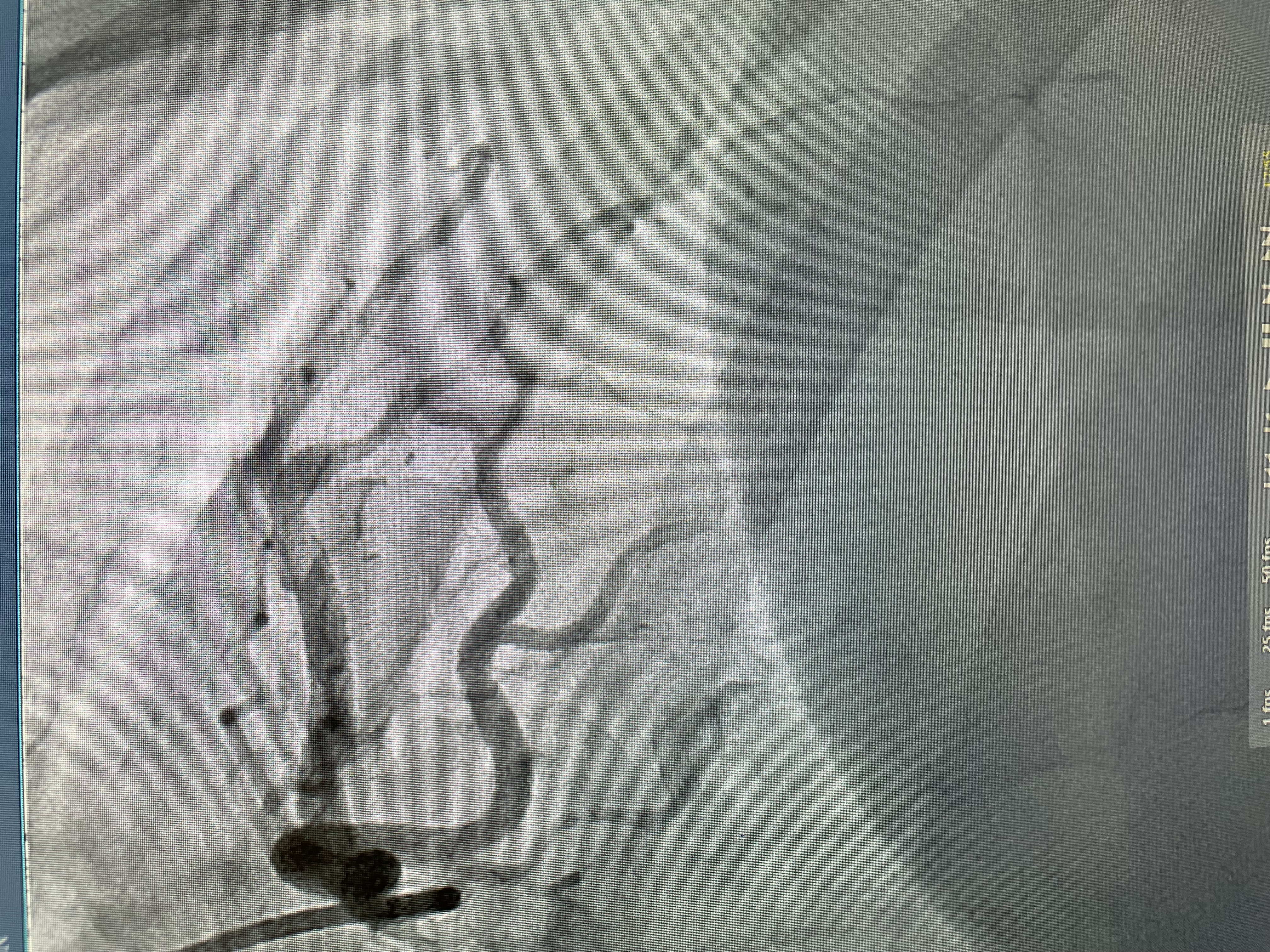
Final ID: Sa1035
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection: Case series and review of associated cardiovascular risks
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) has emerged as an important cause of ACS, myocardial infarction, and sudden death particularly among young women and individuals with few conventional atherosclerotic risk factors. We reveiwed possible risk factors that could predispose to SCAD.
Methods:
We reviewed 13 consecutive patients presenting with SCAD across three different institutions over a period of 5 yrs and determined risk fatcors associated with this disase entity.
