Final ID: Mo3033
PCSK9 Inhibitors for ASCVD Risk Reduction in Asian Populations — a meta-analysis of efficacy and safety profiles
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Dyslipidemia is increasingly prevalent in the Asia-Pacific region, correlating with higher mortality rates for ASCVD among this population. Statins, the cornerstone for dyslipidemia management, face higher intolerance in Asians compared to other races. PCSK9 inhibitors have emerged as a promising therapeutic additive to other lipid-lowering therapies. However, current trials predominantly involve caucasian populations, emphasizing the need for efficacy data across other ethnic groups. This meta-analysis aims to analyze the efficacy and safety profile of PCSK9i in Asian populations at high risk for ASCVD.
Methods
We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane for RCTs from the past 10 years on PCSK9i vs. placebo in Asian populations at risk for ASCVD. Efficacy was measured by the mean difference in LDL levels from baseline. Safety parameters included ALT/AST, CK levels, and binding antibodies. Analysis was done with Review Manager, assessing heterogeneity with I^2 statistics.
Results
Eleven studies in Singapore, Japan, the Philippines, India, South Korea, China, and Taiwan included 5443 patients (73% male, mean age 60.6, mean baseline LDL 114 mg/dL) with follow-up from 12 weeks to 16 months. Inclisiran was used in 3 studies, evolocumab in 5, alirocumab in 2, and tafolecimab in 1, alongside statins or ezetimibe.
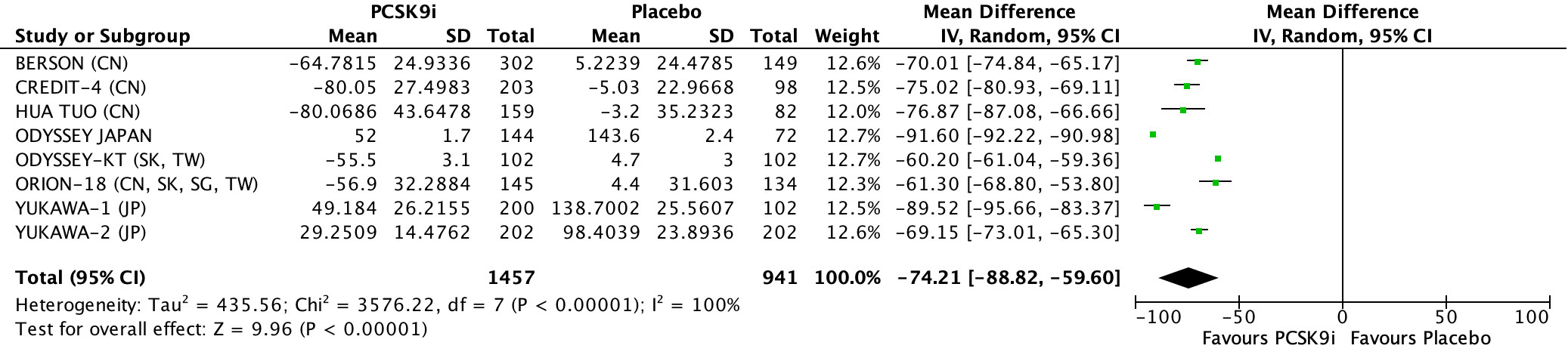
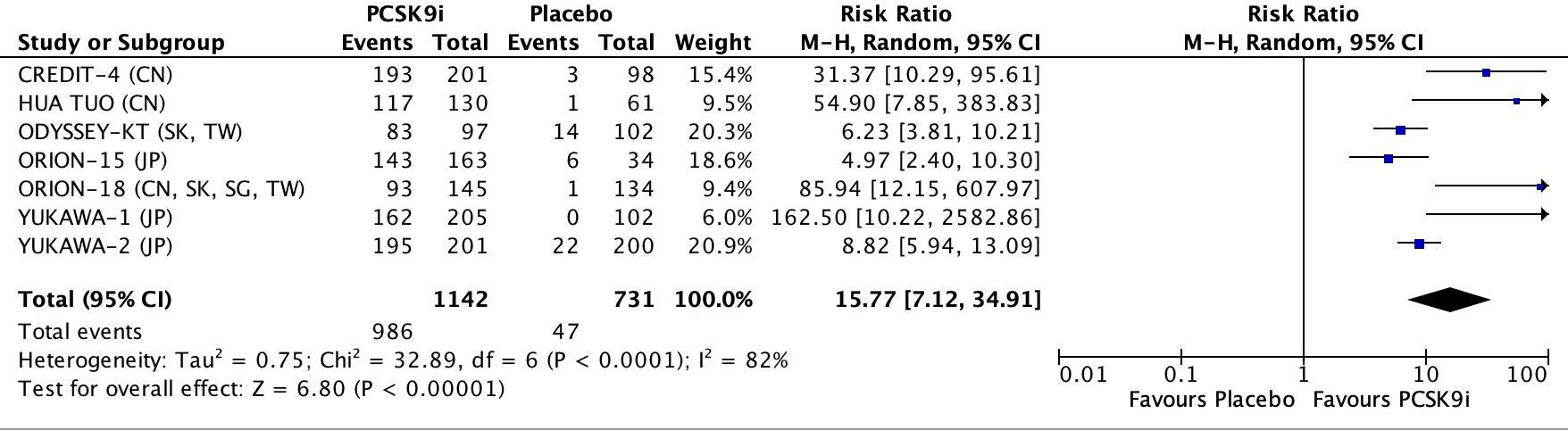
PCSK9i reduced LDL by -74.21 mg/dL and increased the likelihood of >50% LDL reduction compared to placebo (RR: 37.41, 95% CI: 16.31-85.82, P < 0.00001; I^2: 0%). PCSK9i significantly improve the achievement of LDL levels <70 mg/dL compared to placebo (RR: 15.77; 95% CI: 7.12 - 34.91, P < 0.00001; I^2: 82%)
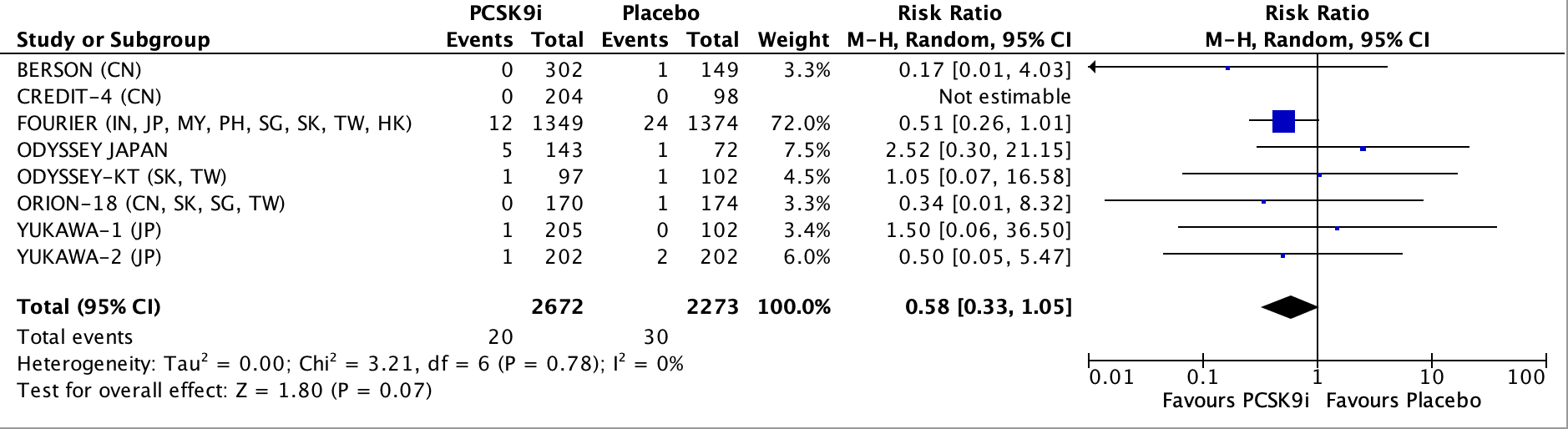
Adverse events showed a non-significant risk of >3x ULN increase in ALT/AST (RR 0.58; 95% CI: 0.33-1.05; P = 0.78, I^2: 0%) and >5x ULN increase in creatine kinase (RR 0.32; 95% CI: 0.07-1.49; P = 0.97; I^2 = 0%). No significant difference in binding antibodies was observed (RR: 2.50, 95% CI: 0.13-49.47, P = 0.55; I^2 = 65%)
Conclusion
In Asian populations, PCSK9 inhibitors effectively lower LDL levels without significant adverse events. The considerable heterogeneity in LDL reduction may result from variations in dosing, different agents used, baseline LDL levels, and geographical diversity. Future research should explore effects across more ethnicities to enhance generalizability.
