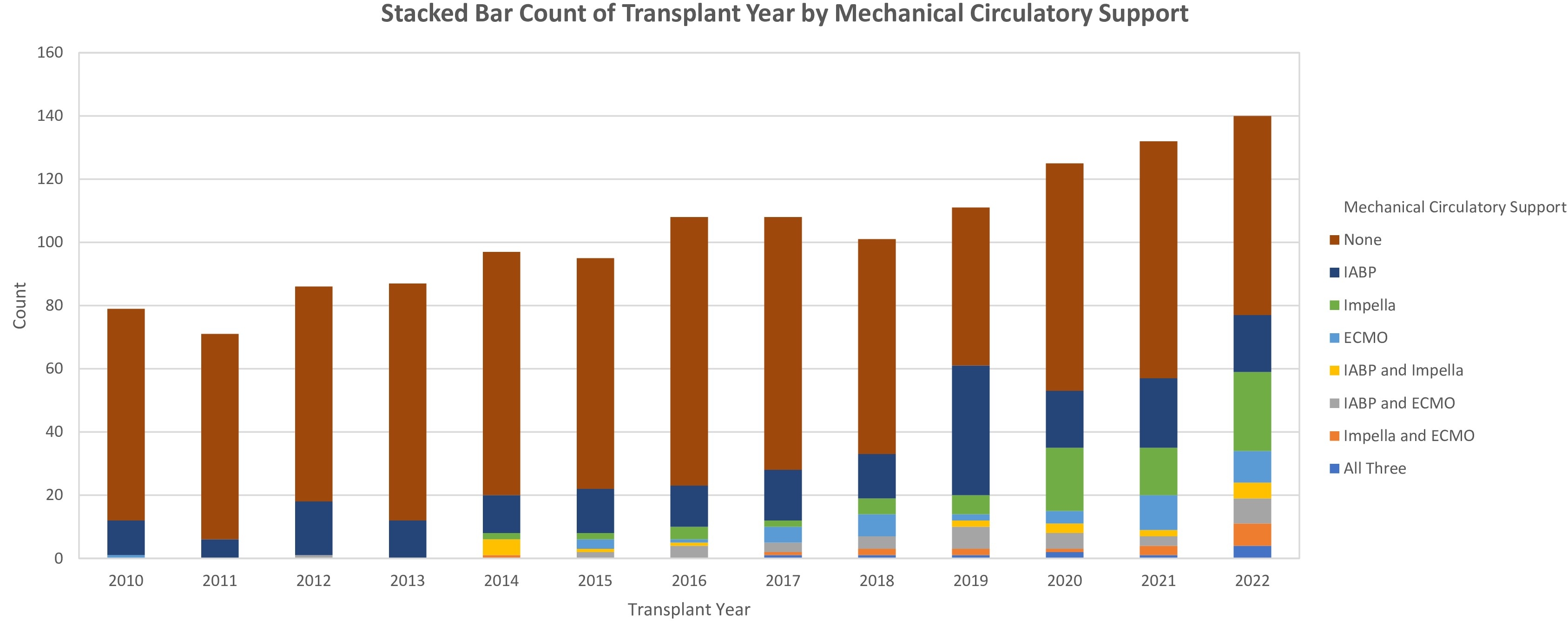
This retrospective study covering 2010 to 2022 comprehensively analyzed 1513 heart transplant patients. The cohort consisted of 1071 (70.78%) males and 442 (29.21%) females, 31.9% were bridged through STMCS. 76.7% of Caucasian and 16.1% were African American.The mean utilization of STMCS was 20.08% before the UNOS policy change, increasing to 53.81% after that (p < 0.001).
