Final ID: MDP153
Safety and Efficacy of Early Direct Oral Anticoagulants Versus Low Molecular Weight Heparin in Patients with Ischemic Stroke and Immobility: A Multi-National Database Study
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background. Low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is the preferred anticoagulant for venous thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis in patients with ischemic stroke and reduced mobility. However, some patients may have indications for early direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) and are continued on this therapy rather than transitioning to LMWH. Whether outcomes differ between these groups is unknown. We compared the safety and efficacy of early DOACs versus LMWH from a large retrospective database.
Methods. Patients within the TriNetX Research Network receiving either DOACs or LMWH within 72 hours of ischemic stroke and a Modified Rankin Scale of 4-5 were included. A 1:1 propensity score matching analysis was performed using 27 covariables including demographic information, comorbidities, and medications. Chi-square and independent t-tests were used in bivariable analyses. Outcomes were all-cause mortality, VTE, intracranial and extracranial hemorrhage at 30 and 90 days.
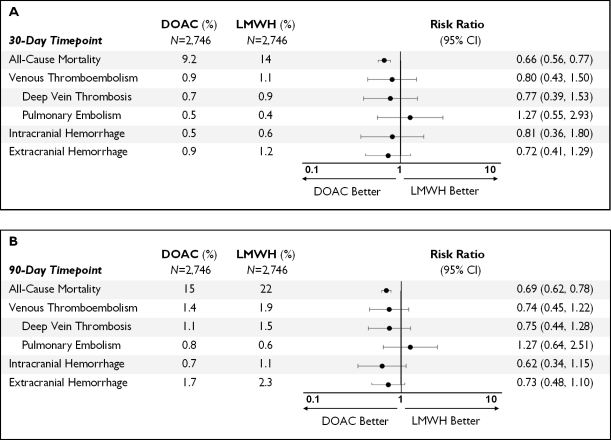
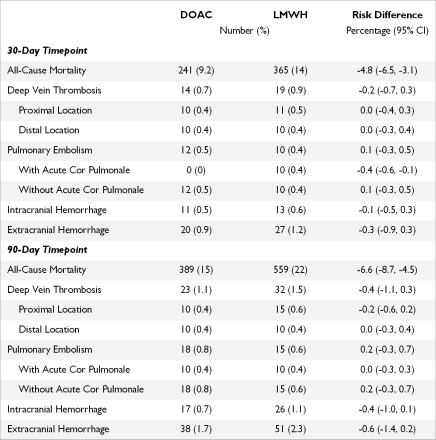
Results. Of 5,492 propensity-matched patients, mean age was 73±13, and 43% were male. Mortality in the DOAC group was significantly lower than in the LMWH group at 30 days (RR=0.59, 95% CI: 0.51-0.69) and 90 days (RR=0.63, 95% CI: 0.56-0.71). Risk of VTE was not significantly different at 30 days (RR=0.80, 95% CI: 0.43-1.50) or 90 days (RR=0.74, 95% CI: 0.45-1.22). Risk of intracranial hemorrhage was not significantly different at 30 days (RR=0.81, 95% CI: 0.36-1.80) or 90 days (RR=0.62, 95% CI: 0.34-1.15).
Conclusions. In patients with acute ischemic stroke and reduced mobility, early use of DOACs was associated with lower mortality compared to early use of LMWH.
Methods. Patients within the TriNetX Research Network receiving either DOACs or LMWH within 72 hours of ischemic stroke and a Modified Rankin Scale of 4-5 were included. A 1:1 propensity score matching analysis was performed using 27 covariables including demographic information, comorbidities, and medications. Chi-square and independent t-tests were used in bivariable analyses. Outcomes were all-cause mortality, VTE, intracranial and extracranial hemorrhage at 30 and 90 days.
Results. Of 5,492 propensity-matched patients, mean age was 73±13, and 43% were male. Mortality in the DOAC group was significantly lower than in the LMWH group at 30 days (RR=0.59, 95% CI: 0.51-0.69) and 90 days (RR=0.63, 95% CI: 0.56-0.71). Risk of VTE was not significantly different at 30 days (RR=0.80, 95% CI: 0.43-1.50) or 90 days (RR=0.74, 95% CI: 0.45-1.22). Risk of intracranial hemorrhage was not significantly different at 30 days (RR=0.81, 95% CI: 0.36-1.80) or 90 days (RR=0.62, 95% CI: 0.34-1.15).
Conclusions. In patients with acute ischemic stroke and reduced mobility, early use of DOACs was associated with lower mortality compared to early use of LMWH.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Meta-analysis of Folic Acid Supplementation Efficacy in Cardiovascular Diseases Prevention.
Calderon Martinez Ernesto, Camacho Davila Karen Fabiola, Pinto-colmenarez Rafael, Arruarana Victor, Arvelaez Pascucci Joanne, Castillo Jaqueline Livier, Alonso Ramirez Angie Carolina, Ghattas Patricia, Giron De Marza Maria, Sosaya Zuñiga Briggitte Solange, Martinez Lilan Jonathan David, Paredes Romero Enrique
A peptoid derivative of alpha-calcitonin gene related peptide improves cardiac function in pressure-overload heart failure miceKumar Ambrish, Deloach Sarah, Dipette Donald, Potts Jay