Results:
13 patients presented with SCAD represented % 0.5 of the total number of patients who underwent cardiac cathaterizations for chest pain requiring admissions. 11/13 (84%) were female. 5/13 (38%) were Caucasian or Hispanic, and 3/13 (23%) were African-American. Mean age age was 49.3 + years. 8/13 (61%) had associated hyperlipidemia with LDL levels > than 110 mg/dL, 9/13 (64%) had an A1c < 5.6% and only 1/13 (0.07%) had A1c of 6.4%. HTN was present in 6/13 (46%) of patients, and family history of SCD or heart disease were only seen in 2/13 (15%). None of the patients had features suggestive of associated fibromuscular dysplasia or connecive tissue disease. D-dimer was elevated in 5/13 (38%) with average value of 1578 ng/dL. Inflammatory markers were reviewed, only 3 patient has had ESR and CRP ordered, and only 1/3 had a mildly elevated CRP 3.9 mg/dL. Only 1/13 (0.07%) required intervention which was due to further drop in her ejection fraction requiring PCI, with improvement in her symptoms. All patients were treated with dual anti-platelet therapy for 1 year, 1 was discontinued due to persitent chest pain and decision was made to treat with only aspirin. Traditionally, risks for SCAD were thought to be due to non-atheresclerotic factors, however our case series shows that more then 60% of patients had elevated LDL's and 46% with hypertension, implying that traditional atheresclerotic risk factors should not be ignored and may play a crucial role. Autoimmune diseases were not found in any of our patients.
Conclusion and implications:
In this series patients who had SCAD had conventional risk factors of CAD including HLD and hypertension. The variability of co morbidities makes the identification of specific risk factors very difficult and none of the patients had Fibromuscular dysplasia or any signs of inflammation. Elevated D Dimer was also seen in a majority of patients, and all but one was managed medically with a favorable outcome
Spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) has emerged as an important cause of ACS, myocardial infarction, and sudden death particularly among young women and individuals with few conventional atherosclerotic risk factors. We reveiwed possible risk factors that could predispose to SCAD.
Methods:
We reviewed 13 consecutive patients presenting with SCAD across three different institutions over a period of 5 yrs and determined risk fatcors associated with this disase entity.
Results:
13 patients presented with SCAD represented % 0.5 of the total number of patients who underwent cardiac cathaterizations for chest pain requiring admissions. 11/13 (84%) were female. 5/13 (38%) were Caucasian or Hispanic, and 3/13 (23%) were African-American. Mean age age was 49.3 + years. 8/13 (61%) had associated hyperlipidemia with LDL levels > than 110 mg/dL, 9/13 (64%) had an A1c < 5.6% and only 1/13 (0.07%) had A1c of 6.4%. HTN was present in 6/13 (46%) of patients, and family history of SCD or heart disease were only seen in 2/13 (15%). None of the patients had features suggestive of associated fibromuscular dysplasia or connecive tissue disease. D-dimer was elevated in 5/13 (38%) with average value of 1578 ng/dL. Inflammatory markers were reviewed, only 3 patient has had ESR and CRP ordered, and only 1/3 had a mildly elevated CRP 3.9 mg/dL. Only 1/13 (0.07%) required intervention which was due to further drop in her ejection fraction requiring PCI, with improvement in her symptoms. All patients were treated with dual anti-platelet therapy for 1 year, 1 was discontinued due to persitent chest pain and decision was made to treat with only aspirin. Traditionally, risks for SCAD were thought to be due to non-atheresclerotic factors, however our case series shows that more then 60% of patients had elevated LDL's and 46% with hypertension, implying that traditional atheresclerotic risk factors should not be ignored and may play a crucial role. Autoimmune diseases were not found in any of our patients.
Conclusion and implications:
In this series patients who had SCAD had conventional risk factors of CAD including HLD and hypertension. The variability of co morbidities makes the identification of specific risk factors very difficult and none of the patients had Fibromuscular dysplasia or any signs of inflammation. Elevated D Dimer was also seen in a majority of patients, and all but one was managed medically with a favorable outcome
More abstracts on this topic:
Aortic Dissection-Related Mortality in Hypertensive U.S. Adults: A 25-Year Portrait of Trends and Disparities From 1999 to 2023
Ahmed Syed Areeb, Saeed Humza, Unus Ahmad Talha, Afaq Rana Muhammad, Mayo Jawad Zafar, Goyal Priya
3D Aortic Geometry is Informative for Risk of Adverse Aortic EventsPirruccello James