Dyslipidemia is increasingly prevalent in the Asia-Pacific region, correlating with higher mortality rates for ASCVD among this population. Statins, the cornerstone for dyslipidemia management, face higher intolerance in Asians compared to other races. PCSK9 inhibitors have emerged as a promising therapeutic additive to other lipid-lowering therapies. However, current trials predominantly involve caucasian populations, emphasizing the need for efficacy data across other ethnic groups. This meta-analysis aims to analyze the efficacy and safety profile of PCSK9i in Asian populations at high risk for ASCVD.
Methods
We searched PubMed, Scopus, and Cochrane for RCTs from the past 10 years on PCSK9i vs. placebo in Asian populations at risk for ASCVD. Efficacy was measured by the mean difference in LDL levels from baseline. Safety parameters included ALT/AST, CK levels, and binding antibodies. Analysis was done with Review Manager, assessing heterogeneity with I^2 statistics.
Results
Eleven studies in Singapore, Japan, the Philippines, India, South Korea, China, and Taiwan included 5443 patients (73% male, mean age 60.6, mean baseline LDL 114 mg/dL) with follow-up from 12 weeks to 16 months. Inclisiran was used in 3 studies, evolocumab in 5, alirocumab in 2, and tafolecimab in 1, alongside statins or ezetimibe.
PCSK9i reduced LDL by -74.21 mg/dL and increased the likelihood of >50% LDL reduction compared to placebo (RR: 37.41, 95% CI: 16.31-85.82, P < 0.00001; I^2: 0%). PCSK9i significantly improve the achievement of LDL levels <70 mg/dL compared to placebo (RR: 15.77; 95% CI: 7.12 - 34.91, P < 0.00001; I^2: 82%)
Adverse events showed a non-significant risk of >3x ULN increase in ALT/AST (RR 0.58; 95% CI: 0.33-1.05; P = 0.78, I^2: 0%) and >5x ULN increase in creatine kinase (RR 0.32; 95% CI: 0.07-1.49; P = 0.97; I^2 = 0%). No significant difference in binding antibodies was observed (RR: 2.50, 95% CI: 0.13-49.47, P = 0.55; I^2 = 65%)
Conclusion
In Asian populations, PCSK9 inhibitors effectively lower LDL levels without significant adverse events. The considerable heterogeneity in LDL reduction may result from variations in dosing, different agents used, baseline LDL levels, and geographical diversity. Future research should explore effects across more ethnicities to enhance generalizability.
More abstracts on this topic:
A major uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate impairs macrophage efferocytosis and accelerates atherogenesis: a potential mechanism for cardiovascular risk in chronic kidney disease
Jha Prabhash, Kasai Taku, Vromman Amelie, Holden Rachel, Libby Peter, Tabas Ira, Singh Sasha, Aikawa Elena, Aikawa Masanori, Lupieri Adrien, Sonawane Abhijeet, Le Thanh-dat, Becker-greene Dakota, Chelvanambi Sarvesh, Turner Mandy, Nakamura Yuto, Passos Livia
A Qualitative Study of Perspectives on South Asian Dietary Practices: Exploring a Framework for Culturally Tailored Food-is-Medicine InterventionsKaloth Srivarsha, Fitzgerald Nurgul, Bacalia Karen Mae, Kalbag Aparna, Setoguchi Soko