Disparity Analysis
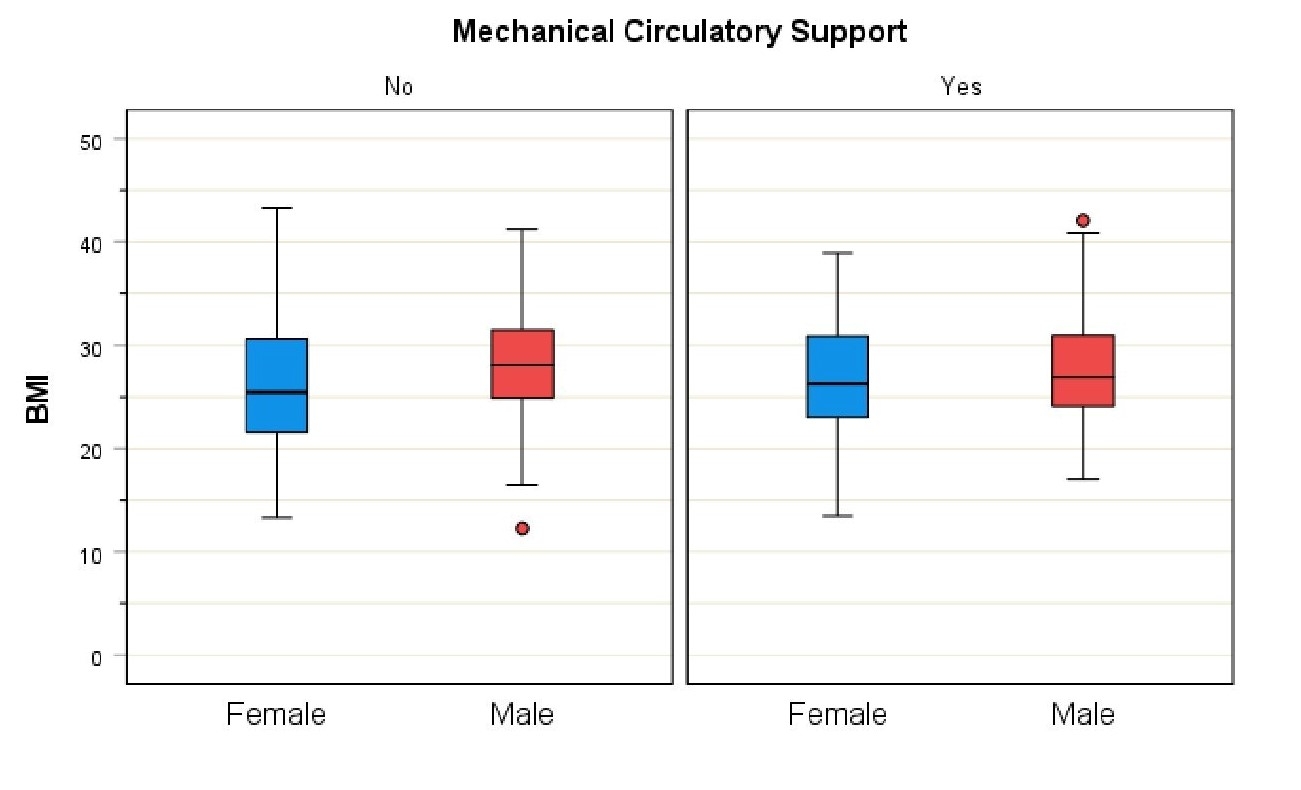
There was a statistically significant difference in STMCS utilization between white and black patients (p= 0.008) but no difference in between obese and non-obese cohorts (P=0.362).Wait time was similar among the genders (p=0.161) and different races (p=0.302).
Survival Analysis
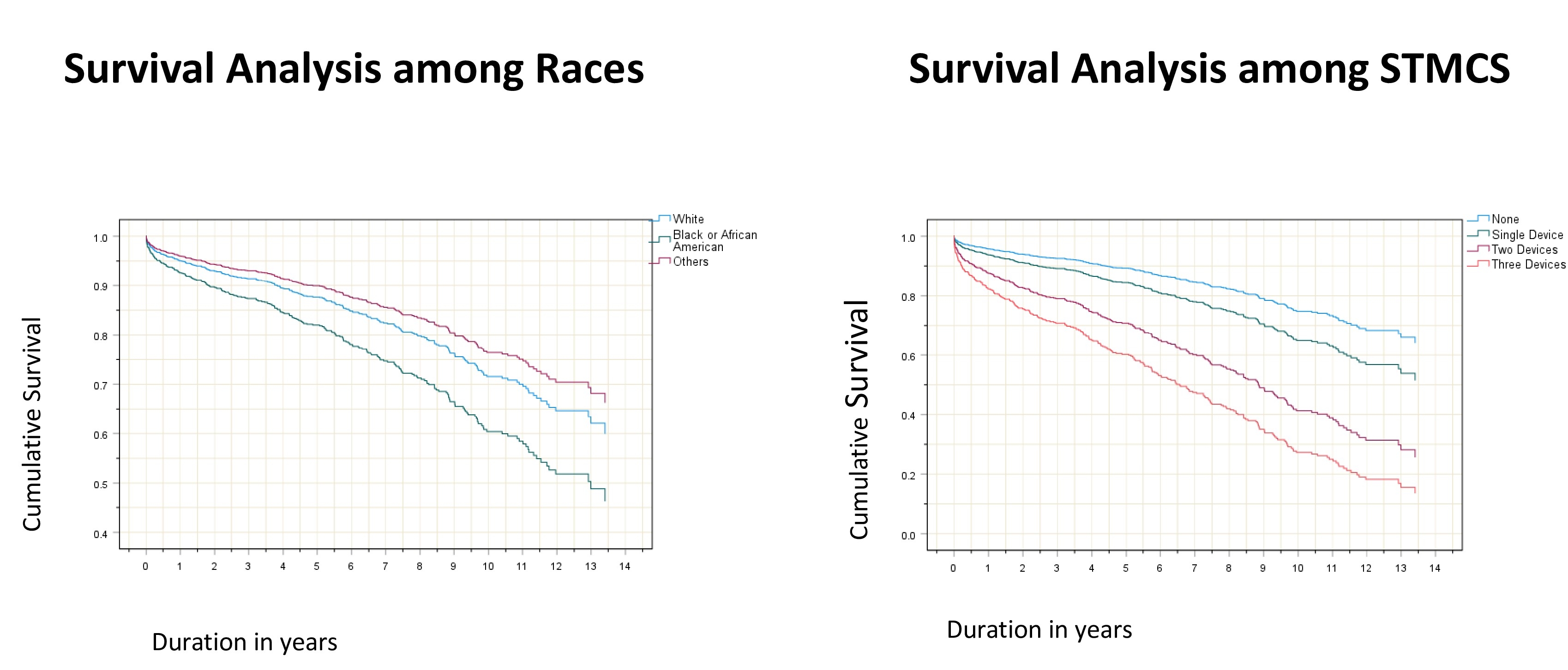
There is a significant survival discrepancy between patients bridged through MCS and those without STMCS(p< 0.001). However, yearly trend analysis showed an evolving survival trajectory favoring STMCS users. There are statistically significant survival differences among whites and blacks (P =0.008) but similar among the genders (p=0.589).
Summary
The study reveals significant changes in the trend of transplants regarding STMCS utilization since the UNOS guideline. There are substantial differences in survival between STMCS vs. non-STMCS groups and among the races.There was a significant difference in STMCS utilization among the races.
In the landscape of organ transplantation, heart transplantation stands as a life-saving procedure for patients with end-stage heart failure. Comprehensive analyses of transplant programs are imperative to optimize outcomes and understand the complexities.
Hypothesis
This study hypothesizes that an increasing trend of heart transplant service and short-term mechanical circulatory support (STMCS) is the bridge to transplant; the UNOS (United Network for Organ Sharing) guideline positively impacts STMCS utilization. Even with the standard of care, there might be a disparity in receiving care in terms of gender and race.
Goal/ Aims
By examining this center's collective experience, this research provides valuable insights into the evolving landscape of heart transplantation, ultimately contributing to advancements in patient care and transplant policy.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study includes heart transplant patients in a single large transplant center. For statistical analysis, Cox regression, Mann-Whitney test, Kruskal Wallis, and Chi-Square test were used in IBM SPSS 25.
