Final ID: Mo2181
Effect of Beta Blockers on Exercise Capacity, Diastolic Function, and Quality of Life in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: In recent landmark HFpEF trials, 75-80% of patients are taking beta blockers (BB) without clear evidence of clinical or symptomatic benefit. Patients with HFpEF commonly have comorbidities that have been classically managed with BB (AF, CAD, HTN), though the utility of this medication class for these conditions is being reconsidered. It remains unclear what impact BB use, in patients with HFpEF, has on exercise capacity, diastolic function, and quality of life.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that BB use is associated with worse exercise capacity, diastolic function, and quality of life in HFpEF patients.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was completed using deidentified patient data from the INDIE-HFpEF and RELAX clinical trials (two trials of HFpEF patients). Patients were divided into two groups based on BB use at trial enrollment. The primary outcomes were exercise capacity, diastolic function, and quality of life at baseline evaluation. A multivariate logistic regression model was used to assess for statistically significant differences after controlling for potentially confounding variables including age, sex, BMI, AF, prior MI, COPD, DM, HTN, serum creatinine, and NYHA functional class.
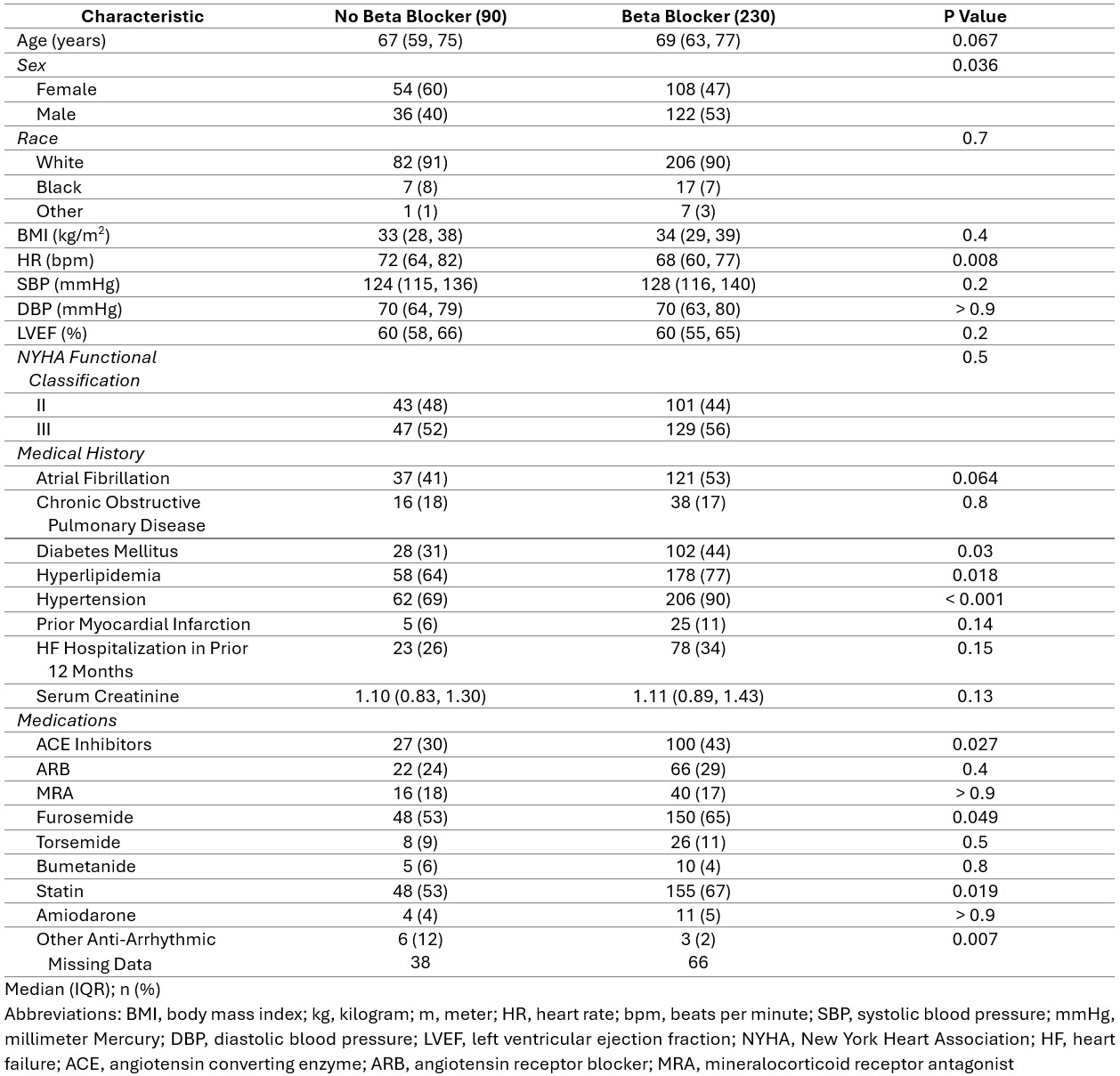
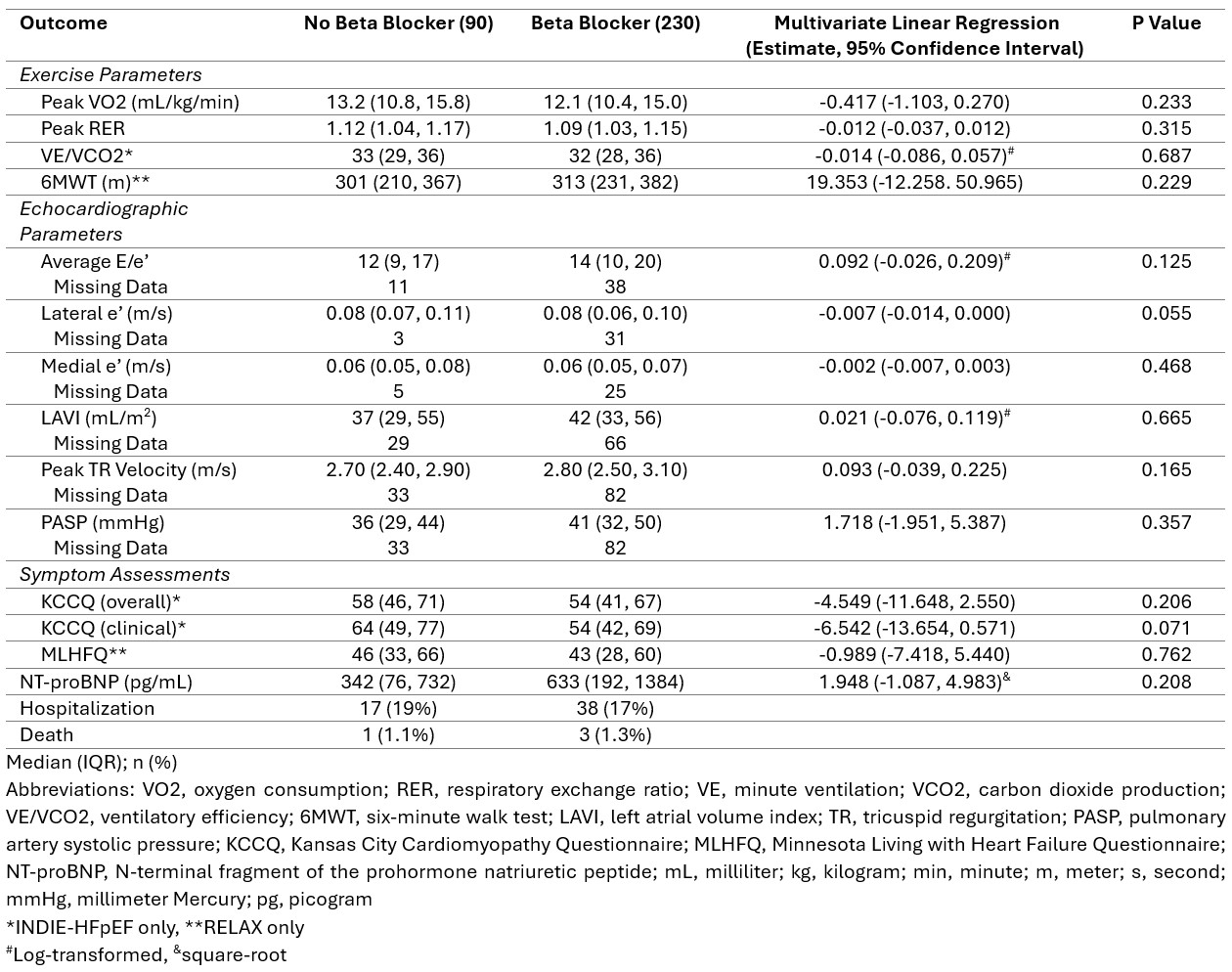
Results: A total of 320 patients were included in this analysis, with 230 on BB (72%). Baseline demographics are shown in Table 1. Patients studied were older (68 years old), white (90%), obese (average BMI 34 kg/m2) individuals with an average LVEF of 61%. Outcomes and multivariate linear regression results are shown in Table 2. After controlling for potential confounding variables, there were no differences in baseline exercise capacity [peak VO2 (mL/kg/min): 12.1 vs 13.2, P=0.233], diastolic function [average E/e’: 14 vs 12, P=0.125; LAVI (mL/m2): 42 vs 37, P = 0.665; peak TR velocity (m/s): 2.8 vs 2.7, P = 0.165; PASP (mmHg): 41 vs 36, P = 0.357], quality of life [KCCQ: 54 vs 58, P = 0.206; MLHFQ 43 vs 46, P = 0.762], or NT-proBNP (633 vs 342; pg/mL, P = 0.208) in HFpEF patients on BB compared to those not on BB.
Conclusion: There was no association with BB use and worse exercise capacity, diastolic function, or quality of life in HFpEF patients. This may be due to heterogenous treatment effects, with differing impact of BB based upon the underlying pathophysiology of unique HFpEF phenotypes. To definitively determine the impact of BB use in patients with HFpEF, both on clinical outcomes and symptoms, randomized controlled trials are necessary.
Hypothesis: We hypothesized that BB use is associated with worse exercise capacity, diastolic function, and quality of life in HFpEF patients.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was completed using deidentified patient data from the INDIE-HFpEF and RELAX clinical trials (two trials of HFpEF patients). Patients were divided into two groups based on BB use at trial enrollment. The primary outcomes were exercise capacity, diastolic function, and quality of life at baseline evaluation. A multivariate logistic regression model was used to assess for statistically significant differences after controlling for potentially confounding variables including age, sex, BMI, AF, prior MI, COPD, DM, HTN, serum creatinine, and NYHA functional class.
Results: A total of 320 patients were included in this analysis, with 230 on BB (72%). Baseline demographics are shown in Table 1. Patients studied were older (68 years old), white (90%), obese (average BMI 34 kg/m2) individuals with an average LVEF of 61%. Outcomes and multivariate linear regression results are shown in Table 2. After controlling for potential confounding variables, there were no differences in baseline exercise capacity [peak VO2 (mL/kg/min): 12.1 vs 13.2, P=0.233], diastolic function [average E/e’: 14 vs 12, P=0.125; LAVI (mL/m2): 42 vs 37, P = 0.665; peak TR velocity (m/s): 2.8 vs 2.7, P = 0.165; PASP (mmHg): 41 vs 36, P = 0.357], quality of life [KCCQ: 54 vs 58, P = 0.206; MLHFQ 43 vs 46, P = 0.762], or NT-proBNP (633 vs 342; pg/mL, P = 0.208) in HFpEF patients on BB compared to those not on BB.
Conclusion: There was no association with BB use and worse exercise capacity, diastolic function, or quality of life in HFpEF patients. This may be due to heterogenous treatment effects, with differing impact of BB based upon the underlying pathophysiology of unique HFpEF phenotypes. To definitively determine the impact of BB use in patients with HFpEF, both on clinical outcomes and symptoms, randomized controlled trials are necessary.
More abstracts on this topic:
Age-related Differences in Peak Oxygen Uptake in Patients with Multimorbidity Undergoing Cardiac Rehabilitation
Gomes Pauline, Miller Sophie, Chacin-suarez Audry, Olson Thomas
A Finding of Unique Peak Exercise Level in Respiratory Exchange Ratio during Bicycle Ergometric Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing in Healthy SubjectsNakayama Atsuko, Sakuma Hiroki, Iwata Tomoharu, Kashino Kunio, Isobe Mitsuaki, Tomoike Hitonobu