Result
Trends
This retrospective study covering 2010 to 2022 comprehensively analyzed 1513 heart transplant patients. The cohort consisted of 1071 (70.78%) males and 442 (29.21%) females, 31.9% were bridged through STMCS. 76.7% of Caucasian and 16.1% were African American.The mean utilization of STMCS was 20.08% before the UNOS policy change, increasing to 53.81% after that (p < 0.001).
Disparity Analysis
There was a statistically significant difference in STMCS utilization between white and black patients (p= 0.008) but no difference in between obese and non-obese cohorts (P=0.362).Wait time was similar among the genders (p=0.161) and different races (p=0.302).
Survival Analysis
There is a significant survival discrepancy between patients bridged through MCS and those without STMCS(p< 0.001). However, yearly trend analysis showed an evolving survival trajectory favoring STMCS users. There are statistically significant survival differences among whites and blacks (P =0.008) but similar among the genders (p=0.589).
Summary
The study reveals significant changes in the trend of transplants regarding STMCS utilization since the UNOS guideline. There are substantial differences in survival between STMCS vs. non-STMCS groups and among the races.There was a significant difference in STMCS utilization among the races.
More abstracts on this topic:
Candidemia in Patients with Left Ventricular Assist Device-A Case Series
Johnson Adedoyin, Sama Jacob, Eltayeb A.a Abdalla, Rao Roopa, Schenkelberg Laurie, Ilonze Onyedika
Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms in a Veterans Affairs Health System: Longitudinal Outcomes and Risk FactorsGomez Axel, Carroway William, Ge Liang, Boskovski Marko, Tseng